Unit 8 Review- Organisms and Environments 6.12A&B– Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. 1.
advertisement
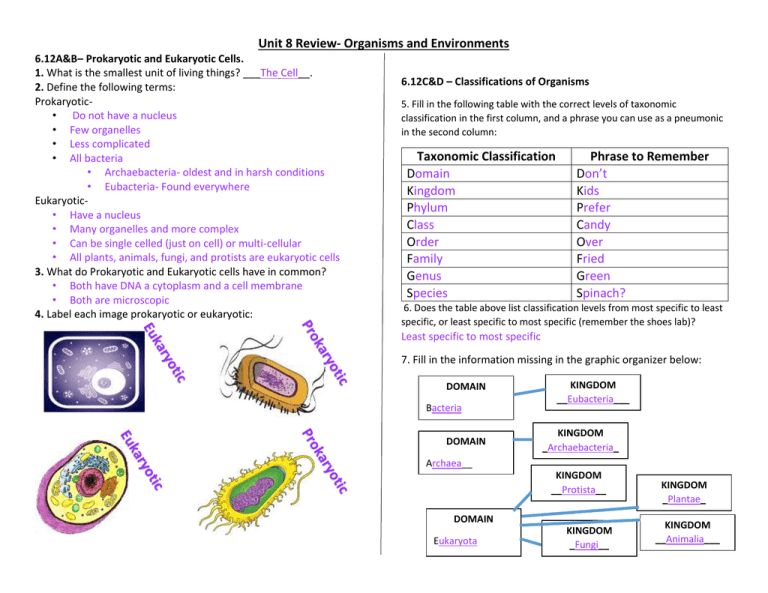
Unit 8 Review- Organisms and Environments 6.12A&B– Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. 1. What is the smallest unit of living things? ___The Cell__. 2. Define the following terms: Prokaryotic• Do not have a nucleus • Few organelles • Less complicated • All bacteria • Archaebacteria- oldest and in harsh conditions • Eubacteria- Found everywhere Eukaryotic• Have a nucleus • Many organelles and more complex • Can be single celled (just on cell) or multi-cellular • All plants, animals, fungi, and protists are eukaryotic cells 3. What do Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells have in common? • Both have DNA a cytoplasm and a cell membrane • Both are microscopic 4. Label each image prokaryotic or eukaryotic: 6.12C&D – Classifications of Organisms 5. Fill in the following table with the correct levels of taxonomic classification in the first column, and a phrase you can use as a pneumonic in the second column: Taxonomic Classification Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Phrase to Remember Don’t Kids Prefer Candy Over Fried Green Spinach? 6. Does the table above list classification levels from most specific to least specific, or least specific to most specific (remember the shoes lab)? Least specific to most specific 7. Fill in the information missing in the graphic organizer below: DOMAIN Bacteria DOMAIN Archaea__ DOMAIN Eukaryota KINGDOM __Eubacteria___ _______________ _KINGDOM _Archaebacteria_ _______________ KINGDOM _ __Protista__ _______________ _ KINGDOM _Fungi__ _______________ _ KINGDOM _Plantae_ _______________ KINGDOM _ __Animalia___ _______________ _ Unit 8 Review- Organisms and Environments 8. Look at the table below and fill in the information that is missing. DOMAIN NAME:__Eukaryota_ Kingdom: Kingdom: Kingdom: Kingdom: Plantae Animalia Fungi Protista Multicellular Multicellular Both Unicellular # of Cells (Uni/MultiCellular) Type of Cells Eukaryotic Eukaryotic Eukaryotic Eukaryotic (Prokaryotic/ Eukaryotic) Feeding Type (Auto/HeteroTrophic) Mode of Reproduction (Sexual/Asexual Autotroph Both Organism This level of an ecosystem includes: One individual living thing Population Heterotroph Both This level of an ecosystem includes: All organisms of the same kind living in one area Sexual Both Both Community wooden spoon Biotic tree puppy wooden spoon and write a description of each level. Heterotroph 9. Judging from the table above, what are the four traits we should know about an organism before trying to sort it into a domain or kingdom? i. Number of Cells (Unicellular or Multicellular) ii. Type of cells (Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic) iii. Feeding Type (Autotroph or Heterotroph) iv. Mode of Reproduction (Sexual or Asexual) 6.12E&F – Interactions in an Ecosystem 10. Sort the six items below into the correct columns on the table below: tree water cement glass 11. In the pyramid below, label the levels of the desert ecosystem shown puppy Abiotic cement water glass This level of an ecosystem includes: All interacting populations in an ecosystem Ecosystem This level of an ecosystem includes: All living and nonliving things interacting in an certain environment 12. The following is a description of a fish tank ecosystem: In a glass fish tank filled with 40 gallons of water, there lived a group of six goldfish. The goldfish shared the tank with a starfish, some rocks, and a frog. The lightbulb at the top of the tank kept it filled with bright light and also kept the temperature of the tank warm. Some fungi grew on the side of the tank as well. -Circle all the biotic factors of the fish tank’s ecosystem. -Underline all the abiotic factors of the fish tank’s ecosystem. -Name the population that lives in the tank’s ecosystem: Six Goldfish