River Civilizations
advertisement

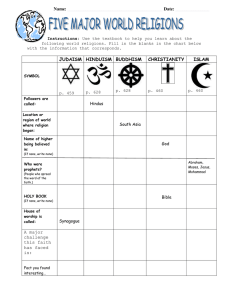
River Civilizations Questions that need to be answered. (essential questions) Why would people move around rivers? What did they consider technology? Why do some civilizations fail? What would have happened if the Chinese didn’t invent things? What made religion spread? Why did people shape their lives around religion? geography the study of the earth and its inhabitants physical geography had a major impact on the world’s early settlements prehistory time period before writing important developments that led to the forming of small villages: agriculture domestication of animals civilization a complex culture with five characteristics: advanced cities advanced technology complex institutions government organized religion education record keeping specialized workers Mesopotamia land near the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers (mostly modern-day Iraq) includes the land of Sumer site of the world’s 1st civilization invented writing (cuneiform) empire a political unit in which a number of different peoples or nations are controlled by a single nation Hammurabi (c. 1810 - c. 1750 BC) king of Babylon (Mesopotamian city) developed one of the world’s first law codes Eye for an eye Phoenicia (1500-500 BC) located along the Mediterranean coast (modern-day Lebanon) expert sailors developed a large trading network developed the alphabet Egypt civilization that developed along the Nile River in North Africa Used symbols to write- Hieroglyphics ruler was a god-king called a pharaoh some early pharaohs were buried in giant pyramids Egyptian civilization lasted about 3000 Indus River Valley (India) India’s 1st civilization developed along the Indus and Ganges Rivers Has grown to over 1 billion people China China’s 1st civilization developed along the Huang (Yellow) River Chinese government became dominated by dynasties Has grown to over 1 billion people dynasty a series of rulers from a single family Qin Dynasty unified Chinese culture currency roads measurement language The people weren't treated well overtaxed Han Dynasty China’s longest dynasty created a highly structured society Han Dynasty Also gave us: Iron technology The Plow Wheelbarrow Seismograph Compass ships rudder Hot air balloon Embroidery and the… Silk Road ancient interconnected trade routes across and around Asia trade along the Silk Road was a major factor in the development of most of the great ancient civilizations of Asia, Africa, and Europe Cultural diffusion-sharing between cultures World Religions Monotheism belief in one god Most religions today believe this way Polytheism belief in many gods Hinduism India’s major religion no known founder main beliefs: polytheism- many gods caste system - hereditary social system karma - action and reaction reincarnation - literally "to be made flesh again" Vedas Hinduism’s oldest holy texts Siddhartha Gautama - Buddha Indian born in warrior caste attained enlightenment & given the title of Buddha founder of Buddhism religion that broke away from Hinduism main beliefs: polytheism- many gods reincarnation- come back as something else living the Four Noble Truths - how to obtain happiness and enlightenment Eightfold Path - instrument of discovery Middle Way - practice of non-extremism nirvana - state of perfect peace Sutras holy texts in Buddhism Confucius (Confucianism) Chinese philosopher ethical system based on the teachings of Confucius main beliefs: social and civic responsibility Five Relationships Analects text that contains the words and acts of Confucius religion of the Jews founded by Abraham main beliefs: monotheism (world’s 1st) Jews are God’s chosen people Ten Commandments a list of religious and moral guidelines foundation of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam Abraham Middle Eastern prophet founder of Judaism Jerusalem Judaism’s, Christianity, and Islam’s holy city Torah Judaism’s holy book written by Moses Judaism Christianity Jesus- founder of Christianity executed by the Jewish leadership for creating the split between Christianity and Judaism religion that broke away from Judaism main beliefs: Ten Commandments monotheism Jesus is the son of God resurrection of the dead Bible Christianity’s holy book made up of 2 parts: Old Testament (Jewish text) New Testament (lives and teachings of Jesus and his followers) Church of the Holy Sepulcher Jerusalem Paul Jew who converted to Christianity Roman citizen brought Christianity to Europe through missionary travels ( missionary) Muhammad (Islam) Arab warrior and prophet founder of Islam religion that began in modern-day Saudi Arabia followers of Islam are called Muslims main beliefs: monotheism- one god Muhammad is God’s greatest and last prophet believe that Jesus was a prophet, not as the son of God) Five Pillars Qur’an Islam’s holy book contains the teachings of Muhammad Mecca Muhammad’s birthplace Islam’s holiest city Ka’bah- temple of Abraham Big Ideas The environment caused the early civilizations to settle around rivers. The Chinese were inventive and were responsible for major technological advancements that influenced civilizations other than their own. Each world religion had specific foundations and affected different areas of the world.