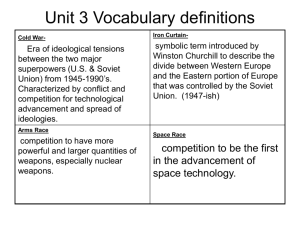
Cold War Conflicts Essential Question: Why didn’t the Cold War cause
advertisement

Topic: Cold War Conflicts Essential Question: Why didn’t the Cold War cause World War III? Chinese Revolution Communists vs. Nationalists Communist leader: Mao Tse-tung (Zedong) Communists vs. Nationalists Communist leader: Mao Tse-tung (Zedong) Communists defeated Nationalists (1949) People’s Republic of China Communists defeated Nationalists (1949) People’s Republic of China Nationalists fled to Taiwan Mao was dictator until his death (1976) Nationalists fled to Taiwan Mao was dictator until his death (1976) United Nations Security Council 5 Permanent members United States, Britain, France, Soviet Union, China 10 current non-permanent: Malaysia Angola New Zealand Chad Nigeria Chile Spain Jordan Venezuela Lithuania 5 Permanent members United States, Britain, France, Soviet Union, China Veto Powers United States, Britain, France, Soviet Union, China Veto Powers Korea Divided at the 38th parallel North Korea = communist South Korea = capitalist North Korea = communist South Korea = capitalist Korean War (1950-1953) North Korea invaded South Korea The UN (United Nations) declared a Police Action North Korea invaded South Korea The UN (United Nations) declared a Police Action The US led UN forces Motivated by containment and the domino theory The US led UN forces Motivated by containment and the domino theory Commander of UN forces MacArthur Commander of UN forces MacArthur China entered the war and helped North Korea MacArthur wanted to use atomic bombs China entered the war and helped North Korea MacArthur wanted to use atomic bombs Truman refused his request MacArthur publicly criticized Truman Truman fired MacArthur Matthew Ridgway MacArthur publicly criticized Truman Truman fired MacArthur Eisenhower was elected President in 1952 Negotiated a peace settlement Eisenhower was elected President in 1952 Negotiated a peace settlement Border almost identical to before the war (38th parallel) South Korea – North Korea Negotiated a peace settlement Border almost identical to before the war (38th parallel) Korean War Map (1950-53) Korean War Map (1950-53) Negotiated a peace settlement Border almost identical to before the war (38th parallel) Discuss Chinese Revolution UN Security Council Korean War Write a sentence explaining how the Korean War ended. Negotiated a peace settlement Border almost identical to before the war (38th parallel) Berlin Wall Built in 1961 by the Soviets Berlin Wall Built in 1961 by the Soviets Separated capitalist West Berlin from communist East Germany Symbol of the divide between East (communist) and West (capitalist) in the Cold War “Death Strip” Separated capitalist West Berlin from communist East Germany Symbol of the divide between East (communist) and West (capitalist) in the Cold War Cuba Fidel Castro Cuba Fidel Castro Took control of Cuba in 1959 Established a communist government Seized American-owned property and businesses in Cuba Established a communist government Seized American-owned property and businesses in Cuba Dictator until 2008 Seized American-owned property and businesses in Cuba Dictator until 2008 U.S. trade embargo against Cuba began in 1960 Dictator until 2008 U.S. trade embargo against Cuba began in 1960 Bay of Pigs Invasion (1961) Failed attempt to overthrow Castro’s communist regime Bay of Pigs Invasion (1961) Failed attempt to overthrow Castro’s communist regime Cuban Missile Crisis (October 1962) Photographs from American U-2 spy planes showed Soviet nuclear missiles being installed in Cuba 90 miles from Florida Photographs from American U-2 spy planes showed Soviet nuclear missiles being installed in Cuba 90 miles from Florida Kennedy’s reaction: Naval blockade Secret negotiations with Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev Naval blockade Secret negotiations with Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev End to the crisis: Soviets agreed to pull missiles out of Cuba US agreed not to invade Cuba and to pull missiles out of Turkey Prevented World War III US agreed not to invade Cuba and to pull missiles out of Turkey Prevented World War III Many Cuban immigrants in the US (mostly Florida) Prevented World War III Many Cuban immigrants in the US (mostly Florida) Discuss Berlin Wall Fidel Castro Bay of Pigs Cuban Missile Crisis Write a sentence explaining why the Cuban Missile Crisis is important. Prevented World War III Many Cuban immigrants in the US (mostly Florida) Vietnam War (1965-73) Vietnam War (1965-73) North Vietnam = communist Led by Ho Chi Minh South Vietnam = capitalist Ngo Dinh Diem Led by Ho Chi Minh South Vietnam = capitalist US supported South Vietnam because of Containment and the Domino Theory South