Student Outcome
advertisement

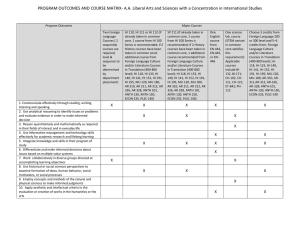
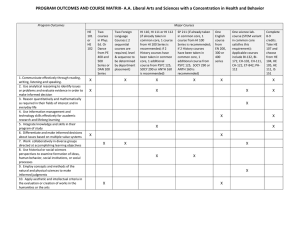
ANTHROPOLOGY PROGRAM MATRIX I 100- and 200-level courses (revised 12/19/05) Student Outcome 1. A broad knowledge of the discipline of anthropology and its four fields 2a. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including genetic variability, heredity, and natural selection in the microevolution of populations. 2b. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including evolutionary processes leading to macroevolutionary change (speciation). 2c. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including major patterns of variation and adaptation in modern human populations. 2d. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including the place of the human species within a broader context of primate biology and evolution, and an appreciation of how studies of our closest relatives shed light of human behavior and adaptation. 2e. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including the evolutionary history of our subfamily Homininae, involving both knowledge of the fossil evidence for human evolution and the influence of cultural innovation on human evolutionary patterns. 2f. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including what it means to say that human beings are biocultural organisms. 3a. An understanding of the anthropological concept of culture, including how knowledge of human cultural learning demonstrates the lack of evidence for the existence of biological “races.” 3b. An understanding of the anthropological concept of culture, including how anthropological views of culture have changed over time. 3c. An understanding of the anthropological concept of culture, including how cultural anthropologists use participant-observation to learn about the ways of life of living peoples. 3d. the importance of symbolic activity in human activities such as language, the arts, and other creative human activities. ANTH 101 Intro to Anth ANTH 130 Intro to World Arch ANTH 140 Intro to Human Origins ANTH 188 Indians of the Americas X X x x X X x X X x X X x X X x X X x X X x X X x x x X x X X ANTH 198 Anth of USA ANTH 230 Intro to Arch ANTH 240 Intro to Bioanth ANTH 250 Intro to Cultural X x x x x ANTH 275 Intro to Museol X X x X X X 1 Student Outcome 3e. An understanding of the anthropological concept of culture, including how cultural patterns vary over time and across the world 3f. An understanding of the anthropological concept of culture, including how cultural anthropologists study contemporary changes in the ways human beings live. 4a. An understanding of anthropological approaches to the human past, including theory in archaeology. 4b. An understanding of anthropological approaches to the human past, including archaeological field methods. 4c. An understanding of anthropological approaches to the human past, including analysis and interpretation of archaeological data. 4d. An understanding of anthropological approaches to the human past, including cultural patterns and cultural change in the human past. 5. Knowledge of major research methods used in anthropology, with firsthand research experience in at least one major formal method. 6. The ability to read, think and evaluate information critically. 7a. The ability to analyze qualitative data. ANTH 101 Intro to Anth x ANTH 130 Intro to World Arch ANTH 140 Intro to Human Origins ANTH 188 Indians of the Americas X X ANTH 198 Anth of USA x x x x X x X x X X X x X x x X X X x X X X X X 8b. Writing skills: the ability to synthesize information. 8c. Writing skills: The ability to analyze and apply anthropological concepts. 9. Knowledge of, and respect for, human cultural diversity worldwide and through time.. 10. Understanding and application of anthropological theory and method to a variety of settings. X X X X X X X X x X X X x x x ANTH 275 Intro to Museol X x x x x ANTH 250 Intro to Cultural X X x X ANTH 240 Intro to Bioanth X 7b. The ability to analyze quantitative data. 8a. Writing skills: the ability to communicate ideas clearly. ANTH 230 Intro to Arch X x x x x x x x x x x x x x X X x x 2 ANTHROPOLOGY PROGRAM MATRIX II 300-level courses and above (revised 5/8/06) Student Outcome 1. A broad knowledge of the discipline of anthropology and its four fields 2a. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including genetic variability, heredity, and natural selection in the microevolution of populations. 2b. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including evolutionary processes leading to macroevolutionary change (speciation). 2c. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including major patterns of variation and adaptation in modern human populations. 2d. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including the place of the human species within a broader context of primate biology and evolution, and an appreciation of how studies of our closest relatives shed light of human behavior and adaptation. 2e. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including the evolutionary history of our subfamily Homininae, involving both knowledge of the fossil evidence for human evolution and the influence of cultural innovation on human evolutionary patterns. 2f. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including what it means to say that human beings are biocultural organisms. 3a. An understanding of the anthropological concept of culture, including how knowledge of human cultural learning demonstrates the lack of evidence for the existence of biological “races.” 