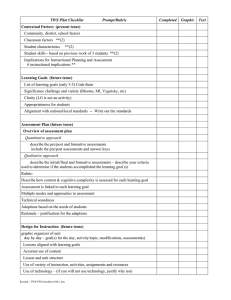
INTRODUCTION TO PORTFOLIO RUBRIC Trait 1
advertisement

INTRODUCTION TO PORTFOLIO RUBRIC Trait Introduction to Portfolio 1 Unacceptable Does not define the purpose of the portfolio. 2 3 Beginning Developing Vaguely defines the Adequately purpose of the defines the portfolio. purpose of the portfolio. 4 Capable Clearly and accurately delineates the purpose of the portfolio. 5 Accomplished Defines the purpose of the TWS portfolio in a professional and articulate manner. There is no description (or a very poor one) of the learning outcomes selected. There is a brief description of outcomes, but the number is less than required. There is an acceptable description of learning outcomes. There is a specific There is an exemplary description of the description of the learning outcomes. outcomes. There are no connections made between the TWS elements, NASAD teaching competencies, NAEA Standards, and the COE Outcomes. The connections made between the elements of the TWS, NASAD teaching competencies, NAEA Standards, and the COE Outcomes are minimal The connections made between the elements of the TWS, NASAD teaching competencies, NAEA Standards, and the COE Outcomes are satisfactory. The connections made between the elements of the TWS, NASAD teaching competencies, NAEA Standards, and the COE Outcomes are clear. The connections made between the elements of the TWS, NASAD teaching competencies, NAEA Standards, and the COE Outcomes are clear and focused. There is no description of the TWS portfolio organization. The description of the organization of the TWS portfolio is vague and not easily understood. The description of the TWS portfolio organization is acceptable. The description of the TWS portfolio organization is logical and in an easy to understand format. The description of the organization is excellent, well thought out, and logical. PHILOSOPHY STATEMENT RUBRIC Trait Philosophy Statement 1 Unacceptable Offers no evidence that the candidate has the K-12 art student as the focus. 2 Beginning Offers minimal evidence that the candidate has the K12 art student as the focus. 3 Developing Offers adequate evidence that the candidate has the K-12 student as the focus. 4 Capable Offers significant evidence that the candidate has the K12 art student as the focus. 5 Accomplished Offers superior evidence that the candidate has the K-12 art student as the focus. Offers no evidence that NASAD teaching competencies and the SPECTRUM model is the framework Offers minimal evidence that NASAD teaching competencies and the SPECTRUM model is the framework. Offers adequate evidence that NASAD teaching competencies and the SPECTRUM model is the framework. Offers significant evidence that NASAD teaching competencies and the SPECTRUM model is the framework. Offers superior evidence that NASAD teaching competencies and the SPECTRUM model is the framework. Offers no evidence that the candidate understands theory and research relevant to art education. Offers minimal evidence that the candidate understands theory and research relevant to art education. Offers adequate evidence that the candidate understands theory and research relevant to art education. Offers significant evidence that the candidate understands theory and research relevant to art education. Offers superior evidence that the candidate understands theory and research relevant to art education. Offers no evidence that the candidate has gained insight into teaching and learning through field experiences and coursework. Offers minimal evidence that the candidate has gained insight into teaching and learning through field experiences and coursework. Offers adequate evidence that the candidate has gained insight into teaching and learning through field experiences and coursework. Offers significant evidence that the candidate has gained insight into teaching and learning through field experiences and coursework. Offers superior evidence that the candidate has gained insight into teaching and learning through field experiences and coursework. Writing Mechanics and Organization Rubric Standard: TWS Portfolio is organized clearly, grammatically correct and written in standard English. Trait 1 Unacceptable 2 Beginning 3 Developing 4 Capable 5 Accomplished Writing Mechanics The use of standard written English is unsatisfactory at this level. More than 10 errors in punctuation, capitalization, subject-verb agreement may exist or excessive fragments or runons may detract from the overall content of the writing. The use of standard written English needs attention. More than 9 errors in punctuation, capitalization, subject-verb agreement may exist or 2 or more fragments or runons may exist. The use of standard written English is adequate with no more than 8 errors in punctuation, capitalization, subject-verb agreement may exist or 1 or more fragments or runons may exist. The use of standard written English is good with no more than 5 errors. The use of standard written English is outstanding with no more than 2 errors in punctuation, capitalization, subject-verb agreement may exist. No fragments or run-ons may exist Syntax Syntax and word choice may be unsatisfactory, or the writing may lack cohesion. Syntax and word choice may need attention, or the writing may lack cohesion. Syntax and word choice are satisfactory, and the writing is cohesive. Syntax and word choice are appropriate, and the writing is cohesive. Syntax and word choice are clearly superior, and the writing is very cohesive. Contextual Factors Rubric TWS Standard: The teacher uses information about the learning/teaching context and