Vietnam = capitalist US supported South Vietnam because of Containment and the Domino Theory Gulf of Tonkin Resolution (1964) gave President Lyndon Johnson (LBJ) authority to send troops US supported South Vietnam because of Containment and the Domino Theory Gulf of Tonkin Resolution (1964) gave President Lyndon Johnson (LBJ) authority to send troops Communists used guerilla warfare Gulf of Tonkin Resolution (1964) gave President Lyndon Johnson (LBJ) authority to send troops Communists used guerilla warfare Americans were young and inexperienced Communists used guerilla warfare Americans were young and inexperienced Tet Offensive (1968) Surprise attack by the communists during the New Year celebration Tet Offensive (1968) Surprise attack by the communists during the New Year celebration Communists proved that US was not winning the war Americans began to mistrust the government’s claims about the war Communists proved that US was not winning the war Americans began to mistrust the government’s claims about the war Home Front Television helped turn public opinion against the war “If I’ve lost Cronkite, I’ve lost the war.” Walter Cronkite Home Front Television helped turn public opinion against the war Many protested the war and the draft Television helped turn public opinion against the war Many protested the war and the draft Kent State University (1970) 4 students were killed during a protest Kent State University (1970) 4 students were killed during a protest 26th Amendment Voting age changed from 21 to 18 26th Amendment Voting age changed from 21 to 18 Paris Peace Accords (1973) The US agreed to withdraw all troops from Vietnam Paris Peace Accords (1973) The US agreed to withdraw all troops from Vietnam In 1975 North Vietnam invaded South Vietnam All of Vietnam became a single, communist nation Ho Chi Minh died in 1969 Ton Duc Thang In 1975 North Vietnam invaded South Vietnam All of Vietnam became a single, communist nation Many Vietnamese fled the country and came to the US Tet Celebration in Orange County, CA All of Vietnam became a single, communist nation Many Vietnamese fled the country and came to the US President Bill Clinton normalized US relations with Vietnam in 1995 Many Vietnamese fled the country and came to the US President Bill Clinton normalized US relations with Vietnam in 1995 Discuss North Vietnam South Vietnam Gulf of Tonkin Resolution Tet Offensive Home Front Paris Peace Accords Write a sentence explaining how the Vietnam War ended. Many Vietnamese fled the country and came to the US President Bill Clinton normalized US relations with Vietnam in 1995 The Cold War Ends Ronald Reagan The Cold War Ends Ronald Reagan The Cold War Ends Ronald Reagan Supervised the most expensive arms buildup in history ($2 trillion) Ronald Reagan Supervised the most expensive arms buildup in history ($2 trillion) The Soviet economy was unable to keep up with Reagan’s arms race Supervised the most expensive arms buildup in history ($2 trillion) The Soviet economy was unable to keep up with Reagan’s arms race Speech in Berlin (1987) “Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall!” Speech in Berlin (1987) “Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall!” Mikhail Gorbachev “Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall!” Mikhail Gorbachev Last leader of the Soviet Union (1985-1991) Mikhail Gorbachev Last leader of the Soviet Union (1985-1991) Glasnost and Perestroika Reforms that brought about the [unintended] fall of communism and the end to the Cold War Glasnost and Perestroika Reforms that brought about the [unintended] fall of communism and the end to the Cold War Berlin Wall Reforms that brought about the [unintended] fall of communism and the end to the Cold War Berlin Wall Anti-communist protests in October 1989 in East Germany Berlin Wall Anti-communist protests in October 1989 in East Germany Wall opened and dismantling began on November 9 Anti-communist protests in October 1989 in East Germany Wall opened and dismantling began on November 9 Symbolic end to the Cold War Wall opened and dismantling began on November 9 Symbolic end to the Cold War Germany reunified into a single nation in October 1990 Helmut Kohl Symbolic end to the Cold War Germany reunified into a single nation in October 1990 Fall of the Soviet Union (1991) Germany reunified into a single nation in October 1990 Fall of the Soviet Union (1991) Broken up into 15 independent nations Fall of the Soviet Union (1991) Broken up into 15 independent nations Official end of the Cold War Broken up into 15 independent nations Official end of the Cold War Discuss Ronald Reagan Mikhail Gorbachev Fall of the Berlin Wall Fall of the Soviet Union Write a sentence explaining how Reagan and Gorbachev helped end the Cold War.