Digestion & Reassembly Oh, YUCK!
advertisement

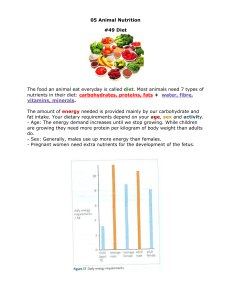
Digestion & Reassembly Oh, YUCK! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Uzl6M1YlU3w 1 Animal Nutrition Why do we eat? We need matter and energy to grow, repair, and maintain our bodies: nutrients (E.g.: carbs, proteins, lipids, water…) Some nutrients cannot be made by our bodies from other materials, so we must get them through our food: Essential nutrients • Essential amino acids – Building the “ALABAMA” protein • Essential fatty acids – E.g., omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids (found in fish and seeds) • Vitamins – E.g., vitamin A, B vitamins, vitamin C, Niacin, Folic acid • Minerals – E.g., calcium, phosphorus, sodium 2 Mammalian Digestive System • Is the digestive tract inside or outside of the body? • Does digestion happen inside or outside of our cells? Fig. 41.10 Stages of Food Processing 3 5 The Mouth • Mechanical digestion - chewing • Chemical digestion - enzyme that hydrolyzes starch & glycogen The Stomach • Secretes acid and an enzyme – HCL (hydrochloric acid) • pH 2 • Disrupts extracellular matrix of cells • Kills most bacteria • Denatures proteins – enzyme • breaks bond between amino acids 6 The Small Intestine - Digestion • • • • Churning Nutrient-rich broth (chyme) enters small intestine Liver secretes bile – helps digestion of fats Pancreas secretes enzymes & chemicals that raise the pH • Small intestine secretes enzymes Food now broken down into monosaccharides, amino acids, glycerol, fatty acids, nucleotides 8 The Small Intestine - Absorption • Nutrients transported across epithelial cells to bloodstream. • Nutrients in bloodstream circulated to all cells in the body and transported across plasma membrane for use in the cell. 9 The Large Intestine 10 • Colon – Recover water for the body • Rectum – Stores feces (undigested material such as cellulose, and lots of intestinal bacteria!) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Large_intestine 11 Starch to glycogen Proteins to (different) proteins Lipids to (different) lipids Polynucleotides to (different) polynucleotides From food cells to our cells!