3b. An understanding of the anthropological concept of culture, including how anthropological views of culture have changed over time. 3c. An understanding of the anthropological concept of culture, including how cultural anthropologists use participant-observation to learn about the ways of life of living peoples. 3d. the importance of symbolic activity in human activities such as language, the arts, and other creative human activities. ANTH 301 Anth and the Arts ANTH 310 (LAm), 311 (Asia), 312 (Africa) ANTH 330 North Amer Arch ANTH 332 Sickness & Health In Prehist ANTH 350 Ethnog Enterprise ANTH 351 Food, Society, Culture x ANTH 352 Human Ecology ANTH 360 Language & Culture ANTH 361 A Global World x x x x x x x x x x x x x X X X X X X X X X X X X x 3 Student Outcome 3e. An understanding of the anthropological concept of culture, including how cultural patterns vary over time and across the world 3f. An understanding of the anthropological concept of culture, including how cultural anthropologists study contemporary changes in the ways human beings live. 4a. An understanding of anthropological approaches to the human past, including theory in archaeology. 4b. An understanding of anthropological approaches to the human past, including archaeological field methods. 4c. An understanding of anthropological approaches to the human past, including analysis and interpretation of archaeological data. 4d. An understanding of anthropological approaches to the human past, including cultural patterns and cultural change in the human past. 5. Knowledge of major research methods used in anthropology, with firsthand research experience in at least one major formal method. 6. The ability to read, think and evaluate information critically. 7a. The ability to analyze qualitative data. ANTH 301 Anth and the Arts ANTH 310 (LAm), 311 (Asia), 312 (Africa) X X 8b. Writing skills: the ability to synthesize information. 8c. Writing skills: The ability to analyze and apply anthropological concepts. 9. Knowledge of, and respect for, human cultural diversity worldwide and through time.. 10. Understanding and application of anthropological theory and method to a variety of settings. ANTH 332 Sickness & Health In Prehist ANTH 350 Ethnog Enterprise ANTH 351 Food, Society, Culture ANTH 352 Human Ecology ANTH 360 Language & Culture ANTH 361 A Global World X X x X X X x X X X x X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X x X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X x X X X X X X X X X 7b. The ability to analyze quantitative data. 8a. Writing skills: the ability to communicate ideas clearly. ANTH 330 North Amer Arch 4 ANTHROPOLOGY PROGRAM MATRIX III 300-level courses and above, continued (revised 5/8/06) Student Outcome 1. A broad knowledge of the discipline of anthropology and its four fields 2a. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including genetic variability, heredity, and natural selection in the microevolution of populations. 2b. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including evolutionary processes leading to macroevolutionary change (speciation). 2c. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including major patterns of variation and adaptation in modern human populations. 2d. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including the place of the human species within a broader context of primate biology and evolution, and an appreciation of how studies of our closest relatives shed light of human behavior and adaptation. 2e. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including the evolutionary history of our subfamily Homininae, involving both knowledge of the fossil evidence for human evolution and the influence of cultural innovation on human evolutionary patterns. 2f. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including what it means to say that human beings are biocultural organisms. 3a. An understanding of the anthropological concept of culture, including how knowledge of human cultural learning demonstrates the lack of evidence for the existence of biological “races.” 3b. An understanding of the anthropological concept of culture, including how anthropological views of culture have changed over time. 3c. An understanding of the anthropological concept of culture, including how cultural anthropologists use participant-observation to learn about the ways of life of living peoples. ANTH 364 Sex & Gender ANTH 369 Myth, Magic & Religion ANTH 370 Applied Anthro ANTH 370 Anth Analysis & Interp ANTH 372 Business & World Culture ANTH 390 Topics in Arch ANTH 391 Topics in Cultural Anth ANTH 392 Topics in Bioanth ANTH 430/ 530 Res Meth In Arch x x x X x X X X X X x X X x x x x X x x X 5 3d. the importance of symbolic activity in human activities such as language, the arts, and other creative human activities. Student Outcome 3e. An understanding of the anthropological concept of culture, including how cultural patterns vary over time and across the world 3f. An understanding of the anthropological concept of culture, including how cultural anthropologists study contemporary changes in the ways human beings live. 4a. An understanding of anthropological approaches to the human past, including theory in archaeology. 4b. An understanding of anthropological approaches to the human past, including archaeological field methods. 