The Great War!
advertisement

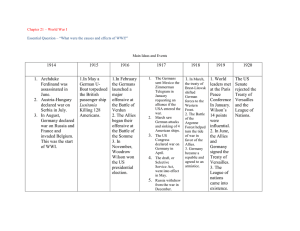
The Great War! The War Years • The war ran from 1914 to 1918. • 4 years is a relatively short time considering we have been fighting the War on Terror now for over 10 years. Why the Great War? • The war was originally called the Great War because no one thought they would need to start numbering them. The Cause or Causes of the Great War • The assassination of the Archduke of AustriaHungary sparked the was but the real causes were brewing for years before the murder of Franz Ferdinand. Europe was like a powder keg or gas leak, all it needed was a spark to blow. The assassination provided that spark. Cause #1 • Nationalism – a feeling of loyalty and unity felt by people who share the same history, culture, and language. How could Nationalism be a cause of the war? • Isn’t it a good thing? Well, two ways actually: one is that not all nations are free but would like to be. For example, Native Americans are a nation of people was live in American and must live by American laws and not native laws. The other way it can be bad is that nations will do what is best for their nation and that could harm another nation, which can result in a war. Examples from WWI • Germany wanted all German speaking areas to become part of Germany and this would mean they might have to take over other countries. • The Bosnians were a part of Austria-Hungary but wanted to be free of their rule. A 19-yearold Bosnian boy acted on behalf of his people. Cause #2 • Imperialism – When one nation tries to take control over another nation. • Remember the main powers of Europe have branched out around the world to improve their power and economy. How did Imperialism become a cause of WWI? • Many European countries were competing for colonies around the globe. Germany was jealous of the vast territory taken by the British and French and wanted some of that land for themselves. Nations in Europe were ready to fight each other over how to divide Africa and other places that didn’t even really belong to them. Cause #3 • Militarism – a policy where a nation rapidly builds up military strength. How did Militarism become a cause of WWI? • All of the major powers at the time (Britain, France, Germany, Russia, USA, Italy, Japan, Ottoman Empire, and Austria-Hungary) all began building massive armies. They all appear to be preparing for war and they make each other very nervous. It also is obvious that if war does break out it will be very destructive and deadly because of the large armies. Ironic Twist • Why were most of these countries building up armies? They were trying to AVOID war. They thought their strength would stop other nations from messing with them. Can you think of a nation that practices this same policy? Old Rivalries Existed • Some of these European countries hadn’t been friends for a very long time. Germany still hated France because of Napoleon. Old feuds and hatreds were many. What is a Rivalry? • Just like North vs. South a rivalry exists when two groups are in competition for something and do not particularly like one another. Industrialization • The countries in Europe began to compete economically. They all wanted wealth but needed resources to do that. Thanks to the modern technology and machines, these countries were able to design bigger and better ways to kill their enemies. Extra Info!!! • People forgot how nasty war could be – There hadn’t been a full-scale war in Europe for 40 years. • There were no veterans around to remind people of the BLOOD and Gore of war. If you have seen war you will do anything to avoid it! There were actually people who thought it would be glorious!! Everyone thought it would be a quick and easy war. That is what happens when people lost their perspective of what war really is… Death!! Alliances • When countries join together for trade or protection, it is a bit like being in a gang. You have each others back! How could this cause W.W.I? • If two countries attack each other, all the allies have to join in. If one member of a gang is jumped, all his friends will join in. In the years before the war two major alliances existed • Triple Alliance: Austria-Hungary, Germany, Italy • Triple Entente: Great Britain, France, Russia • These alliances will change as the war starts. While Europe was readying to explode in 1914, what was up in the USA? • Notice the USA did not belong to an alliance…yet! Isolationism • This was the USA’s foreign policy during the WWI years. It just means America decided to stay out of the war or remain NEUTRAL. • What is foreign policy? • Who decides America’s foreign policy? The Moat Theory • As long was we (USA) had friends to the North and South and Oceans to the East and West… who could mess with us? The USA was like a great castle and the oceans were our personal moat. Why worry about Europe? I guess we were truly ISOLATED from any enemies. There were no planes, missiles, or boats that could attack us. Why was it hard for America to take sides? 1. Most Americans didn’t want war. 2. We were trading partners with most nations in Europe on both sides. 