New CountrySTAT approach
advertisement

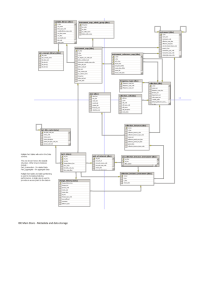
New CountrySTAT approach Overview Work flow Codification: CPC Codifications: HS Codifications: UM Codifications: Flags Codifications: GAUL Codifications: CountrySTAT indicators Codifications: Attributes Preparing tables in CountrySTAT Uploading tables in CountrySTAT Metadata Editor DSD Editor Data Editor Important rules for creating tables Retrieving tables in CountrySTAT Editing an already uploaded dataset Work flow • • Have the data ready • • CVS format No columns with labels Your table is published • • • • • Title Subject Data type Domain Key Create your table following the rules • • • • • • • • CPC 2.1 HS GAUL CountrySTAT indicators Attributes Unit of Measurement Flag • Have the metadata ready • • Upload the values 12/07/2016 3 • Create the DSD structure • Fill all metadata Use the right codification Go to the metadata editor Codifications CPC 2.1 For goods and services HS For trade data UM Unit of measurement Flags To indicate missing and estimated values GAUL For geo data CountrySTAT indicators For all indicators Attributes Characteristics of the indicators Codification: CPC • The Central Product Classification (CPC) constitutes a complete product classification covering all goods and services based on a set of internationally agreed concepts, definitions, principles and classification rules • It provides a comprehensive framework within which data on products can be collected and presented in a format that allows for economic analysis supporting decision-taking and policy-making 12/07/2016 5 Codification: CPC The current version, CPC version 2.1, is the result of a scheduled review of the CPC structure and detail, in order to ensure the classification’s relevance for describing current products in the economy. All detailed structure and explanatory notes can be found at the following link (CPC 2.1 not expanded version): http://unstats.un.org/unsd/cr/registry/regcst. asp?Cl=31 Here all the available correspondences: http://unstats.un.org/unsd/cr/registry/regot.asp?Lg=1 CPC 2.1 : Broad structure Codifications: HS The Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System generally referred to as "Harmonized System" or simply "HS" is a multipurpose international product nomenclature developed by the World Customs Organization (WCO). The Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System (HS) is an exhaustive nomenclature of internationally traded commodities (goods) classified according to the following criteria: – – – – 12/07/2016 raw or basic material degree of processing use or function economic activities 12 Codifications: UM 0101 0102 0103 0104 0105 0106 0107 0108 0109 0110 0111 0112 0113 0114 0115 head Ha ton US$ local currency index thousands units cubic meter kg/capita/yr Kcal/capita/day g/capita/day 1000 US$ Liter Cubic meter/second 0116 0117 0118 0119 0120 0121 0122 0123 0124 0125 0126 0127 Centimeter local currency by ton Degree Celsius Percentage MT or Cubic meter Local currency/hectar Local currency/1 cubic meter Kg/Ha Local currency/Kg 1000 Ha mm Square meter Codifications: FLAGS FLAGS • Category not applicable / Data not available = “m” Data for these categories do not even hypothetically exist and/or data included in another category / Missing data (data exist but were not collected) • Estimated value = “e” Codifications: GAUL The Global Administrative Unit Layers (GAUL) is an initiative implemented by FAO within the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Agricultural Market Information System (AMIS) and AfricaFertilizer.org projects. The GAUL compiles and disseminates the best available information on administrative units for all the countries in the world, providing a contribution to the standardization of the spatial dataset representing administrative units. The GAUL always maintains global layers with a unified coding system at country, first (e.g. departments) and second administrative levels (e.g. districts). Where data is available, it provides layers on a country by country basis down to third, fourth and lowers levels Codifications: GAUL The overall methodology consists in a) collecting the best available data from most reliable sources b) establishing validation periods of the geographic features (when possible) c) adding selected data to the global layer based on the last country boundaries map provided by the UN Cartographic Unit (UNCS) d) generating codes using GAUL Coding System e) distribute data to the users Codifications: GAUL Because GAUL works at global level, unsettled territories are reported. The approach of GAUL is to deal with these areas in such a way to preserve national integrity for all disputing countries . GAUL is released once a year and the target