4c. An understanding of anthropological approaches to the human past, including analysis and interpretation of archaeological data. 4d. An understanding of anthropological approaches to the human past, including cultural patterns and cultural change in the human past. 5. Knowledge of major research methods used in anthropology, with firsthand research experience in at least one major formal method. 6. The ability to read, think and evaluate information critically. 7a. The ability to analyze qualitative data. x X ANTH 364 Sex & Gender ANTH 369 Myth, Magic & Religion X X ANTH 371 Urban Anthro ANTH 372 Business & World Culture X X X x X X 8b. Writing skills: the ability to synthesize information. 8c. Writing skills: The ability to analyze and apply anthropological concepts. 9. Knowledge of, and respect for, human cultural diversity worldwide and through time.. 10. Understanding and application of anthropological theory and method to a variety of settings. ANTH 370 Applied Anthro ANTH 390 Topics in Arch ANTH 391 Topics in Cultural Anth ANTH 392 Topics in Bioanth ANTH 430/ 530 Res Meth In Arch X X X X X x X X X x X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X x X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X x x x x x 7b. The ability to analyze quantitative data. 8a. Writing skills: the ability to communicate ideas clearly. X X 6 ANTHROPOLOGY PROGRAM MATRIX IV (300-level and above, continued) 11/2/05 Student Outcome 1. A broad knowledge of the discipline of anthropology and its four fields 2a. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including genetic variability, heredity, and natural selection in the microevolution of populations. 2b. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including evolutionary processes leading to macroevolutionary change (speciation). 2c. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including major patterns of variation and adaptation in modern human populations. 2d. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including the place of the human species within other living species, especially other primate species, and an appreciation of how studies of our closest relatives shed light of human behavior and adaptation. 2e. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including the evolutionary history of our subfamily Homininae, involving both knowledge of the fossil evidence for human evolution and the influence of cultural innovation on human evolutionary patterns. 2f. An understanding of contemporary evolutionary theory, including what it means to say that human beings are biocultural organisms. 3a. An understanding of the anthropological concept of culture, including how knowledge of human cultural learning demonstrates the lack of evidence for the existence of biological “races.” 3b. An understanding of the anthropological concept of culture, including how anthropological views of culture have changed over time. 3c. An understanding of the anthropological concept of culture, including how cultural anthropologists use participantobservation to learn about the ways of life of living peoples. 3d. the importance of symbolic activity in human activities such s language, the arts, and other creative human activities. ANTH 435 Field Methods In Arch ANTH 438/ 538 x x CRM ANTH 444 Internship ANTH 450/ 550 Ethnog Research Methods ANTH 455 Ethnog Field Research ANTH 463/ 563 Seminar ANTH 470 Anth Analysis & Interp ANTH 471 Cognitive Anthro ANTH 474/ 574 Culture & Family ANTH 480 Theory & Practice In Anth x x x x x x X X X* x x x x x x X X X X X x X* X X X X x X X X X X X x x x x X X X X X X 7 Student Outcome 3e. An understanding of the anthropological concept of culture, including how cultural patterns vary over time and across the world 3f. An understanding of the anthropological concept of culture, including how cultural anthropologists study contemporary changes in the ways human beings live. 4a. An understanding of anthropological approaches to the human past, including theory in archaeology. 4b. An understanding of anthropological approaches to the human past, including archaeological field methods. 4c. An understanding of anthropological approaches to the human past, including analysis and interpretation of archaeological data. 4d. An understanding of anthropological approaches to the human past, including cultural patterns and cultural change in the human past. 5. Knowledge of major research methods used in anthropology, with firsthand research experience in at least one major formal method. 6. The ability to read, think and evaluate information critically. 7a. The ability to analyze qualitative data. 7b. . The ability to analyze quantitative data. 8a. Writing skills: the ability to communicate ideas clearly. 8b. Writing skills: the ability to synthesize information. 8c. Writing skills: The ability to analyze and apply anthropological concepts. 9. Knowledge of, and respect for, human cultural diversity worldwide. 10. Understanding and application of anthropological theory and method to a variety of settings. ANTH 435 Field Methods In Arch ANTH 438/ 538 CRM X X X X X X X X ANTH 444 Internship ANTH 450/ 550 Ethnog Research Methods ANTH 455 Ethnog Field Research X X ANTH 463/ 563 Seminar ANTH 470 Anth Analysis & Interp ANTH 471 Cognitive Anthro ANTH 474/ 574 Culture & Family ANTH 480 Theory & Practice In Anth X x X X x X X X X X x X* x X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X x X X X X X X X X X X X X X X x X* = emphasis will vary depending on subfield of anthropology and topic of seminar. 8