Lecture 11 Review
advertisement

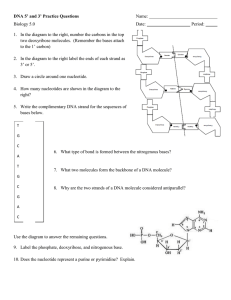
Lecture 11 Review • DNA is the material of heredity • Consists of 4 nucleotides joined between the 3’ carbon of the deoxyribose group of the first nucleotide and the phosphate group of the next nucleotide (which is attached to the 5’ carbon of deoxyribose) • Direction: 5’ to 3’ • Structure: double stranded helix » A pairs with T; G pairs with C DNA in the nucleus • Compacted by interactions with proteins • (1) nucleosomes are formed by DNA interactions with histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 • (2) histone H1 helps nucleosomes interact with each other • (3) this form of DNA forms loops – some portions interact with scaffold, such as the nuclear matrix Cont’d • Heterochromatin – highly compacted DNA • Facultative heterochromatin – is highly compacted in some cells and not in others • Euchromatin – not so tightly compacted DNA (actively transcribed genes) • Metaphase chromosomes – very highly compacted DNA replication • (1) helicase, topoisomerase, ssBP – Opens up DNA and prepares it for replication • (2) primase – adds in short stretches of RNA to act as primers • (3) DNA polymerase III adds deoxyribonucletides to the 3’ end of the RNA primers • Direction of synthesis is 5’ to 3’ Cont’d • Leading strand synthesis vs. lagging strand synthesis….. – Okazaki fragments