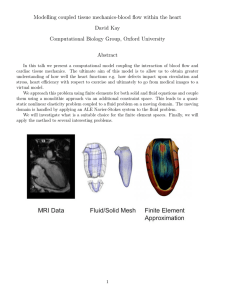
Document 15838819
advertisement

1 2 Right pleural effusion blunting the right costophrenic angle extending posteriorly with some fluid tracking into the major fissure seen on the lateral exam. Upright 3 The difference in an effusion on an upright film and on a supine film with the typical veil type density layering on the supine film and the upright film showing findings more suspicious for an elevated hemidiaphragm due to subpulmonic collection of fluid. Supine 4 5 Small amount of fluid tracking laterally in the right hemithorax. 6 Larger effusion with some fluid tracking into the minor fissure. 7 Fluid tracking into the major fissure on the left 8 Large pleural effusion collecting laterally along the right lateral chest wall with extension into the minor fissure. 9 10 Films show large pleural effusion and its change with decubitus position with the fluid layering dependently – note the beads in the left marker change position to indicate the position of the patient. Decubitus 11 Decubitus 12 13 13 Large subpulmonic effusion colleting under the inferior aspect of the left lower lobe – notice the apparent distance between the gastric bubble and the lung; this is the subpulmonic fluid. 14 Notice how large the effusion is with the decubitus position. Decubitus 14 Normal right costophrenic angle. 15 Supine Upright 16 Subpulmonic effusion collecting on the right. Note change in the effusion with supine positioning. 17 Lateral 18 Opacified hemithorax with mediastinal shift. Notice only one hemidiaphragm is visualized on lateral. 19 20 Patient with a pneumonectomy; notice the opacified chest with shift of the mediastinum towards the side of increased density. This is the distinguishing feature of the shift of the mediastinum towards or away from the opacifying thorax. Pneumothorax and pleural fluid (hydropneumothorax) note the straight air fluid level inferiorly in the right costophrenic angle and the elongated air fluid level on the lateral view. 23 Films show an empyema in the left costophrenic angle – notice the convex margin with the air fluid level. Compare that with the hydropneumothorax with a small amount of air in the pleural space collecting superiorly. 24 26 26 Films shows a pleural pseudo tumor due to loculated fluid tracking in the major fissure on the PA and lateral. 27 The CT Scan shows the loculated fluid simulating a mass. 28 Films show rounded density representing a rounded atelectasis in the right base with some pleural fluid as well. The effusion allows for atelectasis of the lung due to some compression of the effusion. 29 30 On the CT scan this can be seen as atelectatic lung. This is another pseudotumor where the rounded density simulates a mass. Soft tissue window 31 32 Bone window 33 Films shows density laterally in the left hemi thorax on PA view representing loculated pleural fluid collecting along the left lateral chest wall seen on soft tissue and lung windows. LT. LT. 34 Films show loculated effusion collecting on the PA and lateral with vague hazy density over the right hilar region and pleural fluid laterally. 35 34 The loculated fluid seen on the previous film is best demonstrated on this CT scan. 35