Homework: Practice Exam
advertisement

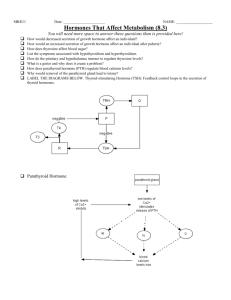
Homework: Practice Exam Grading: Turn in the multiple choice questions to me on a Scan Tron; choose any 4 short essay to complete, and grade yourselves based on my key (available second week of class). Each essay question is worth 10 points. Turn your graded essay questions in to me. There are a few multiple choice questions that go back to the special senses. Guidelines: All information required can be found in your textbook, Applications Manual and/or the notes. I will provide an accessory handout for the last essay question. You are certainly welcome to use outside sources, but are not required to do so. Unless otherwise stated, you are only required to provide as much detail as I provided in my notes. If I want you to go beyond that, I will clearly state so. To my new students: For questions that tap into last quarter, my lecture notes are still on the web, so you can get an idea of the detail I went into. You are welcome and encouraged to work in groups, but keep in mind: all written material must be original. Any papers with duplicate answers (or those in which a few words have been changed here and there) will be severely penalized. Any papers that mimic the book or my lecture outlines will be severely penalized. All work must be in your own words. Each question has many parts. Be very careful that you answer each part, and don’t forget anything. You do not necessarily have to answer the question in paragraphs/full sentences. Some of the questions are best answered with tables or diagrams. Feel free to use them, just be sure to clearly indicate what’s going on. Short Essay 1. a. List 2 hormones that affect the use of energy by cells (glucose &/or fatty acid use, ATP production, gluconeogenesis, glycogenolysis, glycogenesis, lipolysis or fat storage) For each, state the class it belongs to, where it’s produced, two effects that it has, and what stimulates its release. Briefly describe one disorder associated with one of these hormones. Hormone Class Where produced Two effects What stimulates release Disorder (Name hormone and describe): b. Now do the same for 2 hormones that affect calcium in blood and/or bone, either directly or indirectly. Do not describe a disorder for one of these. Hormone Class Where produced Two effects What stimulates release 2. a. Describe one hormone (other than any listed from #1) that is ultimately under the control of the hypothalamus/adenohypophysis. Name the hormone/factor from the hypothalamus, the hormone from the adenohypophysis, and the final hormone and where it comes from (kidney, etc). Describe one effect this final hormone will have on target cells. How do hormones get from the hypothalamus to the adenohypophysis? b. A person with symptoms of hypothyroidism (for example, sluggishness and intolerance to cold) is found to have abnormally low plasma concentrations of T4, T3, and TSH. After an injection of TRH the plasma concentrations of all three hormones increase. Where is the site of the defect leading to the hypothyroidism? c. Vera is receiving very large doses of a cortisol-like drug to treat her arthritis. Theoretically, what should happen to her own production/secretion of cortisol (increase or decrease)? What hormone should a drug mimick if you wanted to increase Vera’s production of GCTH? 3. This example has absolutely no basis in reality. If you know how the hormones can affect their target cells and which use 2nd messengers, you can predict how any hormone, fake or real, will act. Hormone X is a hormone in the Who species (you know, the kind that Horton heard and the Grinch wanted to repress). Hormone X allows the Whos to sing for extended periods of time. It does so by affecting metabolism in a number of different ways. One of the specific effects Hormone X has is in muscle cells of the larynx: it stimulates those cells to increase the number of enzymes involved in ATP production. a. Let’s say Hormone X is a peptide hormone. Describe how it will affect a muscle cell of the larynx, starting with its arrival at the target cell and ending with the production of more active enzyme (be sure to state why there’s more active enzyme) b. Now repeat, only this time pretend Hormone X is a steroid hormone. 