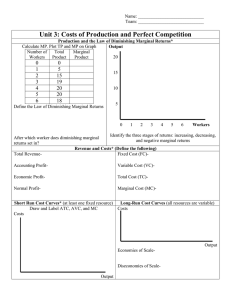
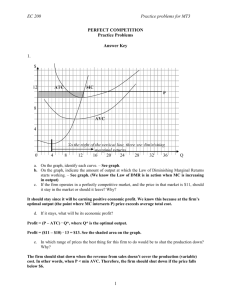
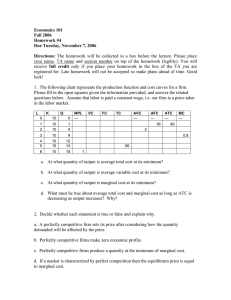
A firm has revenues of $1,000,000 and pays $500,000 in... 3) _______
advertisement

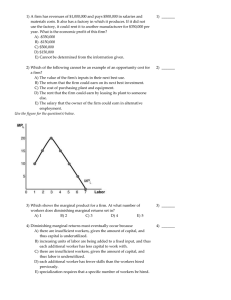
A firm has revenues of $1,000,000 and pays $500,000 in salaries and materials costs. It also has a factory in which it produces. If it did not use the factory, it could rent it to another manufacturer for $350,000 per year. What is the economic profit of this firm? A) -$350,000 B) -$150,000 C) $500,000 D) $150,000 E) Cannot be determined from the information given. 3) _______ 4) Which of the following cannot be an example of an opportunity cost for a firm? A) The value of the firm's inputs in their next best use. B) The return that the firm could earn on its next best investment. C) The cost of purchasing plant and equipment. D) The rent that the firm could earn by leasing its plant to someone else. E) The salary that the owner of the firm could earn in alternative employment. Use the figure for the question(s) below. 4) _______ 8) Which shows the marginal product for a firm. At what number of workers does diminishing marginal returns set in? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 8) _______ 9) Diminishing marginal returns must eventually occur because A) there are insufficient workers, given the amount of capital, and thus capital is underutilized. B) increasing units of labor are being added to a fixed input, and thus each additional worker has less capital to work with. C) there are insufficient workers, given the amount of capital, and thus labor is underutilized. D) each additional worker has fewer skills than the workers hired previously. E) specialization requires that a specific number of workers be hired. 9) _______ 4) _______ 4) The products sold in a perfectly competitive market are A) not homogeneous. B) perfect substitutes. C) differentiated. D) unique to each firm. E) similar but not exactly the same. 5) In a perfectly competitive market, products are not A) differentiated. B) homogeneous. C) exactly the same. D) perfect substitutes. E) undifferentiated. 7) If firms in a perfectly competitive market are earning large economic profits, A) no changes in the number of firms are likely to occur. B) other firms are likely to enter the market. C) resources are likely to leave this market. D) some firms are likely to leave the market. E) the firms in the market will erect barriers to keep rivals from entering. 20) What is the rule that governs production for a perfectly competitive firm? A) Unless p < minimum MC, choose q so that p = ATC. B) Unless p < minimum ATC, choose q so that p = MC. C) Unless p < minimum AVC, choose q so that p = MC. D) Unless p < minimum MC, choose q so that p = AVC. E) Unless p < minimum AVC, choose q so that p = ATC. 5) _______ 21) Which of the following is false? A) A firm in perfect competition has an upward sloping marginal cost curve. B) A firm decides how many units to produce by comparing marginal revenue with marginal cost. C) As long as variable costs are covered, the firm will produce the number of units where MR equals MC. D) If price is below AVC, the firm will not produce any units. E) A firm in perfect competition has a horizontal supply curve. 21) ______ 22) If existing firms in a perfectly competitive market are currently earning economic losses, which of the following is likely to occur as time passes? A) The size of the losses will increase. B) More firms will enter the market. C) The market demand curve shifts to the left. D) Market price for the product increases. E)The market supply curve shifts to the right 22) ______ 7) _______ 20) ______