Homework #5: Part II – Types of costs and... 5) A firm has revenues of $1,000,000 and pays $500,000 in...
advertisement

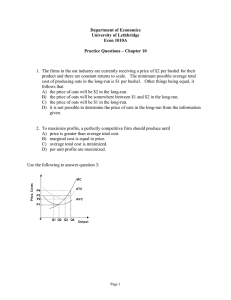
Homework #5: Part II – Types of costs and Perfect Competition 5) 6) A firm has revenues of $1,000,000 and pays $500,000 in salaries and materials costs. It also has a factory in which it produces. If it did not use the factory, it could rent it to another manufacturer for $350,000 per year. What is the economic profit of this firm? A) -$350,000 B) -$150,000 C) $500,000 D) $150,000 E) Cannot be determined from the information given. Which of the following cannot be an example of an opportunity cost for a firm? A) The value of the firm's inputs in their next best use. B) The return that the firm could earn on its next best investment. C) The cost of purchasing plant and equipment. D) The rent that the firm could earn by leasing its plant to someone else. E) The salary that the owner of the firm could earn in alternative employment. 7) In economics, the long run is A) one year. B) a time period in which all inputs can be varied. C) a time period in which there is at least one fixed input. D) five years. E) a time period in which no inputs can be varied. 8) A sunk cost is best described as A) a cost that is not recoverable. B) a transactions cost. C) a marginal cost. D) a cost that varies with output. E) an average cost. 9) 10) Marginal cost is defined as A) VC / Q. B) ΔTC / ΔQ. C) AVC + AFC. D) TC / Q. E) FC / Q. Average total cost is defined as A) TC / Q. B) VC / Q. C) ΔTC / ΔQ. D) ΔVC / ΔQ. E) FC / Q. 11) Average variable cost is defined as A) FC / Q. B) ATC + AFC. C) VC / Q. D) ΔTC / ΔQ. E) TC / Q. 12) Consider the following two statements: I. II. A) B) C) D) If marginal cost is greater than average total cost, average total cost must be rising. If average total cost is greater than marginal cost, marginal cost must be rising. I is true; II is false. Both statements are true. I is false; II is true. Both statements are false. 13) If firms in a perfectly competitive market are earning large economic profits, A) no changes in the number of firms are likely to occur. B) other firms are likely to enter the market. C) resources are likely to leave this market. D) some firms are likely to leave the market. E) the firms in the market will erect barriers to keep rivals from entering. 14) If a large number of firms sell the same product in a market, A) there must be perfect information. B) products cannot be substitutes for each other. C) profits will be zero, even in the short run. D) the actions of one cannot affect the market. E there must be free entry and exit. 15) In a perfectly competitive market, firms have A) no control over quantity, so focus on price. B) no control over price, so focus on other attributes such as quality or marketing. C) no control over price, so focus on quantity. D) no control over quantity, so focus on other attributes such as quality or marketing. E) complete control over price, quantity, and other aspects of the good they produce 16) To maximize profits, firms in perfect competition should A) produce the number of units where the gap between total revenue and total cost is as large as possible. B) raise price. C) try to keep total cost as small as possible. D) lower price. E) produce every unit that increases total revenue Name: __________________________________ Answers for Homework #5 - Turn this sheet in 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Class: 9 AM or 10 AM (circle your class time)