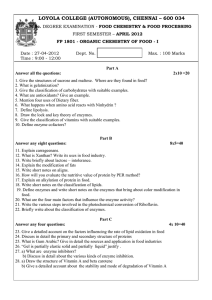
Document 15573394
advertisement

Chemical Reactions and Enzymes 0 As we have seen, living things are made of chemical compounds (Biomolecules), but more importantly chemistry isn’t just what life is made of, chemistry is also what life does. Chemical Reactions 0 Chemical reaction – Change of substances into different ones by breaking and forming of chemical bonds. 0 The chemicals that start a chemical reaction are the reactants. 0 The chemicals produced by a chemical reaction are called products. Energy in Reactions 0 Activation energy is the amount of energy that needs to be absorbed to start a chemical reaction. Two paths will take you to the same end location. Which one will take less energy to get there and will happen faster? 0 Catalysts are substances that speed up chemical reactions. 0 decrease activation energy 0 increase reaction rate Enzymes 0 Enzymes are special proteins in living organisms that work as catalysts. 0 Enzymes function best in a small range of conditions. 0 Changes in temperature or pH (acidity) can damage (denature) enzyme structure. 0 An enzyme’s function depends on its structure. 0 An enzyme’s structure allows only certain reactants to bind to the enzyme. – Substrates (reactants) – Active site (location of reaction on enzyme) substrates (reactants) Substrate binds to the active site on the enzyme. AKA “lock and key” enzyme Substrates bind to an enzyme at certain places called active sites. Substrates bind to an enzyme at certain places called active sites. The enzyme brings substrates together and weakens their bonds. The catalyzed reaction forms a product that is released from the enzyme. Enzymes 0 Enzymes speed up chemical reactions that take place in cells. 0 Enzymes are very specific, catalyzing only one chemical reaction. 0 Lock and Key concept 0 One Enzyme can catalyze or speed up multiple reactions 0 Enzymes are recyclable Enzyme Videos Short & basic enzyme animation Enzymes - In Summary Activation Energy - Snowman How Enzymes Work Digestive Enzyme Basics Enzyme Function In your journal, list the major enzymes found within our digestive system. Use pages 978-984. (Mouth-1, Stomach-1, Pancreas-3, Small Intestine-4) Name Enzyme: Where Found: Name of of Enzyme: Where Found: Salivary Amylase Mouth Function: Function: Pepsin Stomach Break down proteins Amylase Pancreas Continue breaking down starch Trypsin Pancreas Continues breaking down protein Lipase Pancreas Breaks down fat Maltase Small Intestine Sucrase Small Intestine Lactase Small Intestine Peptidase Small Intestine Break down starches Disaccharides into monosaccharides Dipeptides into Amino Acids