Chapter 13-Viruses
advertisement

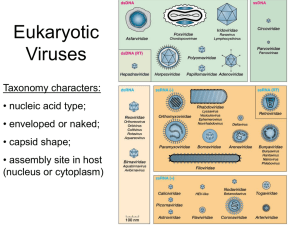
Chapter 13-Viruses General Characteristics of all viruses • • • • Contain a single type of nucleic acid Contain a protein coat Obligate intracellular parasites Are viruses the only obligate intracellular parasites? History began with the Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV) • 1886 Aldolf Mayer showed that a virus was transmissable between plants • 1892 Iwanowski tried to isolate it by filtering with porcelain filter Sizes of viruses Polyhedral virus • Capsid coat made of capsomeres • Nucleic acid inside Helical virus with an envelope • The shape is a long rod • Rabies and Ebola are helical viruses • Influenzae virus is helical with an envelope Bacteriophage: Complex virus Bacterial viruses • • Known as bacteriophages or phages Two different life cycles 1. Lytic cycle-results in lysis of the cell 2. Lysogenic cycle-may result in lysis of the cell or the virus becomes a permanent part of the chromosome by integrating Lytic Cycle Lytic Cycle Growth curve of bacteriophage Lysogenic Cycle How can you study bacteriophages? • Plaque assay -pour agar with bacteria and phage on top of an agar plate -“plaque” develops where virus infected bacterial cell -each plaque is counted as one virus How do animal viruses differ from bacterial viruses? • • • • Attachment Replication of nucleic acid Penetration Uncoating DNA Animal Viruses • Adenoviridae – dsDNA, non-enveloped – First isolated in the adenoids – Cause upper respiratory infections DNA Animal Viruses • Poxviridae – dsDNA, enveloped – Cause small pox (variola) DNA Animal Viruses • Poxviridae – dsDNA, enveloped – small pox virus (variola) DNA Animal Viruses • Herpesviridae (dsDNA, enveloped virus) -simplex 1(cold sores) -simplex 2 (genital herpes) -chicken pox, shingles -epstein barr Herpes simplex-1 • HHV-1 causes fever blisters, HHV-2 genital herpes • Symptoms: fluid filled skin lesions • Treatment: Acyclovir Varicella (chickenpox) and Herpes Zoster (Shingles) • HHV-3 causes chicken pox and latent activation known as shingles • Acquired by respiratory route, 2 weeks later see vesicles on skin • Vaccine established in 1995 for chickenpox Epstein Barr • Causes infectious mononucleosis • Acquire by saliva, incubation period is 4-7 weeks • Identify by -lobed lymphocytes -heterophile antibodies -fluorescent antibody tests Hepadnaviridae • dsDNA, enveloped • Hepatitis B -passes through intermediate stage (RNA) -three particles in blood Dane filamentous sphericle -exposure through blood/body fluids Hepatitis B • Incubation period is ~12 weeks • 10% of cases become chronic, mortality rate is less than 1% • About 40% of the chronic cases die of liver cirrhosis RNA animal viruses • Is there an enzyme in animal cells to replicate RNA? • What does RNA polymerase do? RNA animal viruses • (+) single stranded RNA viruses – RNA serves as mRNA • (-) single stranded RNA viruses – RNA does not code for proteins Picornaviridae (+) ssRNA • Poliovirus • Virus ingested then travels throughout the body • In some cases it impairs the upper motor neurons, less than 1% of all cases • Vaccines – Salk vaccine (IPV) – Enhanced-inactivated polio (E-IPV) – Sabin vaccine Cases of Poliomyelitis in US Picornaviridae (+) ssRNA • Rhinovirus -causes the common cold -100 or more serological types -virus grows best in the nose and conjunctiva Picornaviridae (+) ssRNA • Enterovirus responsible for 90% of viral gastroenteritis – Rotavirus • Most common cause of viral gastroenteritis – Norwalk-like virus • Responsible for local epidemics Rotavirus • Note the shape which gave it the name rota=wheel Picornaviridae (+) ssRNA • Hepatitis A -obtain through fecal-oral route, enters GI tract and multiplies -incubation period is ~4 weeks -symptoms include: anorexia, malaise, nausea, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, fever, and chills lasting 2-21 days Flaviviridae (+) ssRNA, enveloped • Hepatitis C virus – – – – Obtain from blood/body fluids Incubation period averages 6 weeks Hard to screen blood for the virus 85% of all cases become chronic Rhabdoviridae (-)ssRNA, enveloped • Rabies virus -enters the skin and multiplies in skeletal muscle and connective tissue -virus travels along nerves to the CNS causing encephalitis Pathology of rabies Orthomyxoviridae-multiple strands of (-)RNA • Influenza virus – Consists of 8 segments of RNA – Envelope has H spikes (hemagglutinin) and N spikes (neuraminidase) – Incubation is 1-3 days – Symptoms include: chills, fever, headache, muscle aches, may lead to cold-like symptoms Influenza virus Retroviruses: convert RNA to DNA • HIV, Hepatitis B Retroviridae-multiple strands of ()RNA • HIV -infects Helper T cells -requires the enzyme reverse transcriptase -integrates as a provirus -is released by budding, or lyses the cell Proteinaceous infectious particles: PRIONS • 1982 Stanley Prusiner proposed that there were infectious proteins • Caused the disease “scrapie” in sheep • Caused the “mad-cow”disease in 1987 • Human forms suggest a genetic component Prions: How do they replicate? Can viruses cause cancer? • Michael Bishop and Harold Varmus received the 1989 Nobel Prize for cancercausing genes carried by a virus from animal cells • Oncogenes:genes that can be transformed to cause cancer • 10% of cancers have been found to be due to oncogenic viruses