student individual differences to set learning goals, plan instruction and assess learning. Rating → 1 2 3 4 5 Score Indicator ↓ Unacceptable Beginning Developing Capable Accomplished Displays no Displays minimal, Displays some Displays a Displays and knowledge of the irrelevant, or biased knowledge of the comprehensive explains an incharacteristics of knowledge of the characteristics of understanding of depth the community, characteristics of the community, the characteristics understanding of Knowledge of school, and the community, school, and of the community, the characteristics Community, classroom. school, and classroom that may school, and of the community, School and classroom. affect learning. classroom that may school, and Classroom affect learning. classroom that may Factors affect learning with specific data, cited sources, and/or statistics. Displays no Displays minimal, Displays general Displays general Displays and knowledge of stereotypical, or knowledge of and specific explains in-depth student differences irrelevant student differences knowledge of knowledge of Knowledge of (e.g., development, knowledge of (e.g., development, student differences student differences Characteristics interests, culture, student differences interests, culture, (e.g., development, (e.g., development, of Students abilities/disabilities). (e.g., development, abilities/disabilities). interests, culture, interests, culture, interests, culture, abilities/disabilities). abilities/disabilities). abilities/disabilities). Fails to Demonstrates Demonstrates Articulates an Articulates general demonstrate general general understanding of and specific understanding of a understanding of a understanding of a varied learning understanding of Knowledge of variety of variety of variety of modalities and varied learning Students’ approaches to approaches to approaches to multiple modalities and Varied learning among learning among learning among intelligences. multiple Approaches to students, e.g., students and may students and can intelligences. Learning multiple know one or two distinguish between intelligences and/or learning modalities multiple modalities. learning modalities. but not a variety. Knowledge of Students’ Skills and Prior Learning Implications for Instructional Planning and Assessment Displays no knowledge of students’ skills and previous learning and does not indicate either is important. Identifies the value of understanding students’ skills and previous learning but demonstrates its importance for the whole class only. Identifies the value of understanding students’ skills and previous learning for the group and individuals. Displays knowledge of understanding students’ skills and previous learning, including special needs students. Does not provide implications for instruction and assessment based on student individual differences and community, school, and classroom characteristics or provides inappropriate implications. Provides minimal implications for instruction and assessment based on student individual differences and community, school, and classroom characteristics or provides inappropriate implications. Provides general implications for instruction and assessment based on student individual differences and community, school, or classroom characteristics. Provides specific implications for instruction and assessment based on student individual differences and community, school, and classroom characteristics. Articulates an indepth understanding of students’ skills and previous learning for the group and individuals including special needs students. Provides specific implications and analyzes decisions for instruction and assessment based on student individual differences (ELL and inclusion students) and community, school, and classroom characteristics. Learning Goals Rubric TWS Standard: The teacher sets significant, challenging, varied and appropriate learning goals. Rating → Indicator ↓ 1 Unacceptable Goals are not in evidence. 2 Beginning Goals reflect only one type or level of learning 3 Developing Goals reflect several types or levels of learning but lack significance or challenge 4 Capable Goals reflect several types or levels of learning and are significant and challenging. Goals are vague or not in evidence. Goals are not stated clearly and are activities rather than learning outcomes. Goals are not developmentally appropriate; nor address prerequisite knowledge, skills, experiences, or other student needs. Some of the goals are clearly stated as learning outcomes. Some goals are developmentally appropriate and address some prerequisite knowledge, skills, experiences, and other student needs. Goals are not aligned with NAEA, state or COE standards. Some goals are aligned with NAEA, state or COE standards. Most of the goals are clearly stated as learning outcomes Most goals are developmentally appropriate; addresses prerequisite knowledge, skills, experiences and other student needs are considered. Most of the goals are explicitly aligned with NAEA, state and COE standards. Significance, Challenge and Variety Clarity Appropriatenes s for Students Alignment with National, State or Local Standards Goals presented are inappropriate for the class or set unrealistic expectations for students. Fails to develop goals aligned with NAEA, state and COE standards 5 Accomplished Goals are significant and challenge thought and expectations including three or more levels and types. Goals are clearly stated in behavioral terms. Goals demonstrate realistic expectations for all students in addition to providing for students’ critical thinking and reflection. Goals are aligned with NAEA, state, COE standards and are articulated through the lesson presentations. Alignments are explained. Sco re Assessment Plan Rubric TWS Standard: The teacher sets significant, challenging, varied and appropriate learning goals. Rating → Indicator ↓ 1 Unacceptable Minimal plans for pre and post assessments Alignment are provided; with Learning assessments do Goals and not measure Instruction learning goals. 