Newborn Assessment Revised
advertisement

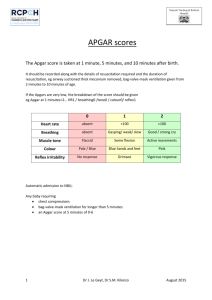
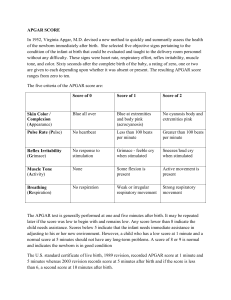
NUR 134 NEO114 M. Johnston, RN-BC, M.Ed. OB Clinical Instructor NSCC Immediate Post Delivery Establish Airway: Suction with bulb syringe Stimulate Check Color: Acrocyanosis Prevent Hypothermia: Clean, stimulate Provide dry blankets Check Tone: Flexion of extremities Drying to prevent hypothermia Apgar Scoring Five categories: score 0-2 Assessed at: 1 minute 5 minutes Apgar Scoring Charts Apgar Scoring Dr. Virginia Apgar "Nobody, but nobody, is going to stop breathing on me!" Weight Measure length Head circumference Newborn Exam Warm, dry surface Adequate lighting Calm infant Check vital signs HR range 110-160 bpm Resp rate 30-60 min Temp. 36.5 – 37.5 C Umbilical cord 3 vessels 2 arteries, 1 vein (AVA) Wharton’s jelly Umbilical Cord Healing 7-10 days Keep clean and dry Observe for infection Fontanels anterior posterior Sutures Head Molding Vernix Caseosa Sebaceous gland secretions White, cheesy protective coating Develops 3rd trimester Decreases as fetus develops Milia sebaceous glands, usu. found on face, nose and chin subsides spontaneously , reassure parents Telangiectatic Nevi “Stork Bites” Erythema Toxicum Most common face, trunk, extremities Found in 70% of newborns Peaks at 24-48 hours old Lanugo Fine, downy hair Develops after 20 wks gestation Mostly disappears by 40 wks gestation Meconium Mongolian spots Moro or Startle Reflex Normal Newborn Reflexes Neonatal Jaundice Physiological Pathologic Phototherapy Phototherapy Cephalohematoma Does not cross suture line Caput Succedaneum extends across the suture line usually disappears in 3-4 days Tongue-tie occurs in approx. 4% of infants Simian Crease (Single palmar crease) Club Foot (Talipes Equinovarus) Pilonidal opening Sacral skin tag Preterm Neonates Maternal Infant Bonding Family Bonding