Animal Classification
advertisement
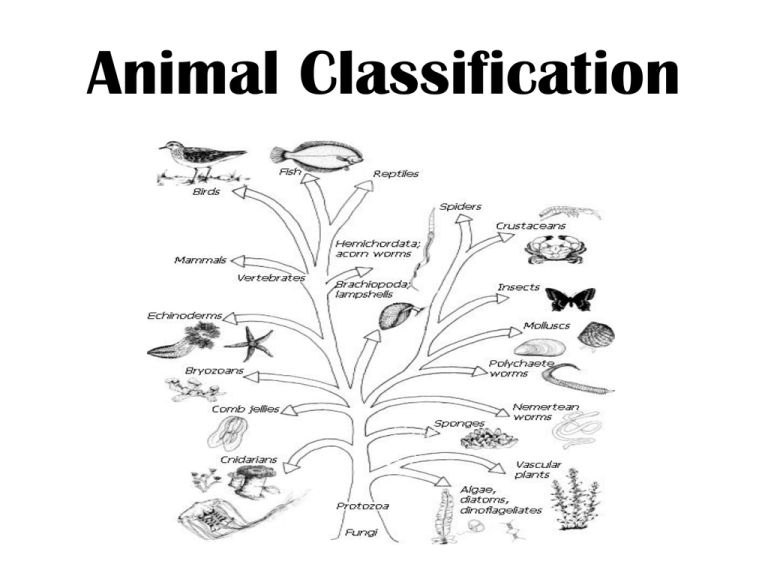
Animal Classification THE ANIMAL KINGDOM BASIC CHARACTERISTICS OF ANIMALS: 1. MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS 2. CAPABILITY OF LOCOMOTION 3. MUST INJEST FOOD NINE ANIMAL PHYLA INVERTEBRATES: (8 PHYLA) ALL LACK INTERNAL SKELETON, SOME HAVE EXOSKELTON OR SHELL VERTEBRATES (CORDATES): (1 phylum) INTERNAL SKELTON MADE OF BONE/ CARTILAGE 1. PORIFERA: • • • • • • ‘Pore- Bearing” Filter feeders Asymmetrical Feed and get rid of wastes thru diffusion Sessile Ex.- sponges 2. CNIDARIA • Have stinging tenacles • Stun prey with toxins • Prey is drawn into mouth and dissolved/ digested • Radial symmetry EXAMPLES: CORAL, JELLYFISH, SEA ANEMONE Polyps: Sea anemones Purple striped jelly, Pelagia panopyra 3. PLATYHELMINTHES: • One opening for ingestion and egestion • Primitive nervous system • Exchange gases by diffusion thru moist membranes • Bilateral symmetry EXAMPLES: PLANARIA, FLUKE, TAPEWORM 5. ANNELIDA • Segmented worms • Each segment has a nervous. circulatory, excretory, muscular system • Bilateral symmetry • First organism with complex body systems EXAMPLES: LEECH, EARTHWORMS 6. ARTHROPODA • • • • Animals with jointed appendages Have an exoskeleton They shed their exoskeleton (molt) We study crustaceans – these are marine arthropods EXAMPLES: SHRIMP, LOBSTER, CRAB, BARNACLE 7. MOLLUSCA • There are 3 classes: gastropods, bi-valves, cephalopods • Have an external shell • Have bi- lateral symmetry • Cephalopods are extremely intelligent • ex.- squid, octopus, cuttlefish, nautilus 8. ECHINODERMATA • • • • • Have spiny bodies Radial symmetry Benthic- bottom dwellers Central mouth on ventral surface ex.- sea urchin, sea star, sea cucumber, sand dollar 9. CHORDATA • Have a backbone that protects the spinal cord • Most developed nervous system • Contains animals that we are most familiar with • ex.- fish, mammals, reptiles, amphibians