Followings are what you will find at the end of... For LEARNING OBJECTIVES: Highlight the main idea for EACH...
advertisement

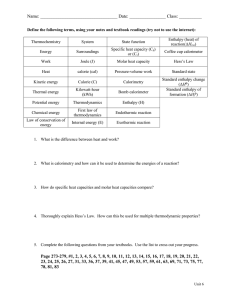
Pre CH6 HW for Silberberg Followings are what you will find at the end of the chapter in your textbook. For LEARNING OBJECTIVES: Highlight the main idea for EACH objective. Ready carefully so you don’t highlight everything. For MASTER THESE SKILLS: Highlight the main idea for each skill. Ready carefully so you don’t highlight everything. For KEY TERMS: Make sure you can define it and/or give an example of it. Pick TWO terms of your choice and actually write the definition or an example. For KEY EQUATIONS AND RELATIONSHIP: Next to EACH, define each term. Be very specific. CHAPTER REVIEW GUIDE Learning Objectives Relevant section (§) and/or sample problem (SP) numbers appear in parentheses. Understand These Concepts 1. The distinction between a system and its surroundings (§6.1) 2. The transfer of energy to or from a system as heat and/or work (§6.1) 3. The relation of internal energy change, heat, and work (§6.1) 4. The meaning of energy conservation (§6.1) 5. The meaning of a state function and why ∆E is constant even though q and w vary (§6.1) 6. The meaning of enthalpy and the relation between ∆E and ∆H (§6.2) 7. The meaning of ∆H and the distinction between exothermic and endothermic reactions (§6.2) 8. The relation between specific heat capacity and heat (§6.3) 9. How constant-pressure (coffee-cup) and constant-volume (bomb) calorimeters work (§6.3) 10. The relation between ∆H and amount of substance (§6.4) 11. The calculation of ∆H values with Hess's law (§6.5) 12. The meaning of a formation equation and the standard enthalpy of formation (§6.6) 13. How a reaction can be viewed as the decomposition of reactants followed by the formation of products (§6.6) Master These Skills 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Determining the change in a system's internal energy in different units (SP 6.1) Calculating PV work done by or on a system (SP 6.2) Drawing enthalpy diagrams for chemical and physical changes (SP 6.3) Solving problems involving specific heat capacity and heat transferred in a reaction (SPs 6.4–6.7) Relating the heat transferred in a reaction to the amounts of substances changing (SP 6.8) Using Hess's law to find an unknown ∆H (SP 6.9) Writing formation equations and using values to find (SPs 6.10, 6.11) Page 278 Key Terms Page numbers appear in parentheses. thermodynamics (251) thermochemistry (251) Section 6.1 system (252) surroundings (252) internal energy (E) (252) heat (q) (252) work (w) (253) law of conservation of energy (first law of thermodynamics) (255) joule (J) (255) calorie (cal) (255) state function (256) Section 6.2 pressure-volume work (PV work) (258) enthalpy (H) (258) change in enthalpy (∆H) (258) exothermic process (259) enthalpy diagram (260) endothermic process (260) Section 6.3 heat capacity (261) specific heat capacity (c) (261) molar heat capacity (C) (261) calorimeter (262) Section 6.4 thermochemical equation (266) Section 6.5 Hess's law (268) Section 6.6 standard state (270) standard enthalpy of reaction (270) formation equation (270) standard enthalpy of formation (270) fossil fuel (273) coal gasification (273) synthetic natural gas (SNG) (273) biomass conversion (273) methanogenesis (273) photovoltaic cell (276) Key Equations and Relationships Page numbers appear in parentheses. 6.1 Defining the change in internal energy (252): 6.2 Expressing the change in internal energy in terms of heat and work (253): 6.3 Stating the first law of thermodynamics (law of conservation of energy) (255): 6.4 Determining the work due to a change in volume at constant pressure (PV work) (258): 6.5 Relating the enthalpy change to the internal energy change at constant pressure (258): 6.6 Identifying the enthalpy change with the heat absorbed or released at constant pressure (259): 6.7 Calculating the heat absorbed or released when a substance undergoes a temperature change or a reaction occurs (261): 6.8 Calculating the overall enthalpy change of a reaction (Hess's law) (268): 6.9 Calculating the standard enthalpy of reaction (271): Answer the following questions. Show your work. • (a) What is "Joule"? (b) Look up Specific heat capacity of ice, liquid water, and steam. Include units. (c) The 'degree' sign next to H0 stands for 'standard condition. List the standard conditions. (d) What is the difference between Hrxn and Hf ?