Vocabulary learning activities are generally learning of vocabulary (Nation, 2001)

N98C0026 – Joanna Yang / 楊鎧綺
Vocabulary learning activities are generally categorized into two types: intentional and incidental learning of vocabulary (Nation, 2001)
One of the first attempts at providing a comprehensive overview of language learning strategies can be found in Oxford (1990)
Receptive and productive vocabulary learning:
The effects of reading and writing on word knowledge (2005)
Learning word pairs and glossed sentences:
The effects of a single context on vocabulary knowledge
Receptive and Productive Vocabulary learning: The effects of reading and writing on word knowledge (Stuart ,2005)
The same amount of time on both tasks, reading task was superior.
The allotted time on tasks depends on the amount of time needed for completion , with writing task requiring more time, the writing task, was more effective.
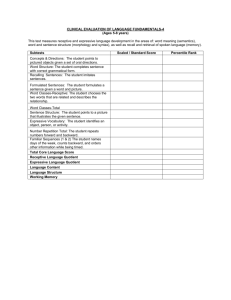
Refer to our textbook p451-453
For both teachers and students
Need to be aware of vocabulary learning limits.
-Language learners can be made aware of these limits by performing learning tasks with different numbers of words to determine how many items they can acquire.
-Teachers who use these learning tasks may be able to set vocabulary learning goals for students.
Using receptive and productive tests to measure an aspect of knowledge and testing multiple aspects of knowledge may give a much more accurate assessment of the degree and type of learning that has occurred.
The factors of selecting contexts (FM British National Corpus)
-the number of words
-the frequency of the words
-the ease in comprehending the sentence
The results suggest
-a single context may have little effect on gaining vocabulary knowledge
-both learning word pairs and learning glossed sentences are effective methods of learning vocabulary
Supporting
The findings of Dempster (1987), Laufer & Shmueli (1997) and contrasting with Griffin (1992) & Seibert (1930).
Expanded upon earlier methodologies by measuring receptive and productive knowledge of orthography, meaning, paradigmatic & syntagmatic association and grammatical functions
Limitations
-It was limited to one type of context – single glossed sentences. Examining the effects of different types of context would be a useful follow-up to this study.
Instrument & Subjects
Vocabulary notebooks Age range from 17 to 20 years
Hand puppet role play Kindergarten/preschool
Word lists Senior high school students
Dictionary referencing Pre-university level
•Target word&Sentence context University 1st year students
•Video tape
Kindergarten
•Picture & CD
Grade 1 and 6
• -The word Attack subtest of the Woodcock Reading
Mastery Tests – Revised (WRMT-R; Woodcock)
•-Test of word Reading Efficiency (TOWRE; Torgesen,
Wanger, & Rashotte
)
TBL University students
-A keyword is generated for the to-be-learned (TBL) word
Word pair lists & sentences University
Word list & cooperative Grade 4th students
Recommendable Journal
The Effect of keeping Vocabulary Notebooks on
Vocabulary Acquisition
JoDee W. & Neval B. (2009).
Learning Teaching Research
13, 403
- Structure similar as thesis
Clear statement
Recent report