Tests Performed Before Surgery
advertisement

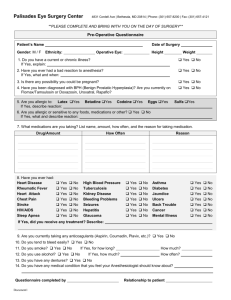
Tests Performed Before Surgery Many surgeons order routine laboratory tests before admission to the hospital, or even before certain outpatient procedures, to identify potential problems that might complicate surgery if not detected and treated early. According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), some of the most common tests performed before surgery (and possible reasons/symptoms for which they are performed) are included in the following list: Chest x-rays - a diagnostic test which uses invisible electromagnetic energy beams to produce images of internal tissues, bones, and organs onto film; may be used to help diagnose causes of shortness of breath, chest pain, cough, fever of unknown origin, and other abnormal heart, respiratory, and lung sounds. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) - a test that records the electrical activity of the heart, shows abnormal rhythms (arrhythmias or dysrhythmias), detects heart muscle damage, and helps determine the cause of chest pain, heart palpitations, and heart murmurs. Urinalysis - may be used to diagnose kidney and bladder infections, and diabetes. Specific types of urinalysis can also detect drugs present in the body. White blood count - may be used to diagnose fever of unknown origin, infection, and use of drugs known to affect white blood counts. The following tests, used on blood and urine specimens, measure certain substances and electrolytes in the body which should be normalized as much as possible before surgery: Glucose Potassium Sodium http://medicalcenter.osu.edu/patientcare/healthcare_services/surgery/preoperative_manag ement/tests_performed_before_surgery/Pages/index.aspx