4. You are an employee for a company who just hired a new manager. On his second day, he came barging into your office telling you that he’s been going through your records and watching your performance, and if things don’t shape up dramatically and soon, you’re outta there. You were completely unaware of any problem and have no idea how to remedy the situation, so everyday for the next month or so you enter the office of eggshells wondering if today is the day you will be fired. Oh, and you have no savings or prospects for jobs and for some reason are ineligible for unemployment compensation. Assuming that you are a reasonably sensitive person (ie, this actually will affect you), a. Briefly describe your Autonomic Nervous System response when the boss came in and barked this information at you. Be sure name the dominating division and to include 4 specific effects of the dominating division. b. Describe your endocrine response starting with the first traumatic event and then the subsequent long-term response (ie, go through the phases of the stress response). Be sure to name the dominant hormones of each phase, and the effects each of the hormones will have. c. Why are the maintenance of blood glucose and the mobilization of lipids the major themes of the long-term response? d. Is the long-term endocrine response designed to help you survive this particular type of crisis? What type/s of crises is it designed to help you survive? Bonus 1 point: Based on the effects of the hormones involved, why do you think that overeating and a lack of exercise might actually make this stress response harmful rather than helpful? 5. You’re a reporter at the scene of a disaster. Actually, you’re a really tiny reporter living inside a biology instructor. The disaster is that one of the instructor’s blood vessels has just been sliced by a scalpel. You’ve arrived at the scene immediately. a. List the 3 phases of hemostasis, and state one event which will happen during EACH phase. b. How do the first platelets on the scene get stuck/activated? c. Name one factor released by platelets/endothelial cells that will promote the clotting process. d. Outline or diagram the biochemical cascade of events that occurs once Factor X is activated. e. Briefly describe one thing that will aid in the clean-up or control of a clot. 6. Tilly, Ermy, Fanny and Si are donating blood. The following shows the results of their blood tests. Assume that all Rh- people have received Rh+ blood in the past. a. Complete the chart by filling in each of their blood types: Anti-A No reaction Agglutination No reaction Agglutination Tilly Ermy Fanny Si b. c. d. e. f. Anti-B Agglutination Agglutination No reaction Agglutination Anti-Rh No reaction No reaction Agglutination Agglutination Type? From which group member/s can Si receive blood? To which group member/s can Si give blood? From which group member/s can Ermy receive blood? To which group member/s can Fanny give blood? Is anyone in this group unable to receive blood from the others (if so, name/s)? Multiple Choice ( .93 point each) Choose the BEST answer for each of the following. Please use a Scan-Tron. 1. Luppe has not been exposed to sunlight for several months. Which of the following might we expect to find severely depressed levels of in his blood? a. Ca2+ b. PTH c. Calcitriol d. Vitamin K e. All of the above 2. Theoretically, who would be most likely to need to take both thyroid hormone and calcitonin as a medication? a. An adult with Grave’s disease b. A person with hyperparathyroidism c. An infant with congenital hypothyroidism (dysfunctional or non-existent thyroid) d. An adult with hypothyroidism e. A child with type I diabetes (dysfunctional pancreas) 3. Which of the following would diffuse across the membrane of its target cell? a. Tri-iodothyronine b. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone c. Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone d. Epinephrine e. Oxytocin 4. The most likely target cell of erythropoietin would be _________, and erythropoietin _______ actually enter the cell to produce its effect. a. Melanocytes; would b. Erythrocytes; would not c. Lymphoid stem cells; would not d. Folllicle cells; would e. Myeloid stem cells; would not 5. Which of the following is not a known role of Ca2+in the body? a. Acts as a second messenger b. Triggers neurotransmitter release c. Involved in muscle contraction d. Acts as a neurotransmitter e. Neither A nor D are known roles of Ca2+ 6. Currently, most of Homer’s body cells are using glucose to make ATP. His adipose cells are taking in fatty acids and storing them as triglycerides. He