Pathogens & Contaminants Corinne Waelti, seecon international gmbh 1
advertisement

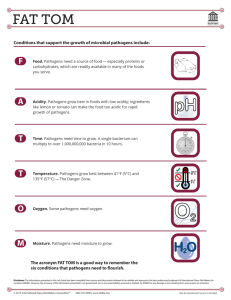
Pathogens & Contaminants Corinne Waelti, seecon international gmbh Pathogens & Contaminants 1 Find this presentation and more on: www.sswm.info. Copyright & Disclaimer Copy it, adapt it, use it – but acknowledge the source! Copyright Included in the SSWM Toolbox are materials from various organisations and sources. Those materials are open source. Following the opensource concept for capacity building and non-profit use, copying and adapting is allowed provided proper acknowledgement of the source is made (see below). The publication of these materials in the SSWM Toolbox does not alter any existing copyrights. Material published in the SSWM Toolbox for the first time follows the same open-source concept, with all rights remaining with the original authors or producing organisations. To view an official copy of the the Creative Commons Attribution Works 3.0 Unported License we build upon, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0. This agreement officially states that: You are free to: • Share - to copy, distribute and transmit this document • Remix - to adapt this document. We would appreciate receiving a copy of any changes that you have made to improve this document. Under the following conditions: • Attribution: You must always give the original authors or publishing agencies credit for the document or picture you are using. Disclaimer The contents of the SSWM Toolbox reflect the opinions of the respective authors and not necessarily the official opinion of the funding or supporting partner organisations. Depending on the initial situations and respective local circumstances, there is no guarantee that single measures described in the toolbox will make the local water and sanitation system more sustainable. The main aim of the SSWM Toolbox is to be a reference tool to provide ideas for improving the local water and sanitation situation in a sustainable manner. Results depend largely on the respective situation and the implementation and combination of the measures described. An in-depth analysis of respective advantages and disadvantages and the suitability of the measure is necessary in every single case. We do not assume any responsibility for and make no warranty with respect to the results that may be obtained from the use of the information provided. Pathogens & Contaminants Find this presentation and more on: www.sswm.info. Contents 1. Introduction 2. Characteristics of Pathogens and Contaminants 3. Pathogens 4. Contaminants 5. References Pathogens & Contaminants 3 Find this presentation and more on: www.sswm.info. 1. Introduction The overall Problem Substances such as pathogens (microorganisms) and contaminants (chemicals and metals) in drinking water may harm both public health and the environment. In developing countries, the contamination of drinking water with pathogens is the major factor for prevalence of diseases. Most often, faeces infiltrating drinking water sources are responsible for contamination with pathogens. Contaminants in drinking water may originate from human activities and natural processes. Pathogens & Contaminants 4 Find this presentation and more on: www.sswm.info. 2. Characteristics of Pathogens and Contaminants Types of Pathogens and Contaminants Pathogens •Bacteria • e.g. Salmonella, Escherichia coli, Campylobacter •Viruses • e.g. Rotavirus, Hepatitis •Parasitic protozoa • e.g. Giardia •Helminths (worms) • e.g. Trichuris trichiura Contaminants • Inorganic chemicals • e.g. nitrate, arsenic, fluoride, chloride • Organic chemicals • e.g. petro-chemicals (oil, diesel), solvents, drugs, pesticides • (Heavy) metals • e.g. cadmium, copper, lead, mercury Microorganisms Pathogens & Contaminants 5 Find this presentation and more on: www.sswm.info. 2. Characteristics of Pathogens and Contaminants Sources of Pathogens and Contaminants Source: BUCHANAN et al. (2010) • Underground storage tanks • Chemical storage • Accidental spills of hazardous materials • Spreading of sewage treatment sludge • Septic systems • Animal feedlots • Storage and spreading of road salt • Underground pipelines or sewers • Use and spilling of fertilisers and pesticides • Landfills • Private and abandoned wells Source: CONSERVATION ONTARIO (2009) Pathogens & Contaminants 6 Find this presentation and more on: www.sswm.info. 2. Characteristics of Pathogens and Contaminants Dispersion of Pathogens and Contaminants