3. Americans had relatives and friends all over Europe that they DID NOT WANT TO KILL!!! The Outbreak of War • Archduke Franz Ferdinand: The young heir to the throne of AustriaHungary was greatly disliked throughout his kingdom because of his political policies. Gavrilo Princip and The Black Hand • Princip was a member of the terrorism group known as the black hand and tried to free Serbia from the clutches of Austria-Hungary. • Imperialism causes Ferdinand’s AustriaHungary to try to control Princip’s nation of Bosnia and Serbia. The War is ON! • Illusions and Surprises: All sides thought the war would be quick and easy. They were shocked at the nastiness and horrible fighting. • Trench Warfare and Stalemates: This was the fighting methods used. • Nationalism causes Princip to want to shoot and kill Ferdinand. • This event is the “SPARK,” but alliances and militarism will cause the situation to explode. Digging a Trench Trench Diagram Weapons of the Great War • Between trench warfare and improved weaponry the loss of life was a staggering 9.7 MILLION people. (roughly 6 million civilians were killed) • At the time, more soldiers lost their lives in WWI then any other war in recorded history. Machine Gun • Machine guns were the trademark weapon of WWI. They had the fire power of 100 guns and needed multiple men to fire the weapon. Machine guns were one of the main reasons for the high death tolls in the trenches. Heavy Artillery • German Heavy Artillery, like Big Bertha, allowed them to bombard Paris from over 7 miles away with 16 inch shells. • There were also large canons and howitzers mounded on railroad cars to make them mobile. Chemical Weapons • Chlorine gas – A deadly poison that burned your throat and lungs as you slowly choked to death. The weather must be right for this gas or it would blow all over you. • Mustard gas – The most deadly weapon of WWI. It could be shot into the trenches and took about 5 weeks to kill the victims. Zeppelin • This was an interesting weapon… They were military blimps that dropped bombs on the enemy. • These did not last long because they were rather easy to shoot down. Tanks • This was the first war in which tanks were used. They moved rather slowly (4-5 mph) and lacked the punch that modern tanks have. Also, tanks were unable to get over trenches which limited their effectiveness. Planes • Planes were used for the first time in warfare in WWI too. The first planes were used for spying, transporting goods and dropping bombs. Later, planes were equipped with machines guns and started fighting while in the air. • “Dog-fighting” is the term used to describe WWI mid air battles. U-Boats • These were German submarines that terrorized Allied shipping boats and played a major role in influencing the United States entry into the war. The Western Front • The fighting on the Western Front was categorized by trench warfare and stalemates. • The sluggish fighting on the Western Front stopped the German’s Schieffen Plan, saved Paris and allowed the rest of the war to play out as it did. Western Front Cont. • Because of the slow fighting many battles were repeated on the same site. – 1st and 2nd Battle of the Marne – 1st, 2nd, and 3rd Battle of Ypers – 1st, 2nd, and 3rd Battle of Aisne Battle of the Marne 1914 • This battle stopped the German offensive outside Paris. • A French counter attack split the Germans in two and even the fight in the Western Front. • 600 Taxi cabs ushered reserve troops from Paris to the front lines. 2nd Battle of Ypers 1915 • A German offensive using poisonous gasses tried to break the French lines. • Although the French took heavy losses they held their lines and stopped the German offensive. Battle of Verdun 1916 • Germans attempted to “bleed the French white” by attacking a historic French city. • This battle only caused harm on both sides” – 550,000 French Casualties – 434,000 German Casualties The Battle of Ameins 1918 • This battle gave the French belief that they could defeat the Germans. • French Tanks finally broke through German lines and crushed their morale. The Eastern Front • While not nearly as popular at the Western Front, the Eastern Front played a major role in the war and in shaping the coming century. Different Type of War • Unlike the Western Front, the Eastern Front maintained traditional warfare categorized by strategy and maneuverability. Battle of Tannenberg 1914 • This battle was a disaster for the Russians. Miscommunication and poor planning led to a complete Russian defeat. Battle of Masurian Lakes 1914 • The second half of the Russian offensive that wasn’t destroyed at Tannenberg retreats after a rather thorough defeat. • These two battles almost completely destroyed Russia’s desire to mass an offensive against Germany. Russian Revolution • With all the military losses the Russian government falls apart leaving the door open for radicals to campaign for control of the country. Lenin and the Bolsheviks • After being exiled from Russia at the onset of war, Vladimir Lenin returned to Russia to lead the Socialist Bolshevik Party to prominence in Russia. • At the end of the war the German’s supported the Bolshevik “Red” Army against Russian “White” Army. Beginning of the End for Russia • This is the turning point in the History for Russia where they transform from a powerful, agricultural monarchy to a Communist, dictatorial power. The United States Enters the War! • We tried to stay neutral! Or did we? • What role did the U.S. play early on? – Neutrality, but we did trade with Allies and Central Powers. (mainly allies) What finally dragged us into the war? • Blockades – When one country tried to cut off shipping to another country. We were shipping to all of them. • The British Blockade of Germany – Britain, with its superior Navy blockaded all of Germany’s ports. No war materials were getting in. What finally dragged us into the war? • The Sussex Pledge – Germany promised to warn all ships before attacking with their subs on March 24, 1916. • The Zimmerman Note – Was an intercepted message between Germany and Mexico. Germany’s foreign secretary sent a note to Mexico asking them to attack the USA so we would leave Germany alone. What finally dragged us into the war? • Propaganda – Just like the Spanish-American propaganda helped to develop public sentiment in favor of joining the war. • The Russian Revolution – Russia