probably had a doughnut ______, and his liver cells are probably _______ glycogen. a. Recently; synthesizing b. Many hours ago; breaking down c. Recently; breaking down d. Many hours ago; synthesizing 7. Goiter can be the result of the overproduction of unfinished: a. Thyroxine b. Reticulocytes c. Erythrocytes d. Calcitonin e. Oxytocin 8. Connie visits her doctor after she stumbles on her stairway and incurs a bone fracture. Her physician conducts a bone density test and determines that her bones are very thin for her age. He then takes a blood sample and finds that she has extremely elevated levels of Ca2+ in her blood. Which structure in her body is he most likely to suspect a problem with? a. The thyroid gland b. The parathyroid glands c. The kidneys d. The adenohypophysis e. No structure, instead he will be interested in her exposure to sun 9. Tryptophan is an essential amino acid, which means that our cells are not able to make it, so we must obtain it from dietary proteins. Hypothetically, which of the following symptoms might you expect if you had a deficiency of tryptophan (actually, you would show symptoms of general protein deficiency rather than symptoms specific to tryptophan): a. Reduced ability to increase heart rate b. c. d. e. Increased occurance of free radical damage in the brain Altered sleep cycles A and B B and C 10. Which of the following would you NOT expect to occur during the Alarm Phase of a stress response? a. More epinephrine and norepinephrine are secreted from the adrenal medullae b. Cardiac muscle fails because of a lack of K+; organs are digested to provide amino acids for gluconeogenesis c. Pupils constrict d. A and B e. B and C 11. Which of the following deficiencies would you expect to have the greatest effect on vision? a. Vitamin D b. Ca2+ c. Vitamin A d. Vitamin K e. K+ 12. Female eggs and male sperm require the help of special “nanny cells” to develop properly. The production of nanny cells is induced by: a. Glucocorticoids b. Epinephrine c. Follicle Stimulating Hormone d. Oxytocin e. More than one of the above 13. How are the retina and the epithalamus related? a. Both send impulses to the visual cortex along the optic nerve b. Both contain populations of photoreceptors that are sensitive to light energy c. The epithalamus communicates with the retina via the mesencephalon to alter photoreceptors’ sensitivity to light energy at different times of the day d. The retina communicates with the epithalamus via the hypothalamus to relay information about day length e. Serotonin is produced by satellite cells in the retina and sent to the epithalamus 14. Which sensory system relies on ciliated cells being pushed against a thick immovable membrane? a. Olfaction b. Gustation c. Vision d. Equilibrium e. Hearing 15. Which sensory system uses a one-cell system, in which the sensory neuron that sends the message to the brain is the same cell that detects the stimulus directly? a. Olfaction b. Vision c. Hearing d. Equilibrium e. None of the above 16. Where does the above sensory system send its nerves? a. Olfactory bulbs b. Visual cortex c. Cochlear nuclei d. Vestibular nuclei e. Cerebellum 17. Hormones are rid/inactivated by: a. Enzymes in tissue interstitial fluids b. Degradation or excretion by liver cells c. Enzymatic degradation at synaptic clefts d. A and B e. A and C 18. Which of the following is NOT a peptide hormone? a. Insulin b. Erythropoietin c. Glucagon d. Progesterone e. Calcitonin 19. What is the role of vitamin A in vision? a. Retinal is a form of vitamin A b. Opsin is a form of vitamin A c. Vitamin A is part of an enzyme that drives some of the reactions that occur in response to light energy d. The iris is pigmented with carotenoids e. None of the above 20. Which of the following does NOT directly promote the secretion of a hormone from another gland? a. Prolactin b. Leutenizing hormone c. Thyroid stimulating hormone d. Adrenocorticotropic hormone e. A and B 21. Evidence of alcohol’s effect on ADH release would logically include: a. Frequent urination b. Bloating c. Dehydration d. A and B e. A and C 22. Which of the following does a mature (mammalian) red blood cell lack: a. Nucleus b. Glycolytic enzymes c. Mitochondria d. A and C e. B and C 23. Calcitonin is made in the ______ by ______. a. Kidneys; follicles b. Islets of Langerhans; beta-cells c. Thyroid gland; c-cells d. Kidneys; beta-cells e. Thyroid gland; follicles 24. Which of the following is secreted FARTHEST (in distance) from the adrenal cortex? a. Glucocorticoids b. Aldosterone c. AntiDiuretic Hormone d. Epinephrine e. Erythropoietin 25. Which of the following is NOT responsible for transferring the energy from sound waves to mechanoreceptors of the inner ear? a. Auditory ossicles b. Tympanic membrane c. Perilymph d. Maculae e. More than one of the above 26. Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH) is secreted by: a. Testes b. Ovaries c. Adenohypophysis d. Neurohypophysis e. Hypothalamus 27. Prostacyclin (PGI2) is a chemical secreted by intact endothelial cells into the plasma/interstitium in response to vessel damage. It affects nearby platelets to limit coagulation and neighboring smooth muscle to encourage vasodilation. Little, if any, released PGI2 affects cells in distant areas. PGI2 is mostly likely a/n: a. Biogenic amine b. Eicosanoid c. Sterol d. Peptide e. Carbohydrate 28. The secretion of which of the following would be affected by exposure to sunlight: a. Calcitriol b. Triiodothryronine c. Melatonin d. Aldosterone e. More than one of the above 29. The role of fibrin in blood clotting is: a. Activates factor X b. Forms a mesh around injured area c. Digests the clot d. Induces vascular spasms e. Activates thrombin 30. Which of the following is NOT a function of erythrocytes related to their shape? a. High surface area: volume b. Allows single file stacking through capillaries c. Allows flexing and bending through really tiny capillaries d. Allows RBC to squeeze through spaces in capillaries to leave the blood and enter tissues 31. Jim has blood type A+. He receives blood from Mary. There is no reaction, and he accepts the blood without a problem. Mary must have blood type: a. A+ b. Bc. ABd. Any of the above are possible e. Not enough information; not all possible types have been presented. 32. Blood pressure can be affected by many factors including overall body blood vessel constriction, heart rate, red blood cell count, Na+ retention and water retention at the kidneys. Which of the following would be unlikely to affect blood pressure at all? a. Aldosterone b. Atrial natriuretic peptide c. Erythropoietin d. Epinephrine e. None of the above 33. Cutting the axons of neurons from the paraventricular nuclei traveling through the infundibulum would affect blood levels of: a. TSH b. Prolactin c. Corticosteroids d. Oxytocin e. FSH 34. Which of the following deficiencies would most likely be the result of chronically high levels of aldosterone? a. Glucose b. Na+ c. K+ d. Ca2+ e. Protein 35. Which of the following is NOT a second messenger? a. cAMP b. Ca2+ c. Protein kinase A d. B and C e. None of the above (all are second messengers in different systems) 36. Which of the following would bind a receptor on the cell membrane rather than enter the cell to have its effect? a. Calcitriol b. Glucagon c. Triiodothyronine d. Aldosterone e. Testosterone 37. Which of the following is NOT produced by the gonads (ovaries or testes)? a. Estrogen b. Testosterone c. Progesterone d. Prolactin e. More than one of the above 38. Which of the following is NOT a derivative of tyrosine? a. Epinephrine b. Norepinephrine c. Dopamine d. Melatonin e. Triiodothyronine 39. When is retinal found in a trans (straight) conformation? a. In the absence of light energy b. When excited by a photon c. When excited by sound waves d. When you hold your head still e. When you are trying to focus on an object which is far away 40. Otoliths are part of ______ and are involved in producing the sense of _______. a. Rhodopsin; vision b. Limbic system; smell c. Cristae; equilibrium d. Maculae; equilibrium e. Organ of Corti; hearing 41. Most plasma proteins are made in the: a. Red marrow b. Liver c. Kidneys d. Thymus e. Pancreas 42. Lowell is blood type O-. He receives blood from Joan. There is no reaction, and he accepts the blood without a problem. Joan must be blood type: a. AB+ b. Oc. Ad. Any of the above are possible e. Not enough information; not all possible types have been presented. 