MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES 多元智慧 4A2C0026 嚴思婷 羅羽秀
advertisement

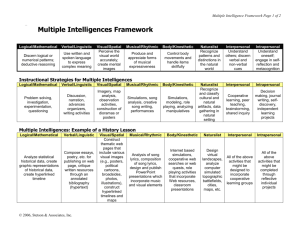
MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES 多元智慧 4A2C0026 嚴思婷 4A2C0079 羅羽秀 4A2C0088 莊婉婷 4A2C0091 洪敏惠 4A2C0093 林筱涵 Proposed by Howard Gardner Gardner chose eight abilities that he held to meet these criteria in 1983. 1. Linguistic (語言智能) 2. Logical/mathematical (邏輯數學智能) 3. Spatial (空間智能) 4. Musical (音樂智能) 5. Bodily/kinesthetic (身體動覺智能) 6. Interpersonal/Social (人際智能) 7. Intrapersonal (內省智能) 8. Naturalist (自然觀察) [ Naturalist was complemented by Gardner in 1999. ] 1. Linguistic (語言智能) High verbal-linguistic intelligence →Facility with words and languages. Good at reading, writing, telling stories and memorizing words along with dates. 為口頭語言運用及文字書寫的能力 結合並運用自如: 句法、音韻學、語義學、語言實用學 這類人在學習時是用語言及文字來思考,喜歡 文字遊戲、閱讀、討論和寫作。 2. Logical/mathematical (邏輯數學智能) Do with : logic, abstractions, reasoning, numbers and critical thinking. Also need the capacity to understand the underlying principles of some kind of causal system. 需要有效運用數字和推理的智能 學習靠推理、提問、實驗 較容易接受可被測量、歸類、分析的事物 3. Spatial (空間智能) Deals with : spatial judgment and the ability to visualize with the mind's eye. 對色彩、線條、形狀、形式、空間之間關係有 高敏感性 學習時用意象及圖像思考 分形象空間智能和抽象空間智能 形象空間-畫家 抽象空間-幾何學家 形象+抽象-建築學家 4. Musical (音樂智能) Do with : sensitivity to sounds, rhythms, tones, and music. High musical intelligence normally have good pitch, sing, play musical instruments and compose music. Sensitivity to rhythm, pitch, meter, tone, melody or timbre. 音樂智能強能察覺、辨別、改變和表達音樂 對節奏、音調、旋律或音色較具敏感性 學習時透過節奏旋律來思考 5. Bodily/kinesthetic (身體動覺智能) Control of one's bodily motions and the capacity to handle objects skillfully Generally good at physical activities. Ex: sports, dance, acting, and making things. Suit to be athletes, dancers, musicians, actors, builders, police officers, and soldiers. 善用身體來表達想法、感覺, 有用雙手靈巧地生產或改造事物的能力 喜歡動手建造東西、戶外活動,常用手勢或其他肢 體語言與人交談 學習時透過身體感覺來思考。 6. Interpersonal/Social (人際智能) This area has to do with interaction with others. High interpersonal intelligence : communicate effectively, empathize easily with others, and may be either leaders or followers. They often enjoy discussion and debate. 對臉部表情、聲音和動作較具敏感性 較喜歡參與團體活動,願意找別人幫忙或教導 他人 通常是團體中的領導者,靠他人的回饋來思考。 7. Intrapersonal (內省智能) Do with introspective and self-reflective capacities. Refers to having : a deep understanding of the self; what one's strengths, what makes one unique, being able to predict one's own reactions or emotions. 能自我瞭解內在情緒、意向、動機、脾氣、欲求、 自律、自知和自尊的能力。 以各種回饋管道中瞭解自己的優劣,常靜思規劃人 生目標,愛獨處,深入自我的方式來思考。 分事件層次(事件成敗的總結)和價值層次(聯繫成敗 和價值觀) 8. Naturalist (自然觀察) Do with nurturing and relating information to one's natural surroundings. This ability was clearly of value in our evolutionary past as hunters, gatherers, and farmers; it continues to be central in such roles as botanist or chef. 能認識植物、動物和其他自然環境 此智能強的人,在打獵、耕作、生物科學上的表現 較為突出。 自然觀察→探索智能: 兩方面探索:對社會的探索和對自然的探索 Likewise revolutionary style Robert Sternberg proposed “three types of smartness.” 1. Componential ability for analytical thinking 2. Experiential ability to engage in creative thinking, combining disparate experiences in insightful ways. 3. Contextual ability : “street smartness” that enables people to “play the game of manipulating their environment.” Daniel Goleman- Emotional Intelligence He places emotion at the highest level of a hierarchy of human abilities. Argued that : 1. The emotional minds is far quicker than the rational mind, springing into action without even pausing to consider what is doing. 2. Its quickness precludes the deliberate, analytic reflection that is the hallmark of the thinking mind.