Acquired Immunity: Humoral Response
advertisement

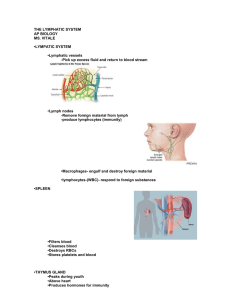
Acquired Immunity: Humoral Response • Distinction of Humoral versus Cell-Mediated Acquired Immunity • Antigens and Antigenic Determinants: Non-self and MHC proteins • Cell Types of the Humoral Response and How they Develop • B and T cell receptors and immunglobulins (antibodies) • Antibody Structure and Classes • Activation of B cells and Clonal Selection • Immunity and Secondary Response Time • Antibody Actions • Passive and Active Immunity • Monoclonal Antibodies • Players in the Cell Mediated Response • Activation of Cytotoxic T and B cells via TH cells • Other T cells and their function • Tissue grafting • Immune disorders: Allergies • Immune disorders: Immunodeficiency Acquired Immune System – Third Line of Defense The Acquired Immune System is: Antigen specific – recognizes and acts against particular foreign substances Discerning -Recognizes “self” from “non-self” Systemic – not restricted to the initial infection site Has memory – recognizes and mounts a stronger attack on previously encountered pathogens Types of Acquired Immunity 1. Humoral immunity • Antibody-mediated immunity in blood and lymph • Cells produce chemicals for defense 2. Cellular (adaptive) immunity of the cellmediated immune system • Cell-mediated immunity • Cells target virally infected cells Acquired Immunity: Humoral Response • Distinction of Humoral versus Cell-Mediated Acquired Immunity • Antigens and Antigenic Determinants: Non-self and MHC proteins • Cell Types of the Humoral Response and How they Develop • B and T cell receptors and immunglobulins (antibodies) • Antibody Structure and Classes • Activation of B cells and Clonal Selection • Immunity and Secondary Response Time • Antibody Actions • Passive and Active Immunity • Monoclonal Antibodies • Players in the Cell Mediated Response • Activation of Cytotoxic T and B cells via TH cells • Other T cells and their function • Tissue grafting • Immune disorders: Allergies • Immune disorders: Immunodeficiency Antigens (Nonself) Antigen: Any substance capable of exciting the immune system and provoking an immune response Antigens Examples of common antigens • Foreign proteins • Nucleic acids • Large carbohydrates • Some lipids • Pollen grains • Microorganisms Antigenic determinants: substances on the surface of antigens to which the immune system actually responds Antigen Receptor in the immune system that "fits" the antigenic determinant Haptens Can Become Antigenic Haptens are small molecules that cannot elicit an antibody response. They can combine with carrier molecules within the body (like proteins) and become antigenic. • Metals (e.g. nickel in jewelry), rubber, glue, preservatives, urushiol/quinone in poison ivy, halothane (anesthetic), some penicillin derivatives Self-Antigens: MHC Proteins Human cells have many surface proteins called major histocompatability complexes (MHC). All body cells have MHC “name-tag” proteins to identify them as belonging to your body (MHC Class I proteins) Cells of the immune system additionally have their own tags called MHC II proteins (“security badges”) Our cells in another person’s body can trigger an immune response because they are foreign; restricts donors for transplants Acquired Immunity: Humoral Response • Distinction of Humoral versus Cell-Mediated Acquired Immunity • Antigens and Antigenic Determinants: Non-self and MHC proteins • Cell Types of the Humoral Response and How they Develop • B and T cell receptors and immunglobulins (antibodies) • Antibody Structure and Classes • Activation of B cells and Clonal Selection • Immunity and Secondary Response Time • Antibody Actions • Passive and Active Immunity • Monoclonal Antibodies • Players in the Cell Mediated Response • Activation of Cytotoxic T and B cells via TH cells • Other T cells and their function • Tissue grafting • Immune disorders: Allergies • Immune disorders: Immunodeficiency Development of Lymphocytes •Developing immunocompetence Positive selection: finding lymphocytes whose receptors bind to foreign antigens Negative selection: killing lymphocytes with receptors to “self” antigens like MHCs T cell maturation and "education" Acquired Immunity: Humoral Response • Distinction of Humoral versus Cell-Mediated Acquired Immunity • Antigens and Antigenic Determinants: Non-self and MHC proteins • Cell Types of the Humoral Response and How they Develop • B and T cell receptors and immunglobulins (antibodies) • Antibody Structure and Classes • Activation of B cells and Clonal Selection • Immunity and Secondary Response Time • Antibody Actions • Passive and Active Immunity • Monoclonal Antibodies • Players in the Cell Mediated Response • Activation of Cytotoxic T and B cells via TH cells • Other T cells and their function • Tissue grafting • Immune disorders: Allergies • Immune disorders: Immunodeficiency B Cell Receptors, T Cell Receptors, and Immunoglobulins T cell B cell Antigen Receptors on T Cells Receptors on B cells Constant regions Variable (binding) regions Secreted (Exported) Immunoglobulin or Antibody (Same V and C Regions as in B cell receptors) Immunoglobulins and Receptors Bind To Antigens Agglutination of antigens Different Classes of Antibodies Any particular B cell always produces the same variable regions in its antibodies but it may change the “constant” stem region. Stems come in five types: A, D, E, G, and M Acquired Immunity: Humoral Response • Distinction of Humoral versus Cell-Mediated Acquired Immunity • Antigens and Antigenic Determinants: Non-self and MHC proteins • Cell Types of the Humoral Response and How they Develop • B and T cell receptors and immunglobulins (antibodies) • Antibody Structure and Classes • Activation of B cells and Clonal Selection • Immunity and Secondary Response Time • Antibody Actions • Passive and Active Immunity • Monoclonal Antibodies • Players in the Cell Mediated Response • Activation of Cytotoxic T and B cells via TH cells • Other T cells and their function • Tissue grafting • Immune disorders: Allergies • Immune disorders: Immunodeficiency Acquired Immunity: Humoral Response • Distinction of Humoral versus Cell-Mediated Acquired Immunity • Antigens and Antigenic Determinants: Non-self and MHC proteins • Cell Types of the Humoral Response and How they Develop • B and T cell receptors and immunglobulins (antibodies) • Antibody Structure and Classes • Activation of B cells and Clonal Selection • Immunity and Secondary Response Time • Antibody Actions • Passive and Active Immunity • Monoclonal Antibodies • Players in the Cell Mediated Response • Activation of Cytotoxic T and B cells via TH cells • Other T cells and their function • Tissue grafting • Immune disorders: Allergies • Immune disorders: Immunodeficiency B Cell Activation and Clonal Selection Humoral immunity movie T cells are also activated by clonal selection during exposure to an antigen.