Cognitive Behavioral Psycho-dramatic Structure & Techniques
advertisement

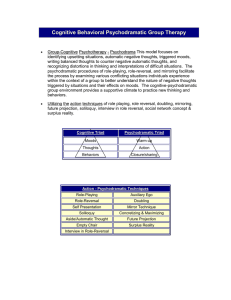
Cognitive Behavioral Psycho-dramatic Structure & Techniques Group-Cognitive Psychotherapy - Psychodrama This model focuses on distressful situations, identifying negative thoughts, moods, and balanced thoughts to counter negative automatic thoughts. The psycho-dramatic procedures of role-playing, role-reversal, and mirroring facilitate the process by examining various conflicting situations individual’s experience within the context of a safe group environment. In this setting one is able to better understand the nature of negative thoughts and their impact upon ones daily life. The cognitive-psycho-dramatic group environment provides a supportive climate to practice new thinking and behaviors. Psycho-dramatic Structure: The protagonist: The person whose story or issue is presented through guided dramatic action. The auxiliary egos: Group members who assume the roles of significant others in the drama. The audience: Group members who witness the drama and who may become involved in auxiliary roles. The stage: The physical space in which the drama takes place. The director/facilitator: A trained psychodramatist who guides participants through each phase of the session. Basic Action Techniques Auxiliary ego- functions as extensions of the protagonist portraying actual or imagined roles. A group member(s) who assume the role(s) of significant others. Contained double - (auxiliary ego) expresses thoughts, feelings, & ideas that are felt but not expressed. Cognitive double - (auxiliary ego) expresses the positive thoughts, & feelings that are thought but not expressed Presentation of self – talking about ‘self’ to group members, i.e. – what brought you to the group? Role-playing – temporarily stepping out of one’s own present role to assume the role of another or of oneself at another time. Soliloquy - (unscripted * spontaneous) - expression of free-floating thoughts, ideas and feelings as one physically moves in the group environment. It clarifies feelings, thoughts and relieves emotional blocking of content. Aside/Automatic Thought - Expressing (immediate) thoughts / feelings when a change of mood is visible/felt. Role reversal - provides a concrete way of actualizing the metaphorical process of ‘putting yourself in the shoes or situation of the other’. Empty-chair - or auxiliary chair technique represents thoughts feelings and ideas of a significant other whom is addressed as in the present. Mirror technique - protagonist steps out of the scene to observe group member(s) reflect/mirror his behavior, thoughts, and feelings. One is able to see how he appears to others as reflected in the mirror portrayed by group members. Minimize – Maximize - the principal of exaggerating, increasing, or maximizing the emotional content of a communication or attitude. (Thoughts/feelings/behavior) - Future Projection – allowing the protagonist the freedom to predict and deal with an event or situation in the future. Data allows one to feel free to express what one would like to have happen. Clarifies goals & objectives in the situation. Surplus Reality – placing self in ‘an unreal setting’ to gather information on thoughts – feelings & behavior that has placed the protagonist in a freeze mode. Usually frees the protagonist to express (by taking away the boundaries) ones thoughts and feelings. Interview In Role-Reversal – Assuming the role of the other for the specific purpose of collecting data for that role as well as collecting critical background information.