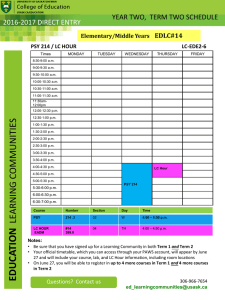
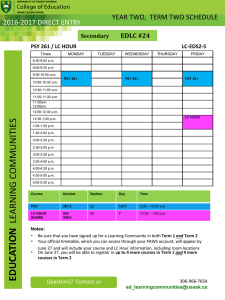
Introduction to MRI: NMR • Physics reminders • NMR phenomena
advertisement

Introduction to MRI: NMR • Physics reminders – Nuclei and atoms – Electromagnetic spectrum and Radio Frequency – Magnets – Vectors • NMR phenomena – nuclei, atoms and electron clouds (molecular environment) – excitation and energy states, Zeeman diagram – precession and resonance quantum vs. classical pictures of proton(s) Psy 8960, Spring ’07 Introduction to MRI 1 Electromagnetic spectrum http://www.nps.gov Psy 8960, Spring ’07 Introduction to MRI 2 Electromagnetic spectrum c = = 3 x 108 m/s / www.yorku.ca/eye/spectru.htm Psy 8960, Spring ’07 Introduction to MRI 3 RF Antennae vs. RF coils Antennae disperse energy Coils focus energy www.yorku.ca/eye/spectru.htm Psy 8960, Spring ’07 Introduction to MRI 4 Nuclei and subatomic particles Psy 8960, Spring ’07 Introduction to MRI 5 Stern-Gerlach experiment: discovery of spin • Discovery of magnetic moment on particles with spins • Electron beam has (roughly) even mix of spin-up and spin-down electrons – Beam should be bent to the side because a force is exerted on moving charge in a magnetic field – Beam was also split vertically, because electrons posses inherent magnetic moment http://www.upscale.utoronto.ca/GeneralInterest/Harrison/SternGerlach/SternGerlach.html Psy 8960, Spring ’07 Introduction to MRI 6 Spin and magnetic moment • Sub-atomic particles have intrinsic angular momentum (spin), L • Aligned with L is , a magnetic moment • The quantum number I determines how many spin states a particle might be found in Lz m z Lz – For a nucleus, the number of protons and neutrons determines I • L and are related by , the gyromagnetic ratio L I(I 1) L Psy 8960, Spring ’07 Introduction to MRI 7 Periodic table: some nuclei are magnetic Psy 8960, Spring ’07 Introduction to MRI 8 Water www.lsbu.ac.uk/water/ Psy 8960, Spring ’07 Introduction to MRI 9 Magnets Dipole in a static field Lowest energy Highest energy B N Units of magnetic field: 1 Tesla = 104 Gauss 0.5 G = earth’s magnetic field ~50 G = refrigerator magnet S E B B Psy 8960, Spring ’07 Introduction to MRI 10 Magnets Dipole in a static field Lowest energy Proton in a static magnetic field Highest energy : magnetic dipole B N S E B B Psy 8960, Spring ’07 Introduction to MRI 11 Single spin-1/2 particle in an external magnetic field Nucleus in free space Nucleus in magnetic field Lz m Lz z Lz 2 z Lz L I(I 1) L Spin-up and spin-down are different energy levels; difference depends linearly on static magnetic field All orientations possess the same potential energy m E B m Psy 8960, Spring ’07 Introduction to MRI 1 2 1 2 12 Resonant frequency m E 1 2 Transition emits energy B m 1 2 Excitation promotes transition • Resonant frequency is determined by gyromagnetic ratio, a property of the nucleus • At 3T, protons resonate at ~128 MHz • At 7T, protons resonate at ~300 MHz Psy 8960, Spring ’07 Introduction to MRI 13 Electromagnetic spectrum c = = 3 x 108 m/s / www.yorku.ca/eye/spectru.htm Psy 8960, Spring ’07 Introduction to MRI 14 Hydrogen spectrum: electron transitions 1 electron volt = 1.6 × 10-19 J Fixed energy transitions result in discrete absorption lines http://csep10.phys.utk.edu/astr162/lect/light/absorption.html Psy 8960, Spring ’07 Introduction to MRI 15 Precession and resonant frequency Lz 2 z Lz Spin-up and spin-down are different energy levels; difference depends linearly on static magnetic field Torque exerted by magnetic force on dipole creates precession. dL B dt Lz B sin( ) B sin( ) Psy 8960, Spring ’07 Lz m E 1 2 E 2 B L B B 1 m 2 Introduction to MRI L B 16 Gyromagnetic (magnetogyric) ratio B L I(I 1) L Psy 8960, Spring ’07 L B B B L Introduction to MRI 17 From spin-1/2 particles to bulk magnetization B M: net (bulk) magnetization isochromat Excitation affects phase and distribution between spin-up and spin-down, rotating bulk magnetization M|| Equilibrium: ~ 1 ppm excess in spin-up (low energy) state creates a net magnetization M M Psy 8960, Spring ’07 Introduction to MRI 18 Information in proton NMR signal • Resonant frequency depends on • Static magnetic field • Molecule • Relaxation rate depends on physical environment • Microscopic field perturbations – Tissue interfaces – Deoxygenated blood • Molecular environment – Gray matter – White matter – CSF Excitation Relaxation Psy 8960, Spring ’07 Introduction to MRI 19 Proton NMR spectrum: ethanol /grupper/KS-grp/microarray/slides/drablos/Structure_determination Psy 8960, Spring ’07 Introduction to MRI 20