2 Beginning Content and methods of assessment lack congruence with learning goals or lack cognitive complexity. The assessments contain no Clarity of criteria for Criteria and measuring Standards for student Performance performance relative to the learning goals. The assessment plan fails to demonstrate evidence of student Multiple assessment Modes and other than after Approaches instructions. Limited knowledge of formal/informal assessments Assessments contain poorly stated criteria for measuring student performance leading to student confusion. The assessment plan includes only one assessment mode and does not assess students before, during, and after instruction. 3 Developing Some of the learning goals are assess through the assessment plan, but many are not congruent with learning goals in content and cognitive complexity. Assessment criteria have been developed, but they are not clear or are not explicitly linked to the learning goals. 4 Capable Each of the learning goals is assessed through the assessment plan; assessments are congruent with the learning goals in content and cognitive complexity. 5 Accomplished All learning goals are assessed by the assessment plan, and provide students with constructive feedback on their learning. Assessment criteria are clear and are explicitly linked to the learning goals. Assessment criteria are linked to learning goals; accurately documenting student learning. The assessment plan includes multiple modes but all are product based (studio) or pencil/paper based (i.e., they are not performance assessments) and/or do not require the integration of knowledge, skills and critical thinking. The assessment plan includes multiple assessment modes (including studio performance, artistic process, written reports, research projects, discussion skills, finalized studio work, etc.) and assesses student performance throughout the instructional sequence. The assessment plan uses formal/informal assessments and student’s selfassessments to assess student performance and effectiveness of the instructional sequence. Score Technical Soundness Adaptations Based on the Individual Needs of Students Assessments are not designed to measure lessons goals and objectives; scoring procedures are inaccurate. Assessments are not valid; scoring procedures are inaccurate; items or prompts are poorly written; directions and procedures are confusing to students. Teacher does not address or link assessments to identified contextual factors. Teacher does not adapt assessments to meet the individual needs of students or these assessments are inappropriate. Assessments appear to have some validity. Some scoring procedures are explained; some items or prompts are clearly written; some directions and procedures are clear to students Teacher makes adaptations to assessments that are appropriate to meet the individual needs of some students. Assessments appear to be valid; scoring procedures are explained; most items or prompts are clearly written; directions, demonstrations, and studio procedures are clear to students. Assessments appear to be valid and clearly written. Assessments data used to document students’ strengths as well as opportunities for learning. Teacher makes adaptations to assessments that are appropriate to meet the individual needs of most students. Teacher’s adaptations of assessments for all students needs to be met. Adaptations are creative and show evidence of outstanding problem-solving skills by teacher candidate. Design for Instruction Rubric TWS Standard: The teacher designs instruction for specific learning goals, student characteristics and needs, and learning contexts. Rating → Indicator ↓ Alignment with Learning Goals Accurate Representation of Content Lesson and Unit Structure 1 Unacceptable No lesson is linked to learning goal. No learning activities are aligned to learning goals. Teacher does not demonstrate purpose and relevancy of content. The lessons within the unit do not demonstrate knowledge of how content is created and developed. 2 Beginning Few lessons are explicitly linked to learning goals. Few learning activities, assignments and resources are aligned with learning goals. Not all learning goals are covered in the design. Teacher’s use of content appears to contain numerous inaccuracies. Content seems to be viewed more as isolated skills and facts rather than as part of a larger conceptual structure. The lessons within the unit are not logically organized (e.g., sequenced). 3 Developing Most lessons are explicitly linked to learning goals. Most learning activities, assignments and resources are aligned with learning goals. Most learning goals are covered in the design. Teacher’s use of content appears to be mostly accurate. Shows some awareness of the big ideas or structure of the discipline. The lessons within the unit have some logical organization and appear to be somewhat useful in moving students toward achieving the learning goals. 4 Capable All lessons are explicitly linked to learning goals. All learning activities, assignments and resources are aligned with learning goals. All learning goals are covered in the design. Teacher’s use of content appears to be accurate. Focus of the content is congruent with the big ideas or structure of the discipline. 