Chapter 9 key points Chemistry 121
advertisement

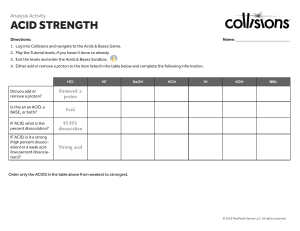
Chapter 9 key points Chemistry 121 Acids and bases • Brønsted-Lowry definition of an acid: a substance that dissociates (donates) an H+ ion. Base: a substance that accepts an H+ ion • Acids dissociate to form their conjugate bases • Acid dissociation constant, Ka, measures the degree of dissociation and therefore strength • Water has a dissociation constant of 10–14, and [H+] and [OH–] of a solution are set by that • pH scale measures the acidity or alkalinity of a solution Titrations and buffers • Salt solutions may be acidic, basic or neutral • A titration is a quantitative neutralization of an acid or a base, in order to determine its concentration • Indicators are chemicals that change color depending on the solution’s pH • Buffers are solution comprising an acid and a salt of its conjugate base that can resist changes in pH due to the addition of acids or bases