A Model For Evaluating Institutional Research Functions AIR 2000
advertisement

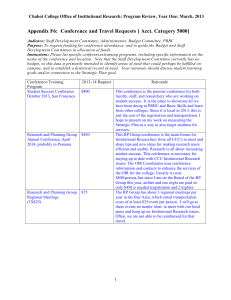
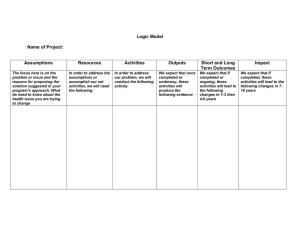
A Model For Evaluating Institutional Research Functions AIR 2000 May 20, 2000 Frank Doherty Director of Institutional Research James Madison University Objectives Learn how to describe what you do. Develop a systematic plan to evaluate the IR functions. Freebie: Learn a method to evaluate other administrative offices on your campus. Schedule 8:00—10:00 Introduction and program design development 10:00 Break 10:15—12:00 Program design development 12:00—1:00 Lunch 1:00—4:00 Evaluation design development 4:00-5:00 Wrap-up and evaluation JMU OIR Evaluation 1992 SACS Visiting Team Report “Although OPA (now OIR) has occasionally evaluated the usefulness of some of its products and services, evaluation has not been established as a routine matter. Thus, the Committee recommends that the University establish regular and ongoing evaluation mechanisms for the institutional research function.” Evaluation Is UserOriented Objective is program improvement and accountability Seek information that will improve office User control of evaluation is very important Elements of the Evaluation Program design Evaluation design Program review team Data collection and analysis Reporting and recommendations Improvement plan Ongoing evaluation Program Design Philosophy You cannot evaluate that which you cannot describe First step in self-study Facilitates clarification of program goals and operation—wonderful communication device Aids the planning process Serves as an implementation guide Provides a sense of the whole Documents program operation Program Design Discrepancy Evaluation Model Systems approach Inputs Processes Outputs Compare performance with standard (gap analysis) OIR Program Design Network Input-Process-Output statements Evaluation Plan Philosophy States intentions publicly Organizes complexity of evaluation effort Facilitates and justifies evaluation resource allocation decisions Serves as a “standard” for judging an evaluation effort Evaluation Design Overall plan for the evaluation Concerns/Issues Program-specific Common Questions Information sources/methodology OIR Evaluation Design Program Review Team Consists of 8-10 staff recommended by office Chair not from office, but appointed by division head Collect data Write report and recommendations Recommendations discussed with division head and supervisor Annual objectives developed to address recommendations Ongoing Program Review OIR program review is conducted every three years Online survey Accountability and use of results Annual objectives based on recommendations Components Components Of An Effective Program Review at James Madison University Summary IR evaluation should be: Thorough User-oriented On-going and accountable OIR evaluation report http://www.jmu.edu/instresrch/present/air99 /oireval.pdf Program Design Exercise Program design consists of two parts Network Input-Process-Output statements Network Numbering and levels Functional dependencies Let’s create a Network IPO Statements Inputs Processes Outputs JMU OIR Network Inputs Things which set processes into motion and keep them running resources receptors staff independent groups/organizations preconditions enabling outputs from other components Processes Described as event-sequences Process descriptions of intended interactions of people, materials and media, and current context in which they take place Be specific indicate who is doing what to whom, how, when, where, and for how long Linked to outputs Outputs—Terminal Two types: terminal objectives and enabling objectives Terminal objectives are changes or products which result from program-controlled processes intended to be fed into the external environment outputs for which the program holds itself accountable—bottom line Outputs—Enabling Enabling objectives result from programcontrolled processes used within program rather than without “enables” the achievement of terminal objectives can be output of one process and input into another IPO Development Exercise Let’s develop an IPO for your office. IPO Exercise Evaluation Plan Address primary needs of area “What do you need to know?” May want to address common institutional issues and questions Customer satisfaction Planning Use of results Etc. Stages of Evaluation Design evaluation Input evaluation * Process evaluation * Output evaluation * Cost-Benefit Analysis Design Evaluation Assessment of substantive adequacy of a program’s design Is this likely to be a good program? Examination of the substance, assumptions, and structure of a program prior to installation. Input Evaluation Appropriate for: New programs and replication efforts Installation evaluation Inputs are present as prescribed by program design Planned processes have been set in motion Design preconditions have been met Stipulated preconditions are critical Fiscal monitoring Process Evaluation Monitors continued operation and sequential accomplishment of enabling objectives Formative: Discrepancy reports used to modify and improve program operations Process Evaluation Sets the stage for summative evaluation Documents and defines “treatment” until program process stable Clarifies relationship between program activities and accomplishment of interim objectives Evaluation plans should emphasize process evaluation Particularly useful during early stages of program operation Output Evaluation Refers to terminal objectives only Have terminal objectives been achieved? Investigation of causation Most useful when preceded by formative evaluation Previous evaluation stages contribute to program stability and improvement Evaluation Design Components Description Evaluation Concern 3-7 aspects of program to be evaluated Evaluation Questions 2 or more performance questions for each concern Design Referent Refers to program design Information Needed Reason for question, kind of information sought Source of Information Where information comes from and how to be analyzed Date Information Needed When discrepancy info needed Selection Criteria Critical functional importance Areas that are problematic Areas of direct concern to external evaluation audiences (i.e. accrediting agency) Areas of concern to internal evaluation audiences (customer satisfaction) Areas where information is needed soon Evaluation Concerns Identification Common models of organization By design component By cross-cutting function By evaluation stage Evaluation Questions Derived from a larger area of concern Guide to collection of performance information What kind of performance information is necessary to answer questions posed? Determine standard for each variable identified Evaluation Questions Develop for each evaluation concern Should direct systematic collection of performance information Evaluation question directs one to performance information Design Referents Relate program design to evaluation design. Design referent should point to a component in the program design and indicate whether the question is related to input, process, or output. Information Needs Provides rationale for each question Explains what kind of information sought Indicates how collected information will be used, and by whom. Information Needs Justification Record keeping Routine monitoring Verification of preconditions Management troubleshooting Functional criticality Accountability Bargain information Information Needs Continued Information need should tell reader purpose of the information (F) for formative (S) for summative Sometimes can be F and S Sources of Information Task #1: Brainstorm information possibilities for each question Task #2: Pick and choose from possibilities Factors to consider: Reliability and validity Cost (time and resources) Report Dates Establish ballpark estimate when discrepancy reports should be available May differ from audience to audience Evaluation Design Exercise Let’s create an evaluation design Evaluation Concerns Evaluation Questions Design Referent Information Needed Source of Information Date Information Needed Data Analysis Questions determine methods Multiple methods used Statistical analysis of data Document review Surveys Interviews Focus groups Reporting and Recommendations Reports are organized by evaluation issue/concern Self-Study team develops recommendations