A Tour of the Cell Categories of Cells Features of Prokaryotic Cells
advertisement

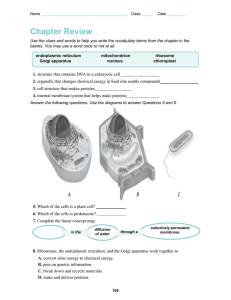
A Tour of the Cell Categories of Cells Features of Prokaryotic Cells Features of Eukaryotic Cells o Membrane Structure o Nucleus and Ribosomes o Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) o Golgi Apparatus o Lysosomes o Vacuoles Energy o Converting Organelles Chloroplasts o Mitochondria Cytoskeleton o Cell Shape o Cell Movement Proteins and Lipids Leave the ER Enroute to the Golgi Chromatin Nucleolus Nuclear envelope Nucleus Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Mitochondrion Cytosol Lysosome Centrioles Centrosome matrix Cytoskeletal elements • Microtubule • Intermediate filaments Plasma membrane Rough endoplasmic reticulum Ribosomes Golgi apparatus Secretion being released from cell by exocytosis Peroxisome Proteins Are Transported in Vesicles to the Golgi Figure 4.11 The Golgi Apparatus • The Golgi apparatus – Refines, stores, and distributes the chemical products of cells. – Acts like a finishing and shipping station (UPS or FedEx) in the cell A Tour of the Cell Categories of Cells Features of Prokaryotic Cells Features of Eukaryotic Cells o Membrane Structure o Nucleus and Ribosomes o Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) o Golgi Apparatus o Lysosomes o Vacuoles Energy o Converting Organelles Chloroplasts o Mitochondria Cytoskeleton o Cell Shape o Cell Movement Focus on Lysosomes Chromatin Nucleolus Nuclear envelope Nucleus Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Mitochondrion Cytosol Lysosome Centrioles Centrosome matrix Cytoskeletal elements • Microtubule • Intermediate filaments Plasma membrane Rough endoplasmic reticulum Ribosomes Golgi apparatus Secretion being released from cell by exocytosis Peroxisome Lysosomes • A lysosome is a membrane-enclosed sac containing digestive enzymes – The enzymes break down macromolecules and ingested debris within vacuoles – Serves as the “Greeting and Garbage Service” of the cell Lysosome Formation Proteins and Lipids Move Through the Endomembrane System Rough ER Phagosome ER membrane Proteins in cisterna Plasma membrane Pathway C: Lysosome containing acid hydrolase enzymes Vesicle becomes lysosome Golgi apparatus Pathway A: Vesicle contents destined for exocytosis Secretory vesicle Secretion by exocytosis Pathway B: Vesicle membrane to be incorporated into plasma membrane Extracellular fluid 3 Fates: A. Exocytosis (export) B. Becomes part of membrane C. Becomes a lysosome Figure 3.20 A Tour of the Cell Categories of Cells Features of Prokaryotic Cells Features of Eukaryotic Cells o Membrane Structure o Nucleus and Ribosomes o Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) o Golgi Apparatus o Lysosomes o Vacuoles & Peroxisomes Energy o Converting Organelles Chloroplasts o Mitochondria Cytoskeleton o Cell Shape o Cell Movement Focus on Vacuoles and Perioxisomes Chromatin Nucleolus Nuclear envelope Nucleus Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Mitochondrion Cytosol Lysosome Centrioles Centrosome matrix Cytoskeletal elements • Microtubule • Intermediate filaments Plasma membrane Rough endoplasmic reticulum Ribosomes Golgi apparatus Secretion being released from cell by exocytosis Peroxisome A Tour of the Cell Categories of Cells Features of Prokaryotic Cells Features of Eukaryotic Cells o Membrane Structure o Nucleus and Ribosomes o Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) o Golgi Apparatus o Lysosomes o Vacuoles Energy o Converting Organelles Chloroplasts o Mitochondria Cytoskeleton o Cell Shape o Cell Movement Mitochondria • Mitochondria are energy conversion factories • Food energy is converted into usable cellular energy (ATP) through cellular respiration Cell Respiration: Food energy + oxygen gas Carbon dioxide + water + ATP A Tour of the Cell Categories of Cells Features of Prokaryotic Cells Features of Eukaryotic Cells o Membrane Structure o Nucleus and Ribosomes o Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) o Golgi Apparatus o Lysosomes o Vacuoles Energy o Converting Organelles Chloroplasts o Mitochondria Cytoskeleton o Cell Shape o Cell Movement Cytoskeleton: Microtubules, Intermediate Filaments, Microfilaments Chromatin Nucleolus Nuclear envelope Nucleus Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Mitochondrion Cytosol Lysosome Centrioles Centrosome matrix Cytoskeletal elements • Microtubule • Intermediate filaments Plasma membrane Rough endoplasmic reticulum Ribosomes Golgi apparatus Secretion being released from cell by exocytosis Peroxisome Cytoskeleton Made of Microfilaments, Intermediate filaments, and Microtubules Cell-cell junctions Muscle contracts using actin protein (and myosin) Cells divide in half with the pinching action of microfilaments Organelle towing A Tour of the Cell Categories of Cells Features of Prokaryotic Cells Features of Eukaryotic Cells o Membrane Structure o Nucleus and Ribosomes o Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) o Golgi Apparatus o Lysosomes o Vacuoles Energy o Converting Organelles Chloroplasts o Mitochondria Cytoskeleton o Cell Shape o Cell Movement o Cell Junctions Cell Junctions: Tight, Desmosomes, and Gap Tight junctions: Impermeable junctions prevent molecules from passing through the intercellular space. Desmosomes: Anchoring junctions bind adjacent cells together and help form an internal tension-reducing network of fibers. Gap junctions: Communicating junctions allow ions and small molecules to pass from one cell to the next for intercellular communication. Testing Diagrams of Cells A Tour of the Cell Categories of Cells Features of Prokaryotic Cells Features of Eukaryotic Cells o Membrane Structure o Nucleus and Ribosomes o Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) o Golgi Apparatus o Lysosomes o Vacuoles Energy o Converting Organelles Chloroplasts o Mitochondria Cytoskeleton o Cell Shape o Cell Movement