beneficiary of GAUL data is the UN community and other authorized international and national partners. Data might not be officially validated by authoritative national sources and cannot be distributed to the general public. A disclaimer should always accompany any use of GAUL data. GAUL keeps track of administrative units that has been changed, added or dismissed in the past for political causes. Changes implemented in different years are recorded in GAUL on different layers. For this reason the GAUL product is not a single layer but a group of layers, named "GAUL Set" . Codifications: GAUL ADM0_NAME ADM1_CODE ADM1_NAME Kenya 51325 Central Kenya 51326 Coast Kenya 51327 Eastern Kenya 51328 Nairobi Kenya 51329 North Eastern Kenya 51330 Nyanza Kenya 51331 Rift Valley Kenya 51332 Western Codifications: CountrySTAT indicators code 0101 0102 0103 0104 0105 Production 0106 0107 0108 0109 0110 0201 Food availability 0202 0203 0301 0302 0303 0304 Trade 0305 0306 0307 Domain indicator Production quantity Production value Yield Area Harvested Area sown Seeds quantity Slaughtered animals Live animals Laying hens Lactating live animals Protein quantity Lipid quantity Food supply quantity Export quantity Export value Import quantity Import value Consumption quantity Re-export quantity Re-export value Machinery 0401 Machines in service 0501 Population Economically active Population 0502 population 0503 Population total density 0504 Population growth Rate 0601 Consumer price 0602 Producer price Prices 0603 Commercial rate 0604 Official rate 0701 Constant prices Value added 0702 Current prices 0801 Agricultural area 0802 Permanent crops area 0803 Temporary crops area Arable land and permanent Land use 0804 crops area 0805 Forest area 0806 Other wooded land 0901 Unemployment Rate Employment 0902 Labourforce Participation Rate 1001 Average rainfall Water Codifications: Attributes Gender code 8001 8002 8003 dimensions Total Male Female Food Agricultural Population code 8011 8012 code 8007 8008 dimensions Agricultural Non-Agricultural Residence code 8004 8005 8006 dimensions Rural Urban Total Field management code 8009 8010 dimensions Rainfed Irrigated dimensions Food Non Food Codifications: Attributes – DAC: Sector DAC 5 CODE 110 111 112 113 114 120 121 122 130 140 150 151 152 160 210 230 240 250 310 311 DESCRIPTION EDUCATION Education, level unspecified Basic education Secondary education Post-secondary education HEALTH Health, general Basic health POPULATION POLICIES/PROGRAMMES AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH WATER SUPPLY AND SANITATION GOVERNMENT AND CIVIL SOCIETY Government and civil society, general Conflict prevention and resolution, peace and security OTHER SOCIAL INFRASTRUCTURE AND SERVICES TRANSPORT AND STORAGE ENERGY GENERATION AND SUPPLY BANKING AND FINANCIAL SERVICES BUSINESS AND OTHER SERVICES AGRICULTURE+FORESTRY+FISHERY AGRICULTURE Preparing tables in CountrySTAT 1° dimension : Year 2° dimension : code and label 3° dimension : code and label Unit of measurement: code and label Value Flag Preparing tables in CountrySTAT 1° dimension : Year 2° dimension : code and label 3° dimension : code and label Unit of measurement: code and label Value Once done, DELETE ALL LABEL COLUMNS Flag Preparing tables in CountrySTAT Preparing tables in CountrySTAT This is how a table should look like after deleting its label columns! year Indicator (code) 1990 0102 1990 0102 1990 0102 1990 0102 1990 0102 1991 0102 1991 0102 1991 0102 1991 0102 1991 0102 1992 0102 1992 0102 1992 0102 1992 0102 1992 0102 1993 0102 1993 0102 1993 0102 species (code) Value Flag 21115 454 21113 15532 21116 1534 21121 19000000 21111 126318 21111 124281 21115 285 21113 16189 21116 2166 21121 19500000 21116 1107 21113 13155 21111 114086 21121 18000000 21115 297 21113 7000 21115 176 21121 17500000 um (code) 0101 0101 0101 0101 0101 0101 0101 0101 0101 0101 0101 0101 0101 0101 0101 0101 0101 0101 Preparing tables in CountrySTAT • Save it and keep the Excel table open • Go in the Metadata Editor • Go in the DSD Editor • Save the file in CVS and close it Important rules for creating tables The Excel spreadsheet must be formatted as text The name of the Excel file must NOT contain any accent and/or symbol and/or numbers and/or empty spaces Always convert to CSV file at the very end and do not open the CSV file afterwards! Important rules for creating tables NEVER use comma or dot for separating the thousands e.g. one thousand: NO 1.000 NO 1,000 YES 1000 Always use a dot for separating decimals e.g. three dot four: NO 3,4 YES 3.4 In each “value cell” input only a numeric value or only text in the other column e.g. two tons: NO 2 tons YES 2 called “unit” write tons Uploading tables in CountrySTAT Uploading tables in CountrySTAT METADATA • Definition: a metadata is a data defining a data. – Metadata on statistical data (to insure quality of data): units, source, contact, creation date, last-updated date … – And additional statistical metadata (methodology, survey/census, frequency of data collection, etc…) 7/12/2016 METADATA Metadata example Raw data without any data : I don't know the meaning of the data, I suspect it's the age of the races. Data with metadata: With two metadata, (title – name of variable), I know the meaning of the data. 12/07/2016 32 Metadata Editor The more fields are filled in, the more accurate the description of data and the retrieval of the dataset will be. Metadata Editor Once the previous section has been filled, by clicking on each of these elements, new sections will appear. These new sections need to be completed as well. All these information enhance data quality and end-users’ trust in the related data! Metadata Editor After every category has been filled with the right metadata information, click on the “save” button at the top right of the page, in order to get to the next phase of the uploading. DSD Editor The green boxes in the upper right corner signify that the resource has been created and metadata has been correctly stored. The “edit resource” box contains three buttons: • “Metadata”, which brings back the metadata editor tool. • “DSD”, to create the DSD structure mirroring the one of your dataset • “Data”, to upload and modify your dataset DSD Editor Start adding columns to the DSD structure by clicking on the “+” sign. The structure should mirror the one of the dataset you wish to upload. • Dimension refers to time and geo information as well as indicators and commodities • Value refers to actual numeric or percentage values • Other refers to flag, unit of measurement columns, etc. DSD Editor Clicking on the “Dimension +” will lead to this page in which the following information can be entered: • Title, which refers to the column header’s name • Supplemental, which refers to supplemental info regarding that column data • Subject, which refers to the type of data contained in the column • Data type, which specifies the type of data chosen in the subject • Domain, which requires the user to choose the appropriate codelist from those available, if needed Once done don’t forget to click here! Once all the columns have been entered, it will look like this! Download DSD if you want to save this DSD structure. Don't forget to save it Next time you’ll just need to upload it and the DSD will automatically show up Data editor Once in the Data editor, the dataset can be uploaded by clicking on “Browse” Don’t forget that the dataset must be in CSV format Data editor Once the dataset you wish to upload is selected, a new interface will open. Here you will have to align the columns of your dataset with the ones you created through the DSD editor. To switch two columns just drag and drop the name of any column. Don’t forget to press the Ok button once everything is ok Data editor Once the dataset is uploaded it will look like this! Retrieving tables in CountrySTAT Tables’ retrieval is driven by the metadata previously stored during the uploading of the dataset. By clicking on the “Search” button, datasets can be retrieved by imposing metadata fields as filters. Retrieving tables in CountrySTAT By clicking on content, the retrieval of datasets can be filtered by selecting “Resource type”, “Reference period” and so on. More than one filter can be selected at once. Retrieving tables in CountrySTAT The more criteria are imposed the more the dataset’s retrieval will be refined since, by selecting more than one filter at once, only datasets compliant with every one of those filters will be shown. Retrieving tables in CountrySTAT Underneath the selectors, a “selection resume” will be displayed showing the selected filters. By clicking on “show result” datasets compliant with the chosen criteria will be displayed. Editing an already uploaded dataset After successfully retrieving a dataset, by clicking on the “Data” button from the “Edit Resource” box, the above-mentioned dataset will be shown Editing an already uploaded dataset • By clicking on the “Pencil” button of any row, a pop-up will be displayed allowing the chosen row to be modified. • By clicking on the “Dustbin” button of any row, the chosen row will be removed from the dataset. Editing an already uploaded dataset A new row can be added to the dataset without uploading it again from the beginning. This can be done by clicking on the “Plus” button located at the bottom left of the page and compiling the newlyappeared pop-up. Editing an already uploaded dataset After all the editing has been done, remember to click on the “Save” button on the top right of the page.