5 Accomplished All lessons are explicitly linked to learning goals, demonstrating critical thinking and reflection in activities and assignments. Most lessons within the unit are logically organized and appear to be useful in moving students toward achieving the learning goals. All lessons within the unit demonstrate how knowledge of content is created and organized and integrates knowledge from other fields of content. Teacher provides cross-content approach to student learning, stressing depth and breadth of content. Score Use of a Variety of Instruction, Activities, Assignments and Resources Use of Contextual Information and Data to Select Appropriate and Relevant Activities, Assignments and Resources A single, instructional modality is used with textbook as only reference. Little variety of instruction, activities, assignments, and resources. Heavy reliance on textbook or single resource (e.g., work sheets). Some variety in instruction, activities, assignments, or resources but with limited contribution to learning. Instruction has not been based upon knowledge of subject matter, students or preassessment data. Instruction has been designed with very limited reference to contextual factors and pre-assessment data. Activities and assignments do not appear productive and appropriate for each student. Technology is inappropriately used and inappropriate rationale is provided. Some instruction has been designed with reference to contextual factors and preassessment data. Some activities and assignments appear productive and appropriate for each student. Teacher uses technology but it does not make a significant contribution to teaching and learning or teacher provides limited rationale for not using technology. Teacher does not use technology during instruction. Use of Technology Significant variety across instruction, activities, assignments, and/or resources. This variety makes a clear contribution to learning. Most instruction has been designed with reference to contextual factors and pre-assessment data. Most activities and assignments appear productive and appropriate for each student. Teacher integrates appropriate technology that makes a significant contribution to teaching and learning or provides a strong rationale for not using technology. Instructional strategic assignments are varied to accommodate individual learners and to achieve lesson goals. All instruction addresses the diverse needs of individual students and contextual factors of community, school and class. Teacher integrates a variety of media and technology into instruction and relates both directly to lesson goals. Instructional Decision-Making Rubric TWS Standard: The teacher uses on-going analysis of student learning to make instructional decisions. Rating → Indicator ↓ Sound Professional Practice Modifications Based on Analysis of Student Learning Congruence Between Modifications and Learning Goals 1 Unacceptable Instructional decisions are inappropriate for age of student, content, and community. 2 Beginning Many instructional decisions are inappropriate and not pedagogically sound. 3 Developing Instructional decisions are mostly appropriate, but some decisions are not pedagogically sound. 4 Capable Most instructional decisions are pedagogically sound (i.e., they are likely to lead to student learning). Teacher treats class as “one plan fits all” with no modifications. Fails to demonstrate evidence of instructional modifications. Limited modifications of the instructional plan have been made, to accommodate individual learners. Some modifications of the instructional plan are made to address individual student needs, but these are not based on the analysis of student learning, best practice, or contextual factors. Inappropriate modification in instruction. Modifications in instruction lack congruence with learning goals. Modifications in instruction are somewhat congruent with learning goals. Appropriate modifications of the instructional plan are made to address individual student needs. These modifications are informed by the analysis of student learning/performance, best practice, or contextual factors. Modifications in instruction are congruent with learning goals. 5 Accomplished Most instructional decisions are pedagogically sound and build on concepts and skills previously learned. Appropriate modifications of the plan are made to individualize instruction. Rational to improve student progress is provided. Modifications in instruction are congruent with learning goals and cites current research as the rationale for the modifications. Score Analysis of Student Learning Rubric TWS Standard: The teacher uses assessment data to profile student learning and communicate information about student progress and achievement. Rating → Indicator ↓ 1 Unacceptable Presentation does not include data. 2 Beginning Presentation is not clear and accurate; it does not accurately reflect the data. 3 Developing Presentation is understandable and contains few errors. 4 Capable Presentation is easy to understand and contains no errors of presentation. Neither analysis of student learning nor visual representation is aligned with learning goals. Analysis of student learning is aligned with learning goals. Visual representations do not include whole class, sub-groups or individual students. Analysis is fully aligned with learning goals and provides a comprehensive profile of student learning for the whole class, subgroups, and two individuals. Interpretation is unsupported by data Interpretation is inaccurate, and conclusions are missing. Analysis of student learning is general with learning goals and/or fails to provide a comprehensive profile of student learning relative to the goals for the whole class, subgroups, and two individuals. Interpretation is technically accurate, but conclusions are missing or not fully supported by data. Clarity and accuracy of Presentation Alignment with Learning Goals Interpretation of Data Interpretation is meaningful, and appropriate conclusions are drawn from the data. 5 Accomplished Contains no errors of presentation. Presentation is communicated with the use of technology and media. Analysis is thorough and complete, recognizing student progress in developing content proficiency. Visual and narrative summaries demonstrate the extent of student progress. Interpretation is comprehensive. Appropriate conclusions are drawn from the data. Candidate has detailed the assessment and evaluation of student gains. Score Analysis is weak and fails to provide subgroup achievement Evidence of Impact on Student Learning Analysis of student learning fails to include evidence of impact on student learning in terms of numbers of students who achieved and made progress toward learning goals. No remediation is provided. Analysis of student learning includes incomplete evidence of the impact on student learning in terms of numbers of students who achieved and made progress toward learning goals. Limited remediation is provided. Analysis of student learning includes evidence of the impact on student learning in terms of number of students who achieved and made progress toward each learning goal. Remediation is specific. A thorough analysis of the learning gains of all students and subgroups is presented. Remediation is specific. Reflection and Self-Evaluation Rubric TWS Standard: The teacher analyzes the relationship between his or her instruction and student learning in order to improve teaching practice. Rating → 1 2 3 4 5 Score Indicator ↓ Unacceptable Beginning Developing Capable Accomplished No evidence or Provides one Provides evidence Uses evidence to Uses evidence to reasons provided possible reason as but simplistic, support conclusions support more than to support evidence to support superficial reasons drawn in “Analysis four conclusions conclusions conclusions drawn are given or of Student drawn in “Analysis of Interpretation drawn in in Analysis of hypotheses to Learning” section. Student Learning” of Student “Analysis of Student Learning. support conclusions section. Explores Learning Student Learning” drawn in “Analysis of multiple hypotheses section. Student Learning” for why some section. students did and others did not meet learning goals. Provides no Rationale for Identifies successful Identifies Reflects on own rationale for why activities or and unsuccessful successful and performance as a some activities or assessments activities or unsuccessful teacher focusing on Insights on assessments presented in assessments and activities and the impact of the Effective were more confusing manner; superficially explores assessments and experience on Instruction successful than insights limited to reasons for their provides plausible student learning. and others. knowledge-based success or lack reasons (based on Current research Assessment instruction and use thereof (no use of theory or research) findings are of formal theory or research). for their success or incorporated as assessments. lack thereof. supportive documentation. Alignment Among Goals, Instruction and Assessment Implications for Future Teaching Does not connect learning goals, instruction, and assessment results in the discussion of student learning and effective instruction and/or the connections are irrelevant or inaccurate. Connections among learning goals, instructions and assessments are irrelevant or inaccurate. Connects learning goals, instructions, and assessment results in the discussion of student learning and effective instruction, but misunderstandings or conceptual gaps are present. Logically connects learning goals, instruction, and assessment results in the discussion of student learning and effective instruction. Connects learning goals, instruction and assessment results in the discussion of student learning and effective instruction. Current research findings are incorporated as supportive documentation. Provides no ideas or inappropriate ideas for redesigning learning goals, instruction, and assessment. Provides limited ideas for redesigning learning goals, instruction, and assessment. Rationale is inadequate; or absent. Provides goals that are not related to the insights and experiences described in this section. Provides ideas for redesigning learning goals, instruction, and assessment but offers no rationale for why these changes would improve student learning. Provides ideas for redesigning learning goals, instruction, and assessment and explains why these modifications would improve student learning. Presents professional learning goals that emerge from the insights and experiences descried in this section. Provides a repertoire of strategies, offering specific alternative actions complete with probable successes for student learning. Provides no professional learning goals. Implications for Professional Development Presents professional learning goals that are not strongly related to the insights and experiences described in this section and/or provides a vague plan for meeting the goals. Presents four or more professional learning goals that clearly emerge from the insights and experiences described in this section. Describes at least two specific steps to meet these goals