Packet 14: Circulation and Respiration 14-1
advertisement

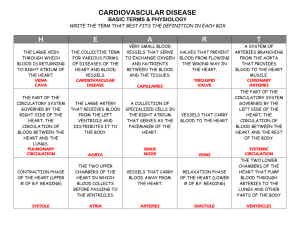
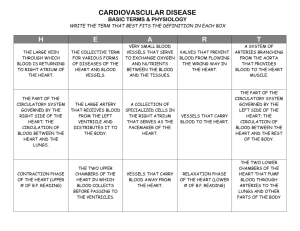
Packet 14: Circulation and Respiration 14-1 Aim: How does the structure of the heart relate to its function? (A) FUNCTIONS OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM The cardiovascular system __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ It functions like a network of highways—connects the muscles and organs of the body through ____________________ that transport blood The cardiovascular system transports different kinds of molecules: 1. _________________________from digested food are transported to all cells in the body 2. _____________________________ from the lungs 3. metabolic wastes, ________________________________ 4. hormones, ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ 5. distributes heat to maintain a ____________________________ ________________________________________________ humans and other vertebrates have closed circulatory systems—this means that ___________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ the cardiovascular system consists of : 1. ______________________________ 2. ________________________________________________________ 3. _______________________________ (B) THE HEART the heart is made up of __________________________________ which function to pump blood the heart has two separate circulatory loops 1. Pulmonary Circulation: right side—pumps __________________________________________ (deoxygenated) blood through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs _________________________________________________________ _______________________________________--the oxygenated blood is then returned to the left side of the heart 2. Systemic Circulation: left side—pumps ___________________________________________ (oxygenated) blood through the arteries to the tissues of the body—oxygen poor blood is then returned to the right side of the heart through veins (C) CIRCULATION OF BLOOD The heart has a wall that divides the right and left sides of the heart The top of the heart is made up of the right and left _____________________ Atria: (singular—atrium) :_____________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Below the atria are the ventricles Ventricles: ___________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ The heart contains a series of valves that prevent blood from moving backward The path of blood through the heart is as follows: 1. _____________________________________: two large veins— superior (above) and inferior (below)—that collect all of the oxygen-poor blood from the body 2. the vena cavae empty blood directly into the _______________________________________ of the heart 3. the blood from the right atrium goes to the _______________________________ 4. as the right ventricle contracts, it sends blood into the __________________________________________________ 5. the pulmonary arteries carry the blood to the ___________________________________________________where oxygen is picked up and carbon dioxide is dropped off 6. the freshly oxygenated blood returns from the lungs to the left side of the heart through the _________________________________, which empty blood directly into the ______________________________________. 7. From the left atrium, the blood is pumped into the ____________________________________________ 8. The left ventricle then forcefully contracts sending the blood to the _____________________________________ 9. The aorta sends the blood to the ___________________________ ________________________________________________________ (D) HEART CONTRACTION Contraction of the heart is initiated by a small cluster of cardiac muscle cells called the sinoatrial node which is embedded in the upper wall of the right atrium These cells acts as the pacemaker of the heart They fire an electrical stimulus in a regular rhythm that is followed by a contraction On average heart contractions occur at a rate of about 72 times per minute—when you sleep it decreases, when you exercise it increases The SA node is controlled by two sets of nerves and is influenced by hormones, temperature and exercise