Migration of contaminants in an unconfined (left) and a confined (right) aquifer. Movement of insoluble contaminants in ground water: Oil spills (lighter than water) accumulate on the water table and spread horizontally. Source: WAL (2010) Pathogens & Contaminants Adapted from FREEZE et al. (n.y.) 7 Find this presentation and more on: www.sswm.info. 2. Characteristics of Pathogens and Contaminants General Effects of Pathogens and Contaminants Drinking water contamination: •Poor drinking water quality •Loss of community’s drinking water supplies Impacts on the environmental system by contaminants: • Loss of ecosystem functions •High costs for restoration and alternative drinking water supplies •Health problems Examples for related economic effects: Examples for related economic effects: • Higher health expenses • Less revenue by fisheries • Restricted work force • Less revenue from tourism Pathogens & Contaminants 8 Find this presentation and more on: www.sswm.info. 3. Pathogens Transmission & Health Risks of Disease Faecal-oral transmission routes: • Fingers • Flies and other insects • Fields (agriculture) • Food • Fluids Health risks: Gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhoea, vomiting and stomach cramps Source: HESPERIAN & UNDP (2004) Pathogens & Contaminants 9 Find this presentation and more on: www.sswm.info. 3. Pathogens Probability of Causing Infections Persistence in the environment Low minimal infective doses Little or no human immunity Amount and variability of pathogens Long latency periods SHUVAL et al. (1986) Pathogens & Contaminants 10 Find this presentation and more on: www.sswm.info. 3. Pathogens Probability of Causing Infections Sanitation system Persistence in the environment Low minimal infective doses Little or no human immunity Source: http://2.bp.blogspot.com/2yIT8xt_stM/TwtB4J9sBqI/AAAAAAAACmY /s_69HHksUA/s1600/Istanbul%20Toilet.gif [Accessed: 05.06.2012] Amount and variability of pathogens Long latency periods SHUVAL et al. (1986) Pathogens & Contaminants 11 Find this presentation and more on: www.sswm.info. 4. Contaminants Health Risks related to contaminated Groundwater Possible health risks: • Cancer • Liver, kidney and nerve problems • Birth defects • Learning disabilities in children Source: WALLIN (1997) Source: http://www.thewaterchannel.tv/tutorial/s ection_4/6.html Pathogens & Contaminants 12 Find this presentation and more on: www.sswm.info. 5. References BUCHANAN, B., DE LA CRUZ, N, MACPHERSON, J., WILLIAMSON, K. (2010): Water Wells that Last for Generations. Edmonton: Alberta Agriculture and Rural Development. URL: http://www1.agric.gov.ab.ca/$department/deptdocs.nsf/all/wwg404 [Accessed: 05.06.2012]. CONSERVATION ONTARIO (Editor) (2009): Wellhead Protection Areas. Newmarket: Conservation Ontario. URL: www.conservationontario.ca/source_protection/files/ODWSP%202009%20Finals/ODWSP_FAQS_wellhead_EN_2009_02_27_WEB.pdf [Accessed: 06.06.2012]. FREEZE, R.A., ATWATER, J., LIEBSCHER, H. (n.y.): Water Stewardship . Ground Water Resources of British Colombia. Victoria: The Province of British Columbia. URL: http://www.env.gov.bc.ca/wsd/plan_protect_sustain/groundwater/gwbc/C05_contamination.html [Accessed: 05.06.2012]. HESPERIAN FOUNDATION (Editor); UNDP (Editor) (2004): Sanitation and Cleanliness for a Healthy Environment. Berkeley: The Hesperian Foundation. URL: www.unwater.org/downloads/EHB_Sanitation_EN_lowres.pdf [Accessed: 05.06.2012]. SHUVAL H.I., ADIN, A., FATTAL, B., RAWITZ, E., YEKUTIEL, P. (1986): Wastewater Irrigation in Developing Countries. Health Effects and Technical Solutions. Washington, D.C.: The World Bank. URL: http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/1986/05/440564/integrated-resource-recovery-wastewater-irrigation-developingcountries-health-effects-technical-solutions [Accessed: 05.06.2012]. WAL, A. van der (2010): Understanding Groundwater & Wells in Manual Drilling. Instruction Handbook for Manual Drilling Teams on Hydro-geology for Well Drilling, Well Installation and Well Development. Papendrecht: Practica Foundation. URL: www.unicef.org/wash/files/04.pdf [Accessed: 06.06.2012]. WALLIN, R. (1997): Wellhead Protection: A Guide for Arizona Communities. TUCSON: Arizona Department of Environmental Quality, Water Quality Division. URL: http://www.unicef.org/wash/files/04.pdf [Accessed: 05.06.2012]. Pathogens & Contaminants 13 “Linking up Sustainable Sanitation, Water Management & Agriculture” SSWM is an initiative supported by: Created by: Pathogens & Contaminants 14