W4118 Operating Systems
Instructor: Junfeng Yang
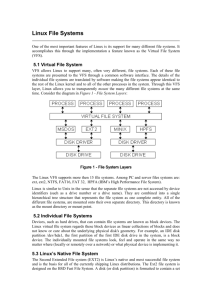
File System Examples
Unix Fast File System (FFS)
Linux Second Extended File System (EXT2)
What were the problems with Unix FS?
How did FFS solve these problems?
What is the EXT2 on-disk layout?
What is the EXT2 directory structure?
Virtual File System (VFS)
What is VFS?
What are the key data structures of Linux VFS?
1
Original Unix FS
From Bell Labs
Simple and elegant
Problem: slow
20KB/s, 2% of maximum even for sequential disk
transfer
inodes
super block
data blocks (512 bytes)
Why so slow?
Blocks too small
Unorganized freelist
Fixed costs per transfer (seek and rotational
delays)
Need more indirect blocks
Consecutive file blocks are not close together
Pay seek cost even for sequential access
No data locality
inodes far from data blocks
inodes of files in directory not close together
Larger Blocks
BSD: increase block to 4096 or more bytes
Faster
However, internal fragmentation
FFS provided a solution
Not a problem now: disks are big and cheap
Unorganized freelist
Leads to random allocation of sequential file
blocks overtime
Initial performance good
Get worse over time
Solution: bitmap for free blocks
E.g., 1000011100
Data Locality
Store related data together
Always find free block nearby
• Keep free space on disks (10%)
Spread unrelated data apart
• Make room for related data
How to Achieve Locality
Each cylinder group contains
Superblock
Inodes
Bitmap of free blocks
Additional info for block allocation
Data blocks
File: store data blocks within a cylinder group
Dir: store files in same dir in a cylinder group
Make room
Spread out directories to cylinder groups
Switch to a different cylinder group for large files
File System Examples
Unix Fast File System (FFS)
Linux Second Extended File System (EXT2)
What were the problems with Unix FS?
How did FFS solve these problems?
What is the EXT2 on-disk layout?
What is the EXT2 directory structure?
Virtual File System (VFS)
What is VFS?
What are the key data structures of Linux VFS?
8
Ext2
“Standard” Linux File System
Previously it was the most commonly used
Serves as a basis for Ext3 which adds journaling
Uses FFS like layout
Each file system is composed of identical block
groups
Allocation is designed to improve locality
inodes contain pointers (32 bits) to blocks
Direct, Indirect, Double Indirect, Triple Indirect
Maximum file size: 4.1TB (4K Blocks)
Maximum file system size: 16TB (4K Blocks)
On-disk structures defined in include/linux/ext2_fs.h
Ext2 Disk Layout
Files in the same directory are stored in the
same block group
Files in different directories are spread
among the block groups
Picture from Tanenbaum, Modern Operating Systems 3 e, (c) 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 0-13-6006639
Block Addressing in Ext2
Twelve “direct” blocks
Inode
Data
Data
Block
Data
Block
Block
BLKSIZE/4
Indirect
Blocks
Indirect
Blocks
(BLKSIZE/4)2
Double
Indirect
Indirect
Blocks
(BLKSIZE/4)3
Triple
Indirect
Double
Indirect
Indirect
Blocks
Indirect
Blocks
Data
Data
Block
Data
Block
Block
Data
Data
Block
Data
Block
Block
Data
Data
Block
Data
Block
Block
Data
Data
Block
Data
Block
Block
Data
Data
Block
Data
Block
Block
Picture from Tanenbaum, Modern Operating Systems 3 e, (c) 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 0-13-6006639
Ext2 Directory Structure
(a) A Linux directory with three files. (b) The same directory after
the file voluminous has been removed.
Picture from Tanenbaum, Modern Operating Systems 3 e, (c) 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 0-13-6006639
File System Examples
Unix Fast File System (FFS)
Linux Second Extended File System (EXT2)
What were the problems with Unix FS?
How did FFS solve these problems?
What is the EXT2 on-disk layout?
What is the EXT2 directory structure?
Virtual File System (VFS)
What is VFS?
What are the key data structures of Linux VFS?
13
VFS
Old days: “the” file system
Nowadays: many file system types and
instances co-exist
VFS: an FS abstraction layer that
transparently and uniformly supports multiple
file systems
A VFS specifies an interface
A specific FS implements this interface
• Often a struct of function pointers
VFS dispatches FS operations through this
interface
• E.g., dir->inode_op->mkdir();
Schematic View of Virtual File
System
Key Linux VFS Data Structures
struct file
struct dentry
information about an open file
includes current position (file pointer)
information about a directory entry
includes name + inode#
struct inode
unique descriptor of a file or directory
contains permissions, timestamps, block map (data)
inode#: integer (unique per mounted filesystem)
Pointer to FS-specific inode structure
• e.g. ext2_inode_info
struct superblock
descriptor of a mounted filesystem