1-2: More Geometric Figures
advertisement

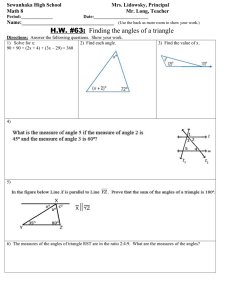
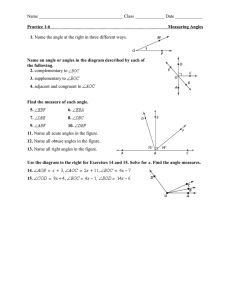
1-2: More Geometric Figures Objectives: 1. To describe angles and angle pairs 2. To identify and name parts of circles Assignment: • P. 10: 11-15 • P. 12: 11-22 • Challenge Problems Objective 1 You will be able to describe angles and angle pairs Angle An angle consists of two different rays (sides) that share a common endpoint (vertex). – Angle ABC, ABC, or B Classifying Angles Surely you are familiar with all of my angular friends by now. C Comes Before S… m1 m2 90 m3 m4 90 m5 m6 180 m7 m8 180 Exercise 1 Is it possible for a pair of angles to be both complementary and supplementary? Can an angle be both the complement of one angle and the supplement of an other angle? Exercise 2 Let ∠𝐴 and ∠𝐵 be complementary angles and let 𝑚∠𝐴 = 2𝑥 2 + 35 ° and 𝑚∠𝐵 = 𝑥 + 10 ° . What is (are) the value(s) of 𝑥? What are the measures of the angles? Adjacent Angles Two angles are adjacent angles if they share a common vertex and a common side but no common interior points ∠𝐴𝐷𝐽 and ∠𝐽𝐷𝐶 are adjacent ∠𝐴𝐷𝐽 and ∠𝐴𝐷𝐶 are nonadjacent Exercise 3 Let’s draw some angles: 1. Two adjacent angles 2. Two nonadjacent angles with a common vertex 3. Two nonadjacent angles with a common side and a common vertex Linear Pairs of Angles Linear Pairs of Angles Two adjacent angles form a linear pair if their noncommon sides form a line. The two noncommon sides are called opposite rays. Linear Pair Postulate If two angles form a linear pair, then they are supplementary. Vertical Angles Vertical Angles Two nonadjacent angles are vertical angles if their sides form two pairs of opposite rays. Vertical angles are formed by two intersecting lines. Vertical Angles Two nonadjacent angles are vertical angles if their sides form two pairs of opposite rays. Vertical Angle Congruence Theorem Vertical angles have equal measures. 𝒎∠𝟏 = 𝒎∠𝟑 𝒎∠𝟐 = 𝒎∠𝟒 Exercise 4: SAT 𝑦 𝑥 𝑧 𝑥 In the figure = 5 and = 4, what is the value of 𝑥? x y z Circle A circle is the set of all coplanar points that are equidistant from a fixed point on the plane. Center Center = fixed point Radius = equal distance Circle A circle is the set of all coplanar points that are equidistant from a fixed point on the plane. D i a m e t e r Center A diameter consists of two radii, but that’s not it’s definition. Chord Chord A chord is a segment whose endpoints are on a circle Diameter Diameter A diameter is a chord that intersects the center of the circle. Exercise 5 Lisa has a circular piece of cardboard with a 10-inch diameter. She wants to cut a 10inch by 2-inch rectangle from the circle. She also wants to cut 10 square pieces that are 1 inch on each side. What information makes this scenario impossible? Secant Secant A secant is a line that intersects a circle in two points. A secant line always contains a chord Tangent Tangent A tangent is a line that intersects a circle at exactly one point. The point of intersection is called the point of tangency Exercise 6 Explain why the wheels on a train are closer to being tangent to the rails than a car tire to the road. 1-2: More Geometric Figures Objectives: 1. To describe angles and angle pairs 2. To identify and name parts of circles Assignment: • P. 10: 11-15 • P. 12: 11-22 • Challenge Problems