Determining Mass Mass is a direct measurement of 1
advertisement

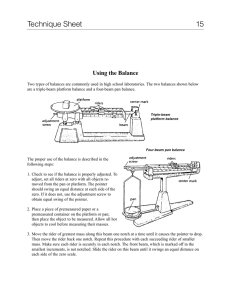
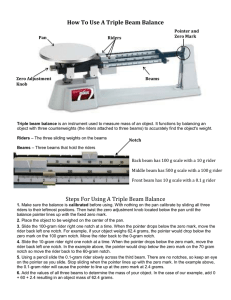
Determining Mass Mass is a direct measurement of the amount of matter in a sample. 1 Multi Beam Balance 2 Here are the steps for using a multi-beam balance properly: • • • Adjust all riders, so that each reads zero. Then check to make sure that the pointer, or beam, swings to "zero" on the center mark. If the pointer does not read correctly, then use the "adjustment screw" to obtain the zero reading. 3 Using a Multi-Beam Balance • Warning: do not place any chemicals onto the balance pan or platform. – All chemicals, solutions, or compounds should be placed into a beaker or other container first • After you place the sample onto the pan or platform, move the largest rider across the beam until the pointer drops. – Then move this rider back once. • Follow this same procedure for the rest of the smaller riders, until the pointer swings to the zero mark. • To record the mass, add the masses shown by each rider. (Note: masses are in grams) 4 Answer: 165.32g 5 Practice Time 6 Double Pan Balance – Need known masses to determine the mass 7 Kind You Will Use Later 8 Electronic Balance Accurate to .01 grams Usually used to weigh solids Have 2 different kinds 9 Analytical Balance Accurate to 0.001 grams 10 Using a Digital Balance 1. Sometimes when nothing is on the balance pan, the mass display will show a non-zero reading. 2. Taring is used to set the mass display to zero. 3. Once the balance has been tared, the mass of any object set on the balance pan will be displayed on the digital readout. 11 Accuracy versus Precision How “Good” is a Mass Measurement 12 Accuracy = of a measurement is how close that measurement is to the true or “exact” value EX: Standard weight = 5.00g 4.98g more accurate than 5.12 g 13 Precision • Precision = making reproducible or repetitive measurements of the same quantity • How fine the divisions are • There will always be some uncertainty because of the limits in the accuracy of your instruments 14 Absolute Value = considered the amount of mass difference between zero and the determined mass - are determining how for “off” the standard the mass is - recorded as a positive answer even if the value resulted in a negative number 15 Value of Error in Minting Pennies •How close the individual volumes are to each other •Calculate as follows % error = calculated volume - actual volume actual volume •Good accuracy is indicated by a relatively low error value. 16 Example: % error in minting pennies = average volume - actual volume actual volume % error in minting pennies = 1.2g - 1.4g 1.4g = 0.14 X 100% = 14 % So there is a 14% error in minting of these particular pennies 17 Determining the % Accuracy of a Balance • Going to calculate the % accuracy of the balance you are using % Accuracy = experimental value X 100% reference or standard value The closer the experimental value is to the reverence or standard value, the greater the accuracy. 18