The Pacific Theatre and Peace
advertisement

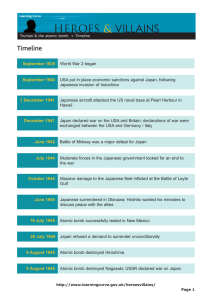
The Pacific Theatre and Peace The Pacific War • U.S. war strategy in the Pacific divided responsibilities between Gen. Douglas MacArthur led forces in a “Island hopping campaign” from Australia to the Philippines, and Admiral Chester Nimitz who commanded the Central Pacific fleet. • Plan was to isolate Japan from its southern conquests • British moved from India to retake Burma The Pacific War • With Japans army bogged down in China – Allies planned to bomb Japan • Island Hopping campaign – American naval version of blitzkrieg: planes from aircraft carriers control the skies while navy and land forces isolated and captured the most strategically Japanese-held islands while by passing the rest • Racial hatred between American & Japanese forces intensified the fighting in the Pacific The Pacific War • Leyte Gulf – Allied invasion of Japanese-held Philippines and the destruction of the Japanese fleet leaving the homeland of Japan undefended against invasion • U.S. naval blockade of Japanese imports and heavy bombing of Japanese cities continually weakened Japanese war capabilities • U.S. capture of strategic Japanese islands: Iwo Jima & Okinawa (April-June 1945) Searching for Peace • Yalta Conference (Feb. 1945) – Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin debated plans for the postwar world • American goal was to enlist the USSR in finishing off the Japanese • Stalin wanted control of Manchuria, China in exchange for joining the • Stalin would only give vague pledges to allow non-communist to participate in the coalition governments in Eastern Europe Searching for Peace • April 12, 1945 – FDR died of a cerebral hemorrhage • Harry Truman – Vice President succeeds FDR • Potsdam Conference (July 1945) – BritishSoviet-American conference where they debated the future of Germany • Potsdam Declaration - Truman made it clear that the U.S. expected to dominate the occupation of Japan Searching for Peace • Goal was to democratize the Japanese political system and reintroduce Japan into the international community - intended to give Japan an opening for surrender • Sec. of state James Byrnes – urged Truman to use the new atomic bomb • U.S. was convinced Japan would fight to the death in an invasion of the homeland • Using the bomb offered a quick end to the war and it might intimidate Stalin End of the war in the Pacific • U.S. dropped the first atomic bomb on August 6, 1945 at Hiroshima (killed approx. 80,000) and the second on Aug. 8 at Nagasaki (killed approx. 40,000) • V.J. Day: Victory in Japan Day - Japan ceased hostilities on Aug. 14th and surrendered formally on Sept. 2nd • Japanese government signed the terms of surrender on the deck of the USS Missouri a battle ship nearly destroyed at Pearl Harbor on Dec. 7th, 1941 Captain Paul Tibbets in the Enola Gay minutes before takeoff to drop the first atomic bomb on Hiroshima, 1945 Harold Agnew carrying the plutonium core of the Nagasaki Fat Man bomb, 1945 The Fat Man on transport carriage, Tinian Island, 1945 Nagasaki, 20 minutes after the atomic bombing in 1945