Lecture 2.5 Leftovers: Elasticity, Market Equilibrium & Interesting Questions
advertisement

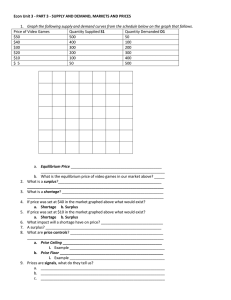
Lecture 2.5 Leftovers: Elasticity, Market Equilibrium & Interesting Questions Demand Elasticity & Total Revenue Change Individual Demand Curve Price per unit price per unit quantity demandedelasticity tot rev $10 1 10 $9 2 -0.10 18 $8 3 -0.22 24 $7 4 -0.38 28 $6 5 -0.57 30 $5 6 -0.83 30 $4 7 -1.20 28 $3 8 -1.75 24 $2 9 -2.67 18 $1 10 -4.50 10 TR Max $40 $30 Ed < 1 $20 Ed > 1 $10 $0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 Ed = 1 Demand Curves • Properties – Marginal Value: (incremental) value of the next unit demanded – Marginal Revenue: (incremental) revenue of next unit sold – Average Revenue: average revenue received for selling a given quantity A Short Quiz Seattle Times Oct 3, 2007 Olympic National Park officials are suggesting raising the price of an entrance pass for motorists — good for seven days — from $15 to $25 starting in 2009, with the fee for individuals such as cyclists climbing from $5 to $12. Season passes would increase from $30 to $50 But public response, particularly from tourist-dependent local businesses has been generally negative said a spokeswoman for Olympic National Park. 1. Illustrate the effect of the increase of the price for park passes on the demand for trips to the park 2. Illustrate how the park fee increase would affect the demand for other tourist-related businesses, e.g., hotels, restaurants. Another Variation • At each price, determine whether there would be a shortage (Qd > Qs) or a surplus (Qs > Qd) • If there was a shortage, how would price adjust to clear the market? • If there is a surplus, how would price adjust to clear the market? # of Pizzas Demand ed Price Per Pizza # of Pizzas Supplie d 1000 $10 400 900 $12 450 800 $14 500 700 $16 550 600 $18 600 500 $20 650 Shortage or Surplus Answers # of Pizzas Demanded Price Per Pizza # of Pizzas Supplied Shortage (-) or Surplus (+) 1000 $10 400 -600 900 $12 450 -450 800 $14 500 -300 700 $16 550 -150 600 $18 600 0 500 $20 650 150 Price (£) The Cobweb Theorem S 11 The Assume Farmers the respond falls initial £5 by equilibrium and planning farmers This In price acreates ‘divergent atomassive cobweb’ - to price increase react is by £7 cutting supply, and the plans ten quantity months for turkey 9. shortage also termed of 9 an million unstable turkeys If demand later, production. the rises, supply the months of shortage turkeys later, is and cobweb the price - Ten theis price forced tends up –to15 pushes million. supply At the the this price market level, upequilibrium. to there will £11be will per 8 and move soon away the process from continues! turkey. be million. a surplus of turkeys and the A divergent price drops. cobweb leads to price instability over time. 7 5 D 8 9 15 17 D1 Quantity Bought and Sold (millions) Cobweb Theorem • http://www.bized.co.uk/current/mind/2004_5/251004.ppt • Hungarian-born economist Nicholas Kaldor (1908-1986) • Simple dynamic model of cyclical demand with time lags between the response of production and a change in price (most often seen in agricultural sectors). • Cobweb theory is the process of adjustment in markets • Traces the path of prices and outputs in different equilibrium situations. Path resembles a cobweb with the equilibrium point at the center of the cobweb. • Sometimes referred to as the hog-cycle (after the phenomenon observed in American pig prices during the 1930s). Useful Websites – Understanding differences between factors that cause shifts in demand or supply • http://hspm.sph.sc.edu/COURSES/ECON/SD/SD.h tml – Basics of demand and supply • http://www.investopedia.com/university/economics/ economics3.asp – Cobweb theorem • http://www.bized.co.uk/current/mind/2004_5/25100 4.ppt Markets for Biodiesel Fuel and Food • Initial conditions – – Corn is a major input (ingredient) to both food and biodiesel Gas prices have significantly increased during the past few years in the automobile gasoline market 1. What is the impact of higher gasoline prices on the demand for biodiesel? 2. What is the impact of higher gasoline prices on the demand for food products? More Questions • #9 City Parks more polluted than country club grounds – Are people who use parks less concerned than those who golf? – Is it an issue of property-right assignment? – CC tend to use fertilizers that seep into the water table. Who owns the water table? Diamond/Water Paradox • Diamonds sell for a much higher price than bottles of water. Does that mean diamonds are more valuable than water? Paul’s example • Two brewers • Two beers: Stout or Lager – What is the opportunity cost? • “Next” best alternative Brewer Gal of Gal of Opp Cost Stout Lager of Stout Opp Cost of Lager Jones 5 10 2 g lager ½ g stout Brown 4 3 ¾ g lager 4/3 g stout