43. The component of hemoglobin that actually binds O2 temporarily is: a. The beta chains b. The alpha chains c. Fe d. Heme 44. The stem cell that gives rise to all erythrocytes, platelets and leukocytes is: a. Megakaryocyte b. Myeloid stem cell c. Lymphoid stem cell d. Hemocytoblast e. Proerythroblast 45. Neutrophils are most closely related to: a. Erythrocytes b. Lymphocytes c. Basophils d. Platelets e. Macrophages 46. Jaundice is a condition in which there is an excess of a yellowish pigment in the blood. Where does that pigment originate? a. Erythrocytes b. Leukocytes c. Kidneys d. Retina e. Melanocytes 47. Sickle-cell anemia is caused by: a. A genetic defect b. An iron deficiency c. A folate deficiency d. A B12 deficiency e. More than one of the above 48. Cholecalciferol: a. Is produced by the thyroid gland b. Enters the blood from the skin c. Increases dietary absorption of Ca2+ d. Stimulates osteoblasts e. Is produced by the adrenal cortex 49. Cells of the Islets of Langerhans would be stimulated by: a. Blood Ca2+ levels b. Blood glucose levels c. Erythropoietin d. Thyroid stimulating hormone e. More than one of the above 50. Plasmin is a protein that will ______ and is indirectly activated by ______. a. Form a mesh around the damaged area of a vessel; Factor X b. Enhance platelet aggregation; platelet factor c. Digest fibrin; thrombin d. A and B e. None of the above 51. Which of the following do NOT occur during the erythroblast/normoblast stages of erythropoiesis: a. Organelles are ejected b. Nucleus is ejected c. Fe is collected d. Hb is synthesized e. Immature RBC is released to the blood 52. The WBC that promotes dilation of vessels and prevents clots from spreading is: a. b. c. d. e. Neutrophil Natural killer cell Macrophage Erythrocyte Basophil 53. Platelets are cell fragments pinched off from: a. Neutrophils b. Lymphoid stem cells c. Megakaryocytes d. Myeloid stem cells e. Hemocytoblasts 54. What will happen to Fe when an erythrocyte is phagocytosed? a. It will be bound by transferrin b. It will travel to the red marrow c. It will travel to the liver d. All of the above e. None of the above; it will be excreted in bile 55. The structure in the eye that changes shape to focus an image is the _______. Under low light conditions, the photoreceptors that are most likely to respond to the incoming light energy are ______. a. Cornea; rods b. Lens; rods c. Sclera; cones d. Lens; cones e. Cornea; cones 56. B-cells, T-cells and Natural Killer cells come from: a. Myeloid stem cell line b. Lymphoid stem cell line c. Megakaryocytes d. Basophils e. Proerythroblasts 57. Which of the following would be most likely to attack a large pathogen like a worm? a. Neutrophils b. Eosinophils c. Basophils d. Platelets e. Erythrocytes 58. Simon is sent to an endocrinonologist after seeing his doctor for diuresis (increased urination). The endocrinologist is concerned that Simon is not producing enough of a certain hormone, and wants to take a look at the organ that produces the hormone. Of the following, where is the endocrinologist most likely to look? a. Simon’s heart b. Simon’s small intestine c. Simon’s adenohypophysis d. Simon’s neurohypophysis e. Simon’s adrenal medullae 59. Cilia of hair cells in the cochlea will be bent by movement of ________. a. Endolymph b. Perilymph c. Aqueous humor d. Plasma e. Mucous 60. Neurotransmitter release at synapses, gap junctions and the release of paracrine factors into the interstitium are all ways that cells can a. Communicate locally b. Send messages to cells in distant parts of the body c. Affect the activity of other cells d. A and C e. All of the above 61. Thyroid hormone is one of the major hormones important for proper growth in children. As you know, thyroid hormone generally increases metabolic activity in the cells is affects (makes them more active and more likely to divide). Based on this information alone, which of the following is theoretically LEAST likely to have many receptors for T3/T4? a. Fibroblasts b. Osteoblasts c. Muscle cells (all types) d. Osteoclasts e. Keratinocytes 62. Which of the following events would I be most likely to observe in red marrow? a. Lipogenesis (making triglycerides) b. Erythropoiesis c. Excretion of biliruben through bile d. Ventricular repolarization e. Gluconeogenesis 63. How many O2 can one hemoglobin carry? a. 2 b. 4 c. 8 d. 16 e. 5 64. Which of the following causes hepatocytes (liver cells) to ultimately increase blood glucose levels; and does so by entering the hepatocyte via passive diffusion and binding receptors within the cell? a. Epinephrine b. Glucagon c. Insulin d. Cortisol e. More than one of the above 65. Which of the following is true of neutrophils but NOT erythrocytes a. Deliver O2 to tissues b. Can squeeze between spaces in capillaries to enter tissues c. Derived from Myeloid stem cells d. Derived from Lymphoid stem cells e. Lack a nucleus