Supply Chain Management Assignment #2: Case: Sport Obermeyer
advertisement
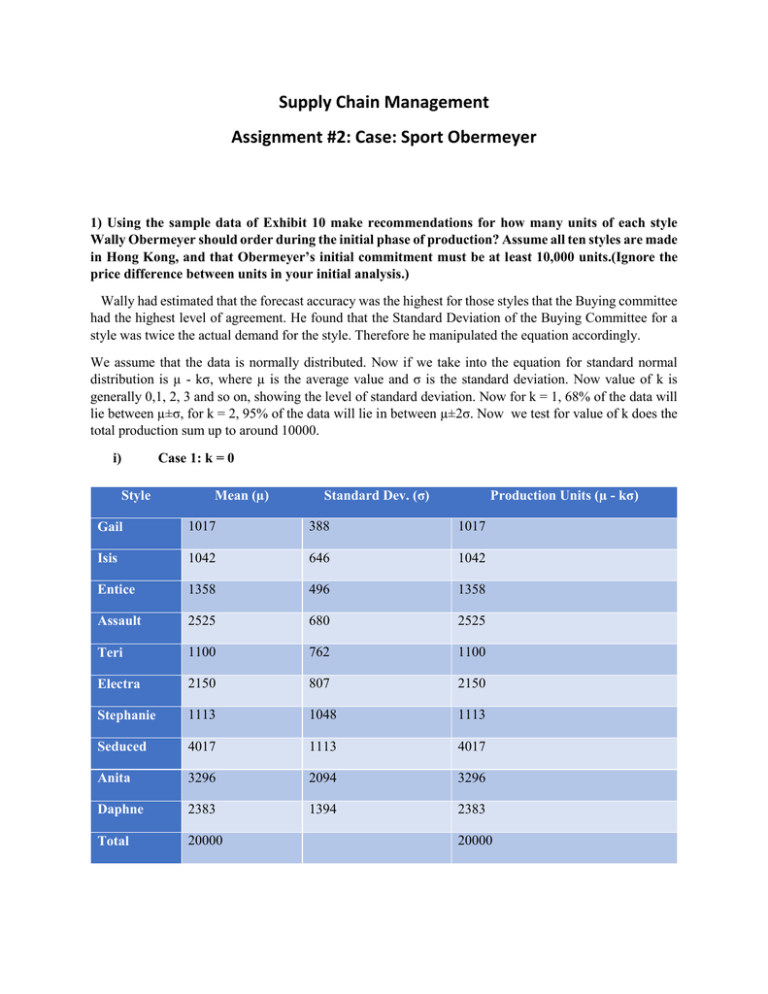
Supply Chain Management Assignment #2: Case: Sport Obermeyer 1) Using the sample data of Exhibit 10 make recommendations for how many units of each style Wally Obermeyer should order during the initial phase of production? Assume all ten styles are made in Hong Kong, and that Obermeyer’s initial commitment must be at least 10,000 units.(Ignore the price difference between units in your initial analysis.) Wally had estimated that the forecast accuracy was the highest for those styles that the Buying committee had the highest level of agreement. He found that the Standard Deviation of the Buying Committee for a style was twice the actual demand for the style. Therefore he manipulated the equation accordingly. We assume that the data is normally distributed. Now if we take into the equation for standard normal distribution is µ - kσ, where µ is the average value and σ is the standard deviation. Now value of k is generally 0,1, 2, 3 and so on, showing the level of standard deviation. Now for k = 1, 68% of the data will lie between µ±σ, for k = 2, 95% of the data will lie in between µ±2σ. Now we test for value of k does the total production sum up to around 10000. i) Style Case 1: k = 0 Mean (µ) Standard Dev. (σ) Production Units (µ - kσ) Gail 1017 388 1017 Isis 1042 646 1042 Entice 1358 496 1358 Assault 2525 680 2525 Teri 1100 762 1100 Electra 2150 807 2150 Stephanie 1113 1048 1113 Seduced 4017 1113 4017 Anita 3296 2094 3296 Daphne 2383 1394 2383 Total 20000 20000 Therefore we see taht this is much more than 10000. Therefore not accepted. ii) Case 2: k = 1 Style Mean (µ) Standard Dev. (σ) Production Units (µ - kσ) Gail 1017 388 629 Isis 1042 646 396 Entice 1358 496 862 Assault 2525 680 1845 Teri 1100 762 338 Electra 2150 807 1343 Stephanie 1113 1048 65 Seduced 4017 1113 2094 Anita 3296 2094 1202 Daphne 2383 1394 989 Total 20000 10573 Now we can see that this value is acceptable. If we test for k = 2, the value will fall below 10000. Therefore, the company should approximately produce the above mentioned units. 2) Can you come up with a measure of risk associated with your ordering policy? This measure should be quantifiable. • In the first production period, we are primarily concerned with markdown risk: – If we under-produce during the initial production period, we have a second production opportunity. • What is the relationship between risk and – Product price – Demand uncertainty – Expected demand 3) Repeat your methodology and assume now that all 10 styles are made in China. What is the difference between the two initial production commitments? The differences between production in HK and China 4) What operational changes would you recommend to Wally to improve performance? Reduce lead times – Computerize processes – Reduce minimum production lot-sizes – Do not commit initial production orders to unproven factory (rework, ramp-up) – Look for subcontractors who can delivery at a faster rate to fill in gaps – Use standardized products 5) How should Wally think (both short term and long term) about sourcing in Hong Kong versus sourcing in China? This year, Wally was expecting to produce about half its products in China. However in the short run run, the company should source its materials from Honk Kong and in the long run from China. Now, the reasons for sourcing from Hong Kong in the short run are: 1) China had the constraint of large minimum order sizes which could limit the company’s ability to increase the range of products it offered or manage the inventory risks. In China, the minimum order size was 1200, where as in Hong Kong it was 600. 2) The workforce in Hong Kong was twice as productive as compared to the Chinese. Therefore, a parka line in Hong Kong that required 10 workers to complete all operations would typically require 40 workers in China. 3) Also, the workers in Hong Kong were able to ramp up their production faster than the Chinese workers. Therefore, this ability, coupled with shorter production lines, enabled the Hong Kong factory to produce smaller orders more efficiently. 4) Also, the company could procure the YKK zippers from the Hong Kong factory faster than from Chin, because the factory of standard YKK zippers was located in Hong Kong. Therefore, on a short term basis, it would be easier for the company to source the products from Hong Kong itself. However, to source materials in the long run, the company should look towards China, because long term will involve large orders. The wages in China were $.16 per hour as compared to $3.84 per hour in Hong Kong. Therefore, if the company wanted to process large orders, it should look towards China rather than Hong Kong dispite the lower productivity of the Chinese workers.



