Key to Review Worksheet for Exam 2 (Ch. 13)
advertisement
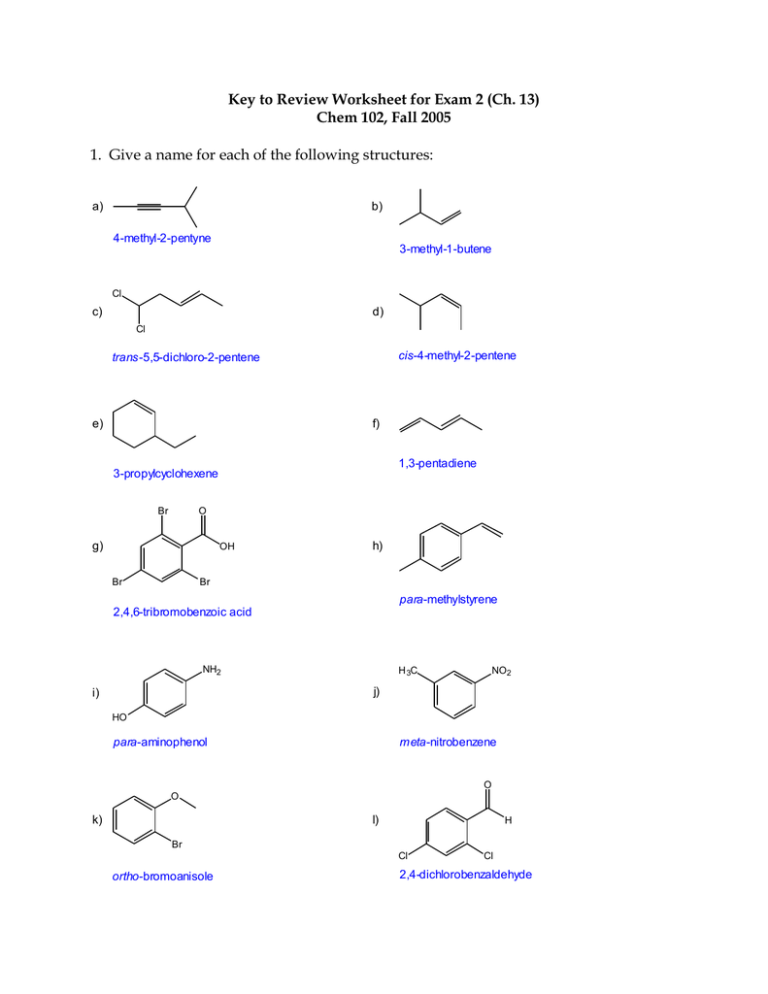
Key to Review Worksheet for Exam 2 (Ch. 13) Chem 102, Fall 2005 1. Give a name for each of the following structures: a) b) 4-methyl-2-pentyne 3-methyl-1-butene Cl c) d) Cl cis-4-methyl-2-pentene trans-5,5-dichloro-2-pentene e) f) 1,3-pentadiene 3-propylcyclohexene Br O g) OH Br h) Br para-methylstyrene 2,4,6-tribromobenzoic acid NH2 H 3C NO2 j) i) HO para-aminophenol meta-nitrobenzene O O k) l) H Br Cl ortho-bromoanisole Cl 2,4-dichlorobenzaldehyde 2. Draw the structure for each of the following names: a) 3-isopropylcyclopentene b) cis-2-hexene c) 1,3-butadiene d) 1-bromo-5-chloro-3-hexyne Br C C e) ortho-fluorophenol OH F f) 2,4-dinitrotoluene O2N NO2 g) para-aminobenzoic acid O H H 2N h) phenylbenzene 3. Give the major product(s) for each of the following reactions: Br a) + HBr Br b) HC C CH3 + Br 2Br 2 Br Cl c) Cl + Br Br Br 2 Cl Cl CH3 CH3 Pt d) + H2 Cat. CH3 e) CH3 + H 2O Acid Cat. OH Br f) + Cl 2 g) + NO 2 Cl FeCl3 H2SO4 + NO2 SO3 H H2SO4 h) + O2N SO 3 4. Give the reactants (and any catalysts) required to make the following products (there may be more than one right answer): OH + H 2O Acid Cat. Cl + HCl Cl H 3C C C CH3 + Cl 2Cl 2 Cl + + SO 3 Br 2 H 2SO4 FeBr3 Cat. Cl SO3 H Br 5. Give the monomer that would form each of the following polymers: Br Br Br a) Br Cl Cl Cl Cl b) Cl Cl Cl O Cl O O c) O 6. Why are alkenes and alkynes more reactive than alkanes? Use drawings to illustrate your answer. Both alkenes and alkynes have pi bonds, while alkanes have only sigma bonds. Because the pi bond electrons are farther from the positively charged nucleus (they result from sideways overlap of p orbitals) than sigma bond electrons, pi bonds are weaker than sigma bonds and can be more easily broken. That makes alkenes ane alkynes more chemically reactive than alkanes. Also, reactions that cause an increase in sigma bonds compared to pi bonds are energetically favorable. Pi bond H2C CH2 Sigma bond 7. Why is benzene more stable (lower energy) than 1,3,5-hexatriene? Use drawings to illustrate your answer. Because benzene is in a ring, the pi electrons are more delocalized than the pi electrons in 1,3,5-hexatriene. In benzene the pi electrons can move freely around the ring, making all 6 carbons equivalent, and all the C-C bonds also equivalent. There are two resonance structures that you can draw for benzene, so benzene has resonance energy that makes it extra stable. It’s ring structure adds extra stability called aromaticity. Resonance Structures Resonance Hybrid 8. Write the arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction: Br + + H HBr Br H Br H + Br H Br + Br