Organization of Nervous Systems Information Processing
advertisement

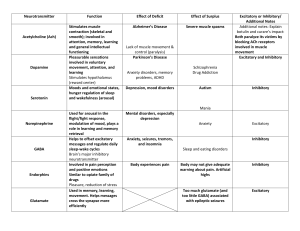
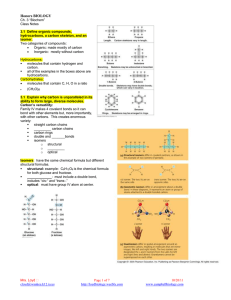
AP Biology Nervous System Notes Ch. Organization of Nervous Systems Page 1012, Fig. 48.2 Information Processing p. 1013, fig. 48.3 Reflexes: Sensory neuron to spinal cord to motor neuron. 1. The reflex is initiated by tapping the tendon connected to the quadriceps (extensor) muscle. 2. Sensors detect a sudden stretch in quadriceps. 3. Sensory neurons convey the information to the spinal cord. 4. The sensory neurons communicate with motor neurons that supply the quadriceps. The motor neurons convey signals to the quadriceps, causing it to contract and jerking the lower leg forward. 5. Sensory neurons from the quadriceps also communicate with interneurons in the spinal cord. 6. The interneurons inhibit motor neurons that supply the hamstring (flexor) muscle. This inhibition presents the hamstring from contracting, which would resist the action of the quadriceps. Neuron Structure p. 1014, fig 48.5 Know parts and functions. Schwann Cells Mrs. Loyd cloyd@waukee.k12.ia.us Page 1 of 3 http://loydbiology.weebly.com 7/12/16 http://www.mybiology.com Action Potentials Varying force of sensory input is transmitted as greater or fewer numbers of action potentials. The amplitude of the A.P. does not change. The action potential is “All or None.” Conduction of an Action Potential The movement of the ion channels to send the action potential along the length of the neuron is like a stadium wave. To participate in a stadium wave you: 1. remain sitting until the wave reaches you. 2. the person next to you begins to stand and you follow just after 3. you stand and throw up your hands 4. bring your hands down, sit down 5. watch the wave move around the stadium 6. wait for another wave. Use the following events to align with the analogy. a) Na+/K+ pump returns ions to original position, repolarizing the axon. b) Na+ ions flood in, a local change (permeability to ions) c) triggering depolarization of neighboring membrane d) Impulse moves along axon to synaptic terminals e) Resting membrane potential X 2 Mrs. Loyd cloyd@waukee.k12.ia.us Page 2 of 3 http://loydbiology.weebly.com 7/12/16 http://www.mybiology.com How do Schwann cells improve the speed of conduction of an action potential? Describe saltatory conduction. A Chemical Synapse Be able to narrate the diagram. p. 1022 How are neurotransmitters involved? Neurotransmitters are secreted from the presynaptic membrane into the synaptic gap where they diffuse to the postsynaptic membrane and bind to receptors there. This may open ion channels that can trigger an action potential (Na+ is excitatory) or open channels for ions that decrease the tendency to develop action potentials (Cl- or K+ are inhibitory). Alcohol, nicotine, and caffeine are drugs that alter the effects of neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitter Acetylcholine Functional Class Excitatory to vertebrate skeletal muscles; excitatory or inhibitory at other sites Gases Amino Acids Biogenic Amines Epinephrine Notes Most common neurotransmitter in verts and inverts. Drugs Nicotine Also a hormone Norepinephrine excitatory or inhibitory Dopamine Generally excitatory Also a hormone Affect sleep, mood, attention, and learning. Serotonin Generally inhibitory GABA Inhibitory Ritalin is chemically similar to norepinephrine and dopamine. Block the reuptake of these transmitters. LSD, mescaline produce hallucinatory effects by binding brain receptors for serotonin and dopamine. Schizophrenia drugs block receptors for dopamine. Prozac treats depression by enhancing the effect of serotonin by inhibiting its uptake after release into synaptic gap. Tranquilizers activate the receptors increasing its effect at inhibitory synapses. NO, CO Mrs. Loyd cloyd@waukee.k12.ia.us Page 3 of 3 http://loydbiology.weebly.com 7/12/16 http://www.mybiology.com