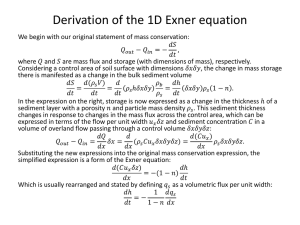
Desertification and Aeolian Sediment Transport in India
advertisement

Desertification and Aeolian Sediment Transport in India Climates of India -Area of Rajasthan is predominantly desert or an arid climate. -Climate is heavily influenced by monsoon season. -32% of land facing threat of desertification -Upward eddie wind currents of greater than 3km/h can lift silt and very fine sand up to 4km Causes of Desertification The Himalayan Water Grab The Source ● Half world’s population dependent ● Historical land and border disputes ● Dynamic and evolving systems o o Hydrologically and Politically ● Seasonal fluctuations and vulnerabilities Observer Complexities of Sediment Load ● ● ● ● Limited Knowledge Climatic evolution Anthropogenic effects Intrabasin and regional variability ● Source/sink dynamics Gangetic river system 2,390tons/km2 annually Sediment delivery influenced primarily by climatic conditions Tropical river system 216tons/km2 annually Sediment delivery influenced by climate and anthropogenic factors Heavily decreased sediment loads Erosion/deposition equilibrium High erosion rate Decreased flow Aggrading environment “Hungry water” Decreasing sediment loads Subsidence from oil extraction Decreasing deltaic aggradation Rising sea level