was getting pounded in the war. Czar Nicholas was forced out of power and the new communist Bolshevik party pulled Russia out of W.W. I in March of 1917. What finally dragged us into the war? • The Germans use U-boats to blockade Britain – The Germans respond with unrestricted submarine warfare around Britain. • The Lusitania – A British passenger ship carrying both passengers and munitions (weapons) was sunk on May 7th, 1915 by a U-boat. Over 100 Americans died. The United States Officially Joins the War • April 6th, 1917 – The Germans sunk 3 more U.S. ships. On this date President Wilson signed Congress’ War resolution. The Senate voted 82 to 6 and the House voted 373 to 50, it’s unanimous… here we come Europe! • We were not ready – At the time we went to war, we had the 16th largest military in the world. Only 100,000 men in uniform! • Pershing to the Rescue? – At first, we only 14,000 troops and 3 billion dollars. General John Pershing, nicknamed “blackjack Pershing,” asked for a million men… and he got them! How did we get the troops? • The Selective Service Act - A draft ordered by Congress. 24 million men registered and 3 million won/lost the lottery and were drafted. American Forces in Europe • The American Expeditionary Forces – Our Fighting force in WW I. Millions head “over there.” – The Doughboys – The nickname of our soldiers in Europe. – Women – Over 25,000 served during WW I as nurses, drivers, clerks etc. – African Americans – Over 300,000 served but were not allowed to do much more than manual labor. “Harlem Hell Fighters” joined a French unit and fought bravely. Naval Convoys • The Amazing Convoys – How would we get our guys “over there” and past the U-boats? CONVOYS!!! We surround our large and slow ships with quick fighting boats. The Final Blows • The Doughboys in Europe – “We dig no trenches to fall back on.” The doughboys went on the offensive and had little interest in trenches. ATTACK!! Effects of the Great War on the American Homeland – A war touches everyone. • How do we pay for the WAR?!?! – Or any war? …….Taxes! – Liberty Bonds – you give the government money now and cash the bond later and collect interest. • Drumming up support with propaganda – Information used to sway public opinion in support of the war. – Just like “freedom fries” they had “police dogs” and Salisbury steak – High schools stop teaching German, police dogs were German shepherds, Salisbury steak was hamburger. • Americans learn how to do with less - We needed supplies for the war so Americans had to conserve supplies. – Rationing – Distributing goods to people in fixed amounts. You get a certain amount and no more. • The limits on our freedom – It became illegal to protest the war or the President. Freedom of Speech??? The Espionage Act • The Espionage Act – It was illegal to write negative stuff about the draft or war effort. Eugene Debs, a socialist and Presidential candidate, was jailed for protesting the draft. The Sedition Act • The Sedition Act – Made it illegal to discuss, say or do anything disloyal, abusive or profane about the American government. The Great War Ends • Armistice – is a cease-fire. The fighting stopped but no war ending treaty will be signed for about 7 months. • 1. 2. 3. 4. The Big Four carve out a Treaty – 1/19/19 Paris Peace Conference– The leaders of 27 countries met in Paris. The four main Playa’s were: Woodrow Wilson (United States) David Lloyd George (England) Georges Clemenceau (France) Vittorio Orlando (Italy) • Wilson’s three allies wanted to destroy Germany with the treaty. Why? • Notice who is missing from the Treaty signing? - Russia… they were busy having a Revolution Fourteen Points • Wilson’s Plan for Peace was called The Fourteen Points – He looked at what caused WW I and tried to stop it from repeating. What would it do? • Create a League of Nations – a world organization that would keep the peace. If one country broke the peace (A.K.A Austria/Hungary) the others would all gang up against them. What would it do? • Elimination of all secret alliances: Russia’s and Serbia’s alliance was not that well know. How might this help stop war? • World would DE-militarize - All nations including the U.S would scale back their standing army What would it do? • All nations would have freedom of the seas, which would end what? Blockades • All nations would have self-determination Have the power to make decisions about their own future What would it do? • “A harsh peace is no peace” – Woodrow Wilson • What does this mean? The Treaty of Versailles • June 28th, 1919 … the war is officially over! • Here is the result… • Germany lost land and colonies. France regained control of Alsace and Lorraine and Germany lost colonies in China, Africa and the Pacific. • Germany had to get rid of almost all its entire military. • Germany had to pay $33 Billion. • The war guilt clause – Blamed the war on Germany which made them responsible for paying Reparations to the Allies. • The Ottoman Empire split up into many Middle Eastern countries Ottoman Empire became Turkey • Austria/Hungary split and lost land too. Yugoslavia, Hungary, Austria, Czechoslovakia, and Poland were all created from Austria-Hungary. An attempt was made to create nations of similar ethnicities; however it was almost impossible to be perfect. This created new minorities. • The new European map was created and Germany, Italy and Austria are mighty MAD!!! • The world had seen something called • 10 million men died • What three monarchies ended? Germany, Austria-Hungary and Russia • Which Country became a new world economic power? United States • The German economy will not recover. German people live in fear of being attacked. The German people will look for someone else to blame the war on.