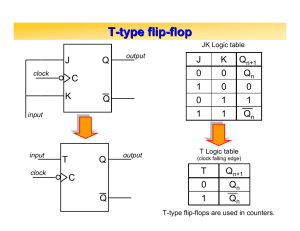
Business Data Communications, Fourth Edition Chapter 4: Communications Equipment
advertisement

Business Data Communications, Fourth Edition Chapter 4: Communications Equipment Learning Objectives • Describe the role of multiplexers in signal transmission • Describe the differences among frequency division multiplexing, time division multiplexing, statistical time division multiplexing, and wavelength division multiplexing • Explain how frequency division multiple access, time division multiple access, and code division multiple access are used in wireless transmission systems Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 2 Learning Objectives • Describe the differences among hubs, bridges, switches, routers, front-end processors, and controllers • Explain how front-end processors are used in a data communications network • Define protocol conversion and why it is needed in data communications networks • List the equipment needed to monitor a network • Define a computer port and explain how data can be directed to different ports Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 3 Introduction • Networks are made up of servers, clients and other equipment • Physical equipment makes up an interface between servers, clients and network • Functions – Combine data signals – Direct and monitor network traffic – Conversion of data to correct format Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 4 Multiplexers • A device that combines data from several devices into a single stream • Multiplexers are used in pairs • Increases efficiency, reduces cost • Idle time is reduced Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 5 Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 6 Multiplexers • Used in WANS, LANs, wireless networks – In WANs, used on point-to-point, multipoint lines – Connection multiplexer in LANs – Multiple radio signals combined on wireless networks Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 7 Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 8 Multiplexers • Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) – Bandwidth divided into narrow bandwidths – Example of FDM circuit – Guardbands used to separate the signals Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 9 Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 10 Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 11 Multiplexers • Frequency Division Multiplexing – Voice-grade circuits • AT&T separates into groups – Supergroup – 60 channels – Mastergroup – 600 channels – Jumbo group – 3600 channels – Used in cable television systems Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 12 Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 13 Multiplexers • Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) – Transmission line divided into time segments – Guard time separate signals – Used on Dataphone Digital Service • Leased digital lines • Maximum speed of 56 Kbps – Used on T-1 lines (1.55 Mbps) – Used on fiber optic networks Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 14 Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 15 Multiplexers • Statistical Time Division Multiplexing (STDM) – Time slots allocated dynamically – Eliminates empty time slots used in TDM – Provides advanced functions over TDM • Data compression • Accumulation and reporting of network statistics • Some error detection and correction Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 16 Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 17 Multiplexers • Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) – Used for analog and digital transmission over fiber optic cables – Optical equivalent of FDM – Allows up to 400 Gbps on a single cable – Problems connecting to copper cables • Conversion between electrical and optical signals • Optical amplifiers – amplifies optical signal Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 18 Multiplexers • Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) – Future may include fiber optic to private homes – Fiber exhaust • Traffic exceeds network bandwidth capacity – Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) • May allow up to 50,000 Gbps • Same as 33 million T-1 lines Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 19 Multiplexers • Frequency Division Multiple Access – Multiple access for analog cellular communication – One user on a frequency at one time – Earliest system • Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS) – US and Canada • Total Access Communication System (TACS) – United Kingdom Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 20 Multiplexers • Time Division Multiple Access – Used for today’s cellular systems – Operates similarly to TDM – Multiple users on a single frequency simultaneously (3 at a time) – Used in conjunction with FDMA Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 21 Multiplexers • Time Division Multiple Access – North American Digital Cellular (NADC) – Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) – Japanese Digital Cellular (JDC) – Personal Digital Cellular (PDC) – Personal Communication Service (PCS) • Assigns phone number to person, not telephone • Number is encoded in a circuit card • Uses GSM and CDPD Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 22 Multiplexers • Time Division Multiple Access – Standards • • • • TIA/CTIS IS-54 (first standard) TIA/CTIS IS-54B (digital voice channels added) TIA/CTIS IS-136A (advanced features) TIA/CTIS IS-136B (short message service) – FDMA/TDMA – advantages and limitations – Enhanced TDMA • Dynamically allocates time slots to users • Makes it twice as efficient as TDMA Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 23 Multiplexers • Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) – Each cellular conversation is assigned a code – Signals are identified by the code – Uses direct sequence spread spectrum – Makes higher speed transmission possible Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 24 Multiplexers • Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) – Standards • TIA/EIA/IS-95 (cellular radio) • ANSI J-STD-008 (CDMA with PCS) – Higher capacity than FDMA and TDMA – CDMA is a controversial technology – Equipment is very expensive – Unproven at this time Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 25 Multiplexers • Configurations – Multiplexer and demultiplexer used together – Inverse multiplexer • Combines high-speed lines between two servers • AKA bonding • Common carriers use it for high-speed services Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 26 Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 27 Multiplexers • Configurations – Connect communications lines to another multiplexer – Cascading multiplexers • Using several levels of multiplexers at several sites • Reduces costs Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 28 Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 29 Interconnecting Devices • Hubs (concentrator) – Combines data from several devices on a single communications line – Not necessarily used in pairs – Placed between clients and the server – Home users may have one to connect multiple computers to an Internet connection Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 30 Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 31 Interconnecting Devices • Bridges – Connects two local area networks – Filters data to determine if it should be passed to another segment • Switches – Adds intelligence to functions of a hub – Backplane – hardware portion of switch – Operates much faster than a hub Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 32 Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 33 Interconnecting Devices • Routers – Connects networks that use different protocols (rules for communication) – Does conversion of data between the networks – Can act as a firewall – Functions • Monitor network traffic • Collect and report network statistics • Provide quality of service functions Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 34 Front-End Processor (FEP) • • • • • Another type of communications controller Located close to the server Performs network management tasks FEP Functions (Table 4-1) Types of Front End Processors – Nonprogrammable – Programmable • Network Control Program (NCP) Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 35 Controllers • Scaled-down version of an FEP – Handles up to 64 devices – Cluster controller • Specifically used with IBM servers – Remote controller • Located a distance from the server – Local controller • Located near the server Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 36 Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 37 Protocol Converters • Translates between protocols on different computers and networks • Hardware converter – Special device • Software converter – Installed on the server • Gateway – Used with LANs Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 38 Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 39 Ancillary Equipment • Diagnostic Equipment – Line monitors • Monitors data as it travels over the medium • Data displayed on a screen – Network sniffer • Monitors all network traffic • Can compare data to historical data for trends – Breakout box • Checks voltage levels • Can isolate a circuit for testing Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 40 Ancillary Equipment • Port Concentrators and Selectors – Port concentrator • Multiple devices connected through a single port • Reduces the need to add additional server ports – Port Selector • Used with dial-up lines to direct data to a port • Special Purpose Modems – RF modem – Fiber-optic modem Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 41 Chapter 4: Communications Equipment 42 Summary • Multiplexers used in pairs to combine data • Concentrator also combines data • Front end processor is a special version of a concentrator • Controllers combine data at remote or local sites • Protocol converters used to translate between different devices Chapter 4: Communications Equipment • Line monitors and breakout boxes are diagnostic equipment • Port concentrators and selectors are used to allow access to computer ports • RF modems are used for wireless connections while fiber optic modems are used for fiber optic lines 43