Biology 160 NAME: _______________________________________ Reading Guide 07: Photosynthesis
advertisement

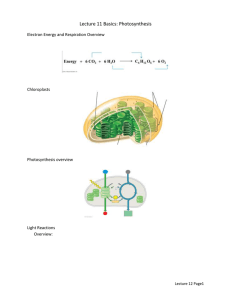
Biology 160 Reading Guide 07: Photosynthesis NAME: _______________________________________ This is DUE: ___________________ Come prepared to share your findings with your group. ** Fill this reading guide out as you are reading the chapters. This will help you to pull out the important information that will help us to understand how cells get energy from food. ** IMPORTANT!!! As before our reading guides are a bit longer now and will become invaluable review sheets for you for the exams. Because of this you will not have to turn in the whole reading guide. On a separate sheet of paper, write up your answers to the “Critical Thinking” questions found on this guide (and all future guides) and turn these in only. The rest of the guide is strongly recommended for you to fill out, but will not be turned in. Reading: Essential Biology, 4th or 5th Ed. (Simon, Reece, & Dickey), Ch 7, all. Lab 04: Photosynthesis and Respiration in Plants While reading these chapters, constantly ask yourself, “How is this information helping me to understand how cells get energy from food?” Chapter 7: 1. To all the words/phrases in the text that are in BOLD: Highlight in your text or rewrite them or organize them in some way (like flash cards or a table) to help you to learn and understand them. 2. Redraw Figure 7.2 here. Pay special attention to the entry/exit of CO2 and O2 through stomata, that the interior cells are filled with chloroplasts, that each chloroplast is filled with thylakoid membrane stacks called grana, and that chlorophyll is built into those thylakoid membranes. Make sure to add chlorophyll to your drawing. 2. Think Back: Just as a reminder…what is a membrane made out of?? Draw a picture. 3. Think Back: What other organelles besides chloroplasts are in a typical plant cell? 4. What is the overall equation for photosynthesis? Label the reactants and the products in this chemical equation. 5. Compare and contrast the overall equations for photosynthesis and cellular respiration. In addition, specifically note the waste products for each process. 6. List the many ways that we could measure the rate of cellular respiration (see Lab 04)? 7. List the many ways that we could measure the rate of photosynthesis (see Lab 04)? 8. What did we measure in Lab 04? 9. From Lab 04: Does a plant perform cellular respiration and photosynthesis? What is your evidence? 10. Redraw Figure 7.3: A Road Map for Photosynthesis. 11. Briefly describe what happens in the “Light reactions.” 12. Briefly describe what happens in the “Calvin cycle.” 13. What is the reduced form of the electron carrier in photosynthesis? 14. Can you confidently answer all of the Checkpoint questions up to this point? If not, write down what questions you still have. 15. What type of energy conversion happens in the Light reactions? 16. What type of energy is sunlight? 17. Describe visible light. 18. OK, I can’t resist putting this question in here because I think it’s so cool: Why are leaves green? 19. Critical Thinking: Which type of photon will have more energy, orange light or blue light? Explain your reasoning. 20. Redraw Figure 7.8 here. Explain in your own words what is happening to the electron. 21. Critical Thinking: Redraw Figure 7.11. Trace the flow of energy through the Light reactions. 22. Critical Thinking: Explain what is happening to the energy of the electrons as they travel through the light reactions (use can use the hard-hat analogy in Figure 7.12). 23. Light reactions: a) Where do they take place in the chloroplast? b) What are the types of energy in the input and output? c) What are the molecules in the input and output? d) Compare and contrast to the electron transport chain in mitochondria during cellular respiration. 24. What happens to water molecules in the Light reactions? 25. Can you confidently answer all of the Checkpoint questions up to this point? If not, write down what questions you still have. 26. What is the advantage of the light reactions producing NADPH and ATP on the stroma side of the thylakoid membrane? 27. What are the names of the molecules that go into and come out of the Calvin cycle (don’t worry about the number of molecules, here, just the names)? 28. What is the function of NADPH in the Calvin cycle? 29. Critical Thinking: Where does the energy from the sunlight eventually end up at the end of photosynthesis? 30. Redraw the “Photosynthesis Road Map” found in the Chapter Review on pg. 117. Specifically pay attention to what the sugar end-product is used for by the plant. 31. Critical Thinking: So are the electrons in the covalent bonds of a water molecule relatively high-energy or relatively low-energy compared to the electrons in the covalent bonds of a sugar molecule? Explain your reasoning.