A Tour of the Cell, Part I CHAPTER 4
advertisement
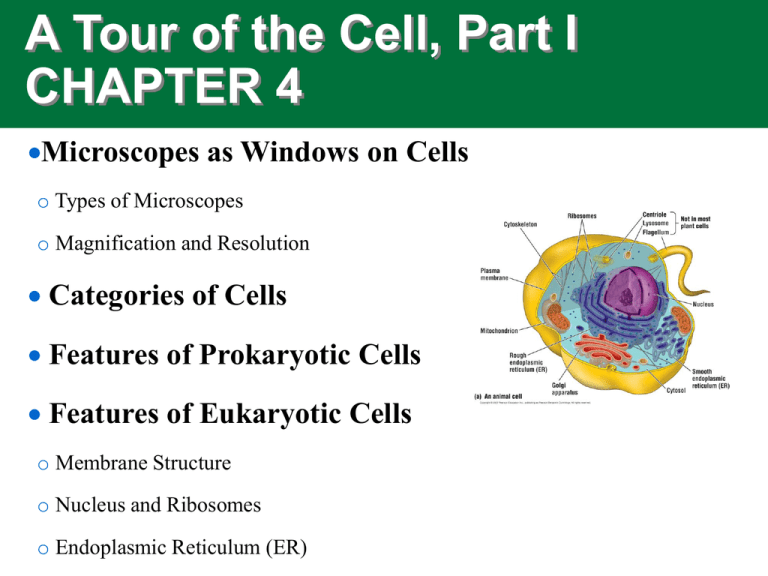
A Tour of the Cell, Part I CHAPTER 4 Microscopes as Windows on Cells o Types of Microscopes o Magnification and Resolution Categories of Cells Features of Prokaryotic Cells Features of Eukaryotic Cells o Membrane Structure o Nucleus and Ribosomes o Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Two Types of Cells Make Up Living Things Prokaryotic cells • Small size (1-10 micrometers) • Single, circular chromosome • No nucleus (DNA in a nucleoid) • Simple construction (no organelles) • Cell wall usually present (murein) Eukaryotic Cells • Larger size (10-100 micrometers) • Multiple linear chromosomes • Nucleus present • Complex construction, many membrane-wrapped organelles • Cell wall sometimes present Cell Membrane Phospholipid bilayer Prokaryotic Cell (Archea and Eubacteria) Chromosome Cytoplasm Reproduces by binary fission Plant Cell (Eukaryote) Central vacuole – garbage dump and internal support Cytoskeleton microtubules form internal framework to hold up cell Mitochondrion – Energy conversion powerhouse Chloroplast – Food production factory Cell wall – external structural support Nucleus – Library for Information storage Golgi Body – shipping and packaging factory Cell membrane – Barrier with selective gates Ribosomes Protein making machines Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)— Subway system and lipid factory Cytoplasm – liquid interior for chemical reactions Reproduces by mitosis or meiosis Animal Cell (Eukaryote) LysosomeDismantling and Garbage Service Cell membrane Centrioles Rope-making factory Mitochondrion Cytoplasm Golgi Body Nucleus Cytoskeleton Ribosomes Endoplasmic reticulum Reproduces by mitosis or meiosis Test Diagram of a Cell




