Chemistry Tutorial
advertisement

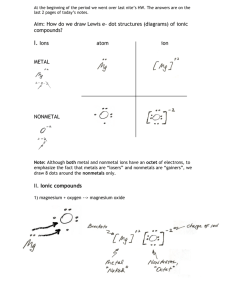
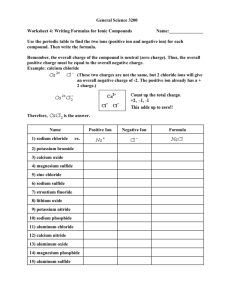
Chemistry Tutorial Introduction: Senior Chemist – Barbara Beatty MSc Senior Chemist - Dawit Teclemariam PhD Chemist Administrator – Paul Vinik MSc Topics Discussed: 1) pH 2) Resistivity 3) Chloride Concentration Measurements 4) Carbonate Concentration Measurements 5) Sulfate Concentration Measurements Periodic Table of Elements – By Dmitri Mendeleev 1869 •Valences •Metals •Transition Metals •Reactivity •Metalloids •Main Group Elements •Noble Gases •Nonmetals •Atomic Number Electron Orbital Theory Reaction Mechanisms: 1) Covalent - Organics 2) Ionic – Sharing of electrons 3) Hydrogen Bonding – H2O Reactivity: 1) Full Shell – Inert gas 2) Distance from Nucleus makes it easier to share electrons 3S2 2P6 2S2 1S2 Nucleus pH • pH = the negative log of the hydronium ion concentration. • pH= -Log[H3O]+ Definitions: Buffer – A solution characterized by the ability to resist changes in pH when limited amounts of acid or base are added to it. Acid – A substance that when dissolved in water increases the hydrogen ion concentration. The proton Donor. Base – A substance that when dissolved in water increases the Hydroxyl Ion concentration. The Proton Acceptor. 0 7 Acidic Neutral 14 Basic Alkaline Neutral Solution: [H3O+] = [OH-] Acidic Solution: [H3O+] > [OH-] Ionic Dissociation: + - • H2O [H3O ] + [OH ] + 2- • H2SO4 2 [H ] + [SO4 ] + - • HCl [H ] + [Cl ] + - • NaOH [Na ] + [OH ] pH Tutorial: http://www.chem.ubc.ca/courseware/pH/index.html Resistance • Ohm’s Law: R = V / I • Resistance (R) – The ratio of the voltage applied to the current that flows through a material. • Resistivity (ρ ): • Conductivity (σ): σ = 1/ρ The conductivity of a solution is related to the dissolved ion concentration, or Ionic Strength. Chloride Ion Concentration Chloride Ion [Cl-] concentration can be measured with numerous instrumentation and chemical methods. The most common technique is titration. Titration is used by most common pool water test kits as well as FM 5-552. AgNO3 + NaCl + K2CrO4AgCl + Ag2CrO4 + KNO3 + NaNO3 + KCl By adding silver nitrate drop wise to an aqueous solution, the product, silver chloride precipitates as a white solid. When there is no more chloride left to make silver chloride, the product becomes silver chromate and this transition is observed as a color shift toward redbrown. Sulfate Ion Concentration Na2SO4 + BaCl2 BaSO4 + 2NaCl Barium sulfate is insoluble in water and subsequently precipitates. By waiting 5 to 10 minutes, the gases in the sample are allowed to escape, but the solids are not given enough time to settle out suspension. After 5 minutes a turbidity measurement is used to assess the quantity of suspended solids. Carbonate Content CaCO3 + HCl CaCl2 + H2CO3 Hydrochloric acid is added to calcium carbonate and calcium chloride and carbonic acid are formed. The products are placed in a filtration funnel and carbon dioxide evolves while the soluble calcium chloride permeates through the filter. By burning the ash free filter paper, the change in mass from the original sample is due to the loss of carbonates. CO2 CaCl2 + H20 + CO2 After Filtration, burn the filter paper and contents. Compare initial weight with final to determine carbonate content.