Structure Determination of Two Stereoisomers of Sevoflurane Dimer by CP-FTMW Spectroscopy
advertisement

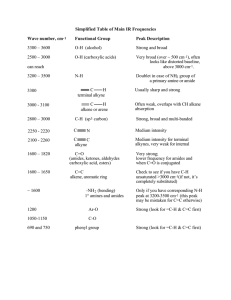
Structure Determination of Two Stereoisomers of Sevoflurane Dimer by CP-FTMW Spectroscopy Nathan A. Seifert, Cristobal Perez, Daniel P. Zaleski, Justin L. Neill, Brooks H. Pate University of Virginia Alberto Lesarri, Montserrat Vallejo-López Universidad de Valladolid Emilio J. Cocincero, Fernando Castaño Universidad del País Vasco Introduction In 2011… Suhm and coworkers observed bands blue-shifted from their monomer peaks and tentatively assigned them to larger sevoflurane oligomers (dimers, ++) Sevoflurane homodimers have a number of potential stabilizing factors: Diastereomeric pair observed in CP-FTMW scan: Donor -OCH2F a solid Lewis base C-H/F hydrogen bonding? Acceptor Two strong deactivating groups (-CF3) Mild donating group (-OCH2F) C-H is a good Lewis acid (SS) [pictured] (SR) [pictured] Experimental Some facts about the new sevoflurane spectrum… 9.1 million averages Dynamic range: 31000:1 Average FWHM: 60 kHz 9,600 lines over 4:1 SNR (1.6 MHz-1) Spectrometer setup identical to sevoflurane-benzene (previous talk) 0.2% sevoflurane in Ne, 1 atm backing pressure Heterochiral Dimer Theory Parameter MP2 B3LYP M06-2X A (% Err vs Exp) 306.56 (0.59%) 299.51 (1.7%) 309.30 (1.5%) B (% Err) 183.87(4.7%) 160.94 (8.3%) 188.37 (7.3%) C (% Err) 174.85 (4.5%) 155.31 (7.1%) 177.53 (6.1%) μa, μb, μc 2.0, 1.4, 0.02 1.2, 1.8, 0.22 2.5, 1.4, 0.13 ΔEbinding (cm-1) -4117.78 -1369.35 -3117.40 ΔEbindingCP (cm-1) -1252.15 64.90 (!) -2062.25 Experiment • Observed all 8 13C isotopologues in natural abundance • Avg. 130 transitions per isotopologue, for a total of 1720 assigned heterochiral transitions Parameter Fit Value A (MHz) 304.70026(39) B (MHz) 175.56391(18) C (MHz) 167.25458(18) ΔJ (kHz) 0.00850(24) ΔJK (kHz) 0.04428(62) ΔK (kHz) -0.0487(13) Nlines 725 σrms (kHz) 7.25 Homochiral Dimer Theory Parameter MP2 B3LYP M06-2X A (% Err vs Exp) 308.11 (0.15%) 308.34 (0.18%) 314.05 (2.0%) B (% Err) 181.76 (3.1%) 174.22 (0.68%) 185.89 (4.5%) C (% Err) 172.83 (1.4%) 168.44 (0.00%) 182.49 (4.6%) μ a, μ b, μ c 1.8, 0.5, 3.3 1.7, 1.2, 2.7 1.9, 1.1, 3.1 ΔEbinding (cm-1) -4216.41 -1412.18 -3376.27 ΔEbindingCP (cm-1) -1275.05 4.36 -2257.76 ΔΔEbCP (cm-1) -22.91 -60.54 -195.12 • Observed all 8 13C and both 18O isotopologues in natural abundance • A total of 1770 assigned homochiral transitions Experiment Parameter Fit Value A (MHz) 307.789308(39) B (MHz) 172.119904(23) C (MHz) 168.437022(23) ΔJ (kHz) 0.011420(29) ΔJK (kHz) 0.029193(43) ΔK (kHz) -0.035955(67) Nlines 1051 σrms (kHz) 8.19 Intermolecular r0 structure fit Homochiral Schema: • Nearly exact procedure also used for fitting heterochiral dimer (no oxygen isotopologues, so purely carbon-containing parameters were fit) • Fix monomer geometry to ab initio (excellent agreement with monomer FTMW results) • Vary three intermolecular parameters (…in theory) • In STRFIT, better results using dummy atom coordinate system and fitting these parameters effectively Structural Results Homochiral σfit = 0.0253 amu Å2 Significant issues with imaginary coordinates R0 Heterochiral σfit = 0.0209 amu Å2 Pictured: MP2/6-311++g(d,p) ab initio structure with r0/rs coordinates as small blue spheres Rs No issues with imaginary coordinates Structural Comparison Homochiral Heterochiral Evaluating the C-H⋯F interactions1: • Typical interactions are around 2.6 Å (average) • <[C-H⋯F] ≈ 135° for a good average C-H⋯F bond • (sevo)2 <[C-H⋯F] ≈ 125-140° 1. H.-J. Schneider, Chem. Sci., 3 (2012), 1381, and references therein. Conclusions • Structural determination of two diastereomers of (sevoflurane)2 • 24 heavy atoms per cluster! • Issues with imaginary coordinates easily overcome by use of a simple intermolecular r0 fit What else can we learn from this spectrum? • The (RR) and (RS) dimers, though spectrally dense, only represent ~40% of the lines > 4:1 SNR • (sevo)1 (w/ isotopes) + (sevo)2 represents somewhere around ~60% of the transitions Therefore, an open question: what else is being formed in the jet? • (sevo)(H2O) is a possibility, but (H2O)2 is weak in this acquisition [a typical indicator of “wetness”] • Higher order (sevo)n clusters? Other isomers? • Discovery bottlenecked mostly by the speed/efficiency of computational methods Acknowledgements Pate Group Brooks Pate Cristobal Perez Simon Lobsiger Luca Evangelisti Thanks for your time! Brent Harris Amanda Steber Nathan Seifert Newcastle University Daniel Zaleski Brightspec Justin Neill Universidad de Valladolid Alberto Lesarri Montserrat Vallejo-López UPV-EHV Emilio J. Cocincero Fernando Castaño Thanks to the NSF for funding: MRI-R2, Award CHE-0960074 Heterochiral Dimer Structure Results Fit Parameter R0 value Rs value MP2/6-311+g(d,p) R(C⋯C) / Å 4.286(9) 4.23(4) 4.124 Θ(Cdonor⋯Cacc-CH2F) / ° 71.5(2) 72.2(12) 73.2 Φ(Ca-C⋯C-Ca) / ° 61.6(4) (pictured) 62(1) 65.6 Lack of imaginary coordinates saves the day for the Kraitchman determination! Alternation of short/long C-F ⋯ H bonds with respect to homochiral isomer Homochiral Dimer Structure Results Fit Parameter R0 value Rs value MP2/6311++g(d,p) R(C⋯C) / Å 4.328(5) 4.33(5) 4.115 Θ(C⋯C-O) / ° 41.5(1) 48(2) 41.4 Φ(O-C⋯C-O) / ° 66.8(7) (pictured) 45(4) 66.3 C-F ⋯ H interactions quite important, unlike in sevoflurane⋯benzene Evaluating the C-H⋯F interactions1: • Typical interactions are around 2.6 Å (average) • <[C-H⋯F] ≈ 135° for a good average C-H⋯F bond • (sevo)2 <[C-H⋯F] ≈ 125-140° 1. H.-J. Schneider, Chem. Sci., 3 (2012), 1381, and references therein.