Ch. 15 - Personality
advertisement

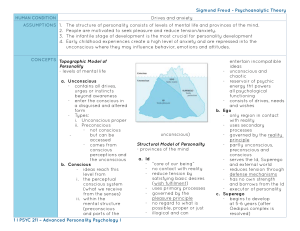
Ch. 15 - Personality What are the perspectives on personality? Psychoanalytic Humanistic Trait Social cognitive The self Psychoanalytic perspective Sigmund Freud The mind is like an iceberg Conscious (Above the water) Unconscious Larger (Below the water) Thoughts Feelings Memories Freud’s personality theory Id = Pleasure principle Ego = Reality principle Sex & violence Hedonistic Mediates between Id and Superego Superego = conscious Pride and guilt Freud’s personality iceberg Ego defense mechanisms Repression Regression Underlies all other defense mechanisms Keeps repressed urges (e.g. incest) from becoming conscious Retreating to an earlier, more infantile stage of development Reaction formation Doing the opposite of what you actually feel Inadequate feelings become bravado “I hate him” becomes ” I love him” Makes unacceptable impulses more acceptable Ego defense mechanisms (Cont.) Projection Rationalization Projecting your unacceptable impulses to others E.g. “He is lying like everyone else.” Thinking up socially acceptable reasons for your negative behavior. E.g. “I only steal from rich people” Displacement Diverts sexual or aggressive energies toward a more acceptable target. E.g. Mad child kicks the pet. How do we evaluate the unconscious? Projective tests Ambiguous stimuli that people “project” information onto Thematic Apperception Test (TAT) E.g. describe or tell a story Patient makes up a story based on ambiguous pictures Rorschach Test 10 inkblots - people discuss what they see in the inkblots Designed to identify people’s inner unconscious feelings Not successful in predicting behavior or diagnosis What is the Humanistic Perspective? The self concept - “Who am I” A basic focus of the Humanistic perspective Maslow’s Self-actualization People strive for self-actualization To be the best you can be After other needs are met for physiological, safety, love, and self-esteem Humanistic Perspective (cont.) Carl Rogers - Person Centered Perspective Unconditional positive regard If we feel accepted, we will be more open and expressive. What is the Trait Perspective? Traits = Characteristic behaviors or disposition E.g. shy, outgoing, friendly, aggressive Myers-Briggs type indicator Describes personalities in complimentary terms Trait Perspective (cont.) MMPI = Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory Most widely used personality inventory Used to identify emotional disorders MMPI = Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory What is the Social Cognitive Perspective? How does learning & thinking & society influence each other? Reciprocal Determinism Albert Bandura Behavior, internal personal factors, and the environment all operate to determine each other. Reciprocal Determinism Locus of control Internal locus of control “I personally control my destiny.” External locus of control “Outside forces which I can not control determine my destiny.” What is Learned Helplessness? Repeatedly faced with traumatic events over which people have no control, people feel helpless, hopeless, and depressed. Exploring your “self concept” Benefits of positive self esteem: More persistent at tasks Less likely to use drugs and conform to group pressure Happier Self serving bias We like to perceive ourselves favorably We contribute successes to our own effort and failure to factors beyond our control.