Matter can cycle through the biosphere matter, they transform it.
advertisement

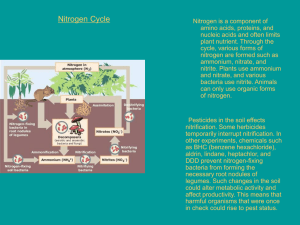
• • • • Matter can cycle through the biosphere because biological systems do not use up matter, they transform it. Matter is Recycled within and between the ecosystems. Matter is assembles into living tissues or passed out of the body as waste. Just think, with every breath you take, you inhale hundreds of oxygen atoms that might have been inhaled by dinosaurs millions of years ago!! Plants and animals need water to live Natural processes constantly recycle water throughout the environment ◦ Animals breathe out water vapor, return water to the environment through urination ◦ Plants pull water from the ground and lose water from their leaves through transpiration 21 The diagram shows physical changes that occur in the water cycle. Which of these shows condensation? AQ BR C S Precipitation D T Run Off of ground water Evaporation • • • • • All life on earth is based on carbon. Carbon is a key ingredient of living tissue. Begins during photosynthesis in which CO2 gas is converted to carbon molecules Carbon molecules are then used for energy and growth As heterotrophs eat plants, they also gain this energy from carbon When the carbon is used, CO2 is released and returned to the atmosphere Glucose C6H12O6 is produced by plants, eaten by animals. Photosynthesis • Animals and plants exhale CO2 which is taken in by plants to make glucose Cellular Respiration • Lightening and bacteria in the ground “fix” Nitrogen into a form usable by plants. It is absorbed by plants, through their roots as nitrates, so they can be used to build amino acids essential for building proteins, enzymes and the nitrogen bases of DNA. All organisms require phosphorus for growth Phosphorus cycles in two ways ◦ In the short term cycle, phosphorus is found in plants, animals eat plants, they die, and the phosphorus returns to the soil ◦ In the long term cycle, phosphorus is washed into the sea and is incorporated into rock WILL REWRITE The paths of water, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorous pass from the nonliving environment to living organisms and then back to the nonliving environment Ground Water: water retained beneath the surface of the Earth Evaporation: water is heated by the sun and reenters the atmosphere Transpiration: water is drawn from stomata in leaves of plants Water that is not evaporated travels from plants to the atmosphere through transpiration and returns to the Earth as rain. Respiration: carbon dioxide is given off as a byproduct of cellular respiration Combustion: carbon is released when fossil fuels are burned Erosion: Shells of dead organisms (made of calcium carbonate) form limestone. As limestone erodes, carbon becomes available for other organisms 79% of the atmosphere is Nitrogen Most organisms cannot use Nitrogen in its atmospheric form Nitrogen Fixation: a few bacteria (found in the soil and on roots of some plants) have enzymes that will break down atmospheric nitrogen and form ammonia Assimilation: absorption and incorporation of nitrogen into plant and animal compounds Ammonification: the production of ammonia by bacteria during the decay of nitrogen-containing urea Nitrification: the production of nitrate from ammonia Denitrification: the conversion of nitrate to nitrogen gas Phosphorous used in ATP and DNA Phosphorous in rock dissolves in water and is absorbed by plants Nonrenewable: Do not replenish themselves naturally Renewable: Replenish themselves naturally Alternative Fuels Recycling (reduce, reuse, recycle)