Programme Specification: BSc Environment and Development 1. Awarding Body
advertisement

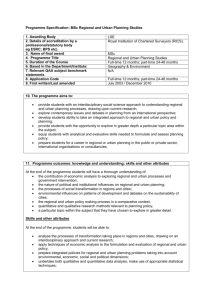
Programme Specification: BSc Environment and Development 1. Awarding Body 2. Details of accreditation by a professional/statutory body, e.g. ESRC; BPS etc 3. Name of final award 4. Programme Title 5. Duration of the course 6. Based in the Department/Institute: 7. Relevant QAA subject benchmark statements 8. UCAS Code 9. First written/last amended LSE N/A BSc (Hons) Environment and Development Three years full-time Geography and Environment Earth sciences, environmental sciences and environmental studies (2007) FK84 BSc/EnvDev October 2009 / November 2012 10. The programme aims to: Provide students with research-focused knowledge and understanding of environmental and development policy at multiple scales; Develop students’ understanding of processes of environmental change as they relate to human well-being and development; Equip students with the skills to analyse critically environmental and development policies; Develop students’ capabilities to communicate effectively their ideas to an appropriate audience; Enable students to progress to higher degrees, or to follow successful careers in private and public sector organisations. 11. Programme outcomes: knowledge and understanding; skills and other attributes 11.1 Knowledge and understanding At the end of the programme, students will have a thorough understanding of: The character of natural systems and the causes and effects of environmental change on human well-being; The application of economics to the design and implementation of environmental and development policies; The theory and practice of environmental science, development studies and environmental policy; The processes and outcomes of environmental and development policy development, including the influence of interaction between actors; The nature and influence of the institutions and instruments of environmental and development policy in various jurisdictions. 11.2 Skills and other attributes At the end of the programme, students will be able to: Critically evaluate the development, implementation and impact of environmental and development policy; Analyse and seek solutions to significant problems in environmental and development policy-making; Apply various techniques of social scientific analysis to relevant issues; Demonstrate the transferability of the information handling and interpretation skills developed during the programme; Communicate effectively – through written essays and oral presentations – on environmental and development matters to an appropriate audience. 12. Teaching, learning and assessment strategies to enable outcomes to be achieved and demonstrated 12.1 Knowledge and understanding Teaching and learning strategies Students acquire their detailed knowledge and understanding of the programme through lectures, classes and guided independent study. Students take four courses a year. Most courses require three or four assessed class assignments (essays and presentations), which provide feedback to students on their level of knowledge and understanding. Many of those involved in teaching the programme are at the forefront of research in environmental and development policy: as such, students have direct insight into current thinking and recent research findings. This aspect of provision is further enhanced through the array of LSE public lectures, which include lectures from senior national and international policy-makers, politicians and researchers in environmental and development fields. All course reading lists are regularly updated: they include hard copy and electronic references to current research and other primary sources – (e.g. official documents and nongovernmental organisation sources). Assessment: A variety of formative and summative assessment techniques are employed to gauge the development of relevant knowledge and understanding: formative assessment centres on class work and feedback from class teachers and, where appropriate, course tutors. Summative assessment methods testing knowledge and understanding feature, depending on the course, one or more of the following - three hour unseen examination, course work essay and field-based project work, independent research project. 12.2 Skills and other attributes Teaching and learning strategies: Skills are developed through guidance and feedback from class teachers and tutors in the context of: Regular lectures; Regular class work, class presentations and the preparation of course essays; One-to-one tutorials; Field-based observation and interpretation; The appropriate use of electronic information sources; Courses in mathematical and economic techniques; The option to plan, conduct and write up an independent research project. Assessment: Formative assessment of skills mainly takes the form of feedback of class tutors on written and presentation-based assignments. This is central to student development in support and development of lecture material. Most courses in the Department of Geography and Environment require the undertaking of a coursework assessed essay, which tests intellectual skills combined with independent study competencies. Summative examinations also test essay-based intellectual skills, but in the context of independent recall and time management competencies. Field-based project work tests field observation and interpretation skills. Students have the option of undertaking an Independent Research Project, which tests the ability to plan, conduct and write up an environmental and development policy investigation conducted on an individual basis. 13. Programme structures and requirements, levels, modules and awards For full programme information see: BSc Environment and Development Programme Regulations Year 1 Environmental Change: Past, Present and Future; Sustainable Development; Environment, Economy and Society One course from a list of approved Year 1 options. A student registered on a BSc programme who has completed the first year of the programme and who has passed examinations in course to the value of at least three course units will be eligible to progress to the second year of the degree. The School may consider an application to progress to the second year of the degree from a student who has not met this requirement and at its discretion the School may allow such a student to progress or to repeat the first year of the programme as appropriate. Year 2 Introduction to Development in the South; Environment: Science and Society; Applied Environmental Economics One course from a list of approved Year 2 options. The course Research Techniques must be taken if the student intends to take the Independent Research Project in Year 3 A student who has completed the second year of the programme, who has passed all examinations in courses from the first year of the programme and who has passed examinations to the value of at least three course units from the second year, will be eligible to progress to the final year. The School may consider an application to progress to the final year from a student who has not met this requirement and, at its discretion, may allow such a student to progress or to repeat the second year of the programme as appropriate. Year 3 Environmental Governance; Environment and Development; Two courses from the list a list of approved Year 3 options. Additional information 14. Criteria for admission to the programme GCSE pass at grade C or better in Mathematics is expected; Usual standard offer: GCE A level – grades A A B; International Baccalaureate: Diploma with 37 points including grades 6 6 6 at Higher level; There are requirements for applicants who have not been taught in English before: GCSE; 7.0 in IELTS; Grade C IGCSE; Grade 6 Cambridge Certificate 1119; Pass grade NEAB; Other qualifications are considered. 15. Indicators of quality RAE Rating 2008: 70% of research at 3* or above. The LSE Careers Centre website provides data on career destinations of LSE graduates. 16. Methods for evaluating and improving the quality and standard of teaching and learning Courses within the degree programme are subject to student feedback, both through regular staff-student liaison committee meetings and the annual student survey; Issues about standards are considered by Departmental and School examination boards; The School’s Undergraduate Studies Sub-Committee and Teaching, Learning and Assessment Committee oversee the quality and standard of undergraduate degree courses and programmes, ensuring that any changes are compatible with developments elsewhere in the School; TLAC review of the Department once every five years; Departments review their programmes according to their own system of periodic review; Course teaching surveys conducted by TQARO.