Where How to What to do Ch. 2 Simplify
advertisement

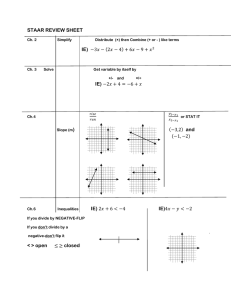
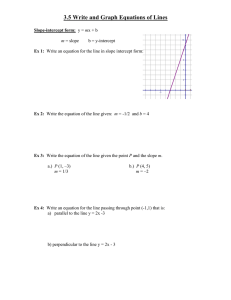
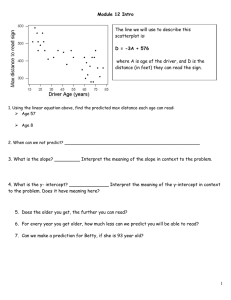
Where Ch. 2 How to Simplify What to do Distribute (×) Combine (+ or - ) like terms IE) −3𝑥 − (2𝑥 − 4) + 6𝑥 − 9 Ch. 3 Solve IE) 𝑥 2 − (𝑥 − 3𝑥 2 ) + 5 Undo what has been done to the variable that is being isolated, by: +/×/÷ IE) −2𝑥 + 4 = −6 IE) −3 = 12𝑦 − 5(2𝑦 − 7) IE) 2𝑥 − 3𝑦 − 4𝑧 = 8 (solve for z) Ch.4 Linear Parent Linear Function Equations Ch.4 Find Slope (m) 𝑦=𝑥 𝑟𝑖𝑠𝑒 𝑦2−𝑦1 𝑟𝑢𝑛 𝑥2−𝑥1 (−3,2) and (−1, −2) Ch. 4 Graph use 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑏 (slope –intercept form) a line m= slope b= y-intercept IE) – 𝟑𝒙 − 𝟐𝒚 = −𝟖 a) use 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑏 change from standard form to slope intercept b) make a table x c)find intercepts(always 0) y x-intercept ( Ch.5 Write y-intercept ,0) (0, ) use 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑏 (slope –intercept form) linear eq. m= slope b= y-intercept IE) IE) (−6,2)and(−1, −3) m= b= Ch.6 Solve IE) −2𝑥 + 6 < −4 IE)4𝑥 − 𝑦 < −2 IE) −3 < 1 − 2𝑥 ≤ 3 IE)5𝑥 − 6 < −16 𝑜𝑟 − 13𝑥 ≤ 39 𝑥−𝑦 <1 4𝑥 + 2𝑦 ≤ −6 Ch.7 Solve a System By Graphing By Substituion 10𝑥 + 5𝑦 = 5 −𝑥 + 3𝑦 = −9 2𝑥 − 3𝑦 = −3 8𝑥 − 4𝑦 = 32 By Elimination 3𝑥 + 4𝑦 = 10 7𝑥 − 4𝑦 = −30 Ch.8 Simplify Exponents Add/Subtract (must be like terms) Coefficients: +/− Exponent: stay same IE) 𝑥 − 𝑥 IE) 𝑥 + 𝑥 2 − 3𝑥 IE) −2𝑥 − 3𝑦 − 3𝑥 + 2𝑦 Multiply Expressions (multiply anything) Coefficients :∗(multiply) Exponents: add exponents IE)𝑥(−𝑥) IE) 𝑥 (𝑥 2 )(−3𝑥) IE)−2𝑥 (−3𝑦)(−3𝑥)(2𝑦) Divide Expressions (divide anything) Coefficients: ∗ (Multiply) Exponents: subtract exponents IE) 𝑥3 𝑥2 IE) −4𝑥 6 𝑦 3 𝑧 2𝑥 2 𝑦 IE) −5𝑎3 𝑏5 𝑐 4 𝑑 6 25𝑎5 𝑏5 𝑐 2 𝑑 10 Product to a Power Coefficient: raise to the exponent Exponents: multiply IE) (2𝑥𝑦 5 )3 IE)(−3𝑥 2 )4 −2𝑚6 IE)( 3𝑛4 ) Negative Exponent Flips the base to numerator or denominator IE) Ch.9 Simplify −2 𝑥 −3 IE) −6𝑦 −3 𝑧 IE)(−4𝑥 −3 𝑦 2 𝑧 −1 ) 𝑥 −2 *get rid of (parenthesis): Distribute then Combine like terms Polynomials IE) (8𝑐 2 − 4𝑐 + 1) + (−3𝑐 2 + 𝑐 − 5) IE) (3𝑚 + 4) − (2𝑚2 − 6𝑚 + 5) IE)𝑥(−𝑥 2 − 4𝑥 − 1) IE)−5𝑎2 (4𝑎3 − 1) IE) (3𝑥 2 )(−2𝑥 4 ) − (−5𝑥)(𝑥 5 ) − 𝑥 5 FOIL IE)(𝑥 + 2)(𝑥 − 8) IE) (7𝑎 − 6) IE)(2𝑥 − 5)(3𝑥 − 4) IE) (7𝑎 − 6)(7𝑎 + 6) Ch.9 Factor try to figure out what multiplies to make the product Factor Ch.10 Quadratics Graph Product 2∗3 6 2𝑥 (𝑥 − 1) 2𝑥 2 − 2𝑥 (𝑥 + 1)(𝑥 + 4) 𝑥 2 + 5𝑥 + 4 (2𝑥 − 3)(3𝑥 − 4) 6𝑥 2 − 17𝑥 + 12 IE)𝑚2 − 10𝑚 + 24 IE)5𝑥 2 + 25 IE) 4𝑥 2 + 2𝑥 − 2 IE)6𝑐 2 + 7𝑐 + 2 Quadratics –Standard Form: 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐 = 0 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐 = 𝑦 Parabola Parent Function/Graph 𝑦 = 𝑥2 To Graph 𝑦 = 2𝑥 2 − 11𝑥 + 5 Find Vertex: 𝑥 = −𝑏 2𝑎 Find y-int: c value (0, ) Find x- int:( ,0)( ,0) Ch. 10 Solve Quadratics Solve 0 = 2𝑥 2 − 11𝑥 + 5 Methods 1. X-intercept (zero’s)(roots) 2. Factoring 3. Quadratic Formula −𝑏±√𝑏2 −4𝑎𝑐 2𝑎 Solve 𝑦 = 2𝑥 2 − 11𝑥 + 5 1. By graphing and finding the x-intercepts – wherever the graph hits the axis is also the solution (usually 2, sometimes only 1, and if none then there is no solution) Solve 𝑦 = 2𝑥 2 − 11𝑥 + 5 ( ,0)( .0) Graph the equation in the calculator and look for the x-intercepts Solve 0 = 2𝑥 2 − 11𝑥 + 5 2. By Factoring Solve 0 = 2𝑥 2 − 11𝑥 + 5 ( )( ) Then set each factor equal to 0 and solve 3. Quadratic Formula Solve 0 = 2𝑥 2 − 11𝑥 + 5 −𝑏±√𝑏2 −4𝑎𝑐 2𝑎 Other Information Parallel lines - ________________ Perpendicular Lines_____________________ Parent Functions Linear: 𝑦 = 𝑥 Quadratic: 𝑦 = 𝑥 2 Domain: Functions: Range: Function Notation: Scale Factors: Similar Figures: Direct Variation: Percents Probability: