The Monroe Doctrine isolationism.
advertisement

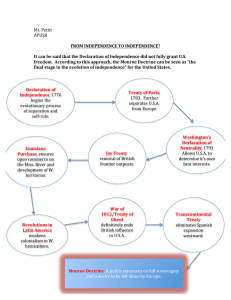
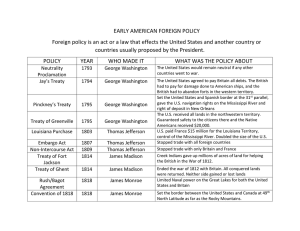
The Monroe Doctrine Attempts were made to better relations with Great Britain but continue political isolationism. Post War of 1812 America: 1. Treaty of Ghent a. British recognize American independence and stop impressment. 2. Rush-Bagot Treaty (1817) (U.S. + G.B.) a. Limited the number of naval vessels on the Great Lakes b. disarmaments on U.S. and British Canadian border. 3. Convention of 1818 a. set official boundary (US/Canada) at the 49th parallel b. est. a demilitarized border c. U.S. gained rights to settle in the Oregon country. 4. Adam – Onis Treaty (1819) (U.S. + Spain) Although President Adams did not authorize Andrew Jacksons invasion of Spanish East Florida. Adams did not stop it. Spain was weak and the U.S. knew it a. U.S. gets East Florida and the ability to claim West Florida b. U.S. gives up claim to Spanish Texas c. U.S. pays $5 million owed by Spain to U.S. citizens for damages. d. settled border dispute in Pacific NORHWEST to the Gulf of Mexico. *U.S. become a transcontinental Power. 5. Monroe Doctrine (1823) Latin American revolutions 1810 Father Hidalgo in Mexico and wins independence later in 1821. Simon Bolivar wins independence for Venezuela, Colombia, Panama, Bolivia, and Peru. San Martin wins it for Chile and Peru. By 1824 most revolutions complete even Brazil from Portugal in 1822. Causes: 1. Spain asks for help from the Quadruple Alliance (formed after the Napoleonic Wars), France, Austria, Russia, and Prussia. 2. U.S. wanted to stop European involvement in Latin America Doctrine: 1. No U.S. involvement in present day European colonies 2. No European involvement in independent countries 3. No future European colonialization * U.S. did not have the military strength to enforce this doctrine, however inadvertently Great Britain would enforce the doctrine in order to maintain trade within the western hemisphere. Effects: 1. Remained in effect for 170 years 2. Demonstrated U.S. expression of nationalistic feelings. What was the goal of American foreign policy? a. Neutrality (taking no sides in a war) b. Recognition of U.S. sovereignty (independence) c. Support for Latin Americans struggle for independence. What were the major causes and results of the War of 1812? a. British impressment (forcing) of U.S. ships, cargo, and servicemen. b. British arming Indians to attack c. “War Hawks” Southern and Western Congressmen who pushed for war with the goal of annexing Canada from Britain. Results: a. U.S. emerged as a respected sovereign nation b. British stopped impressment c. Boosted American nationalism d. created the Era of Good Feelings (1817 – 1825) The Federalist Party widely condemned the war and ceased to be a major force in U.S. politics. James Monroe easily took two terms (1817-1825) To what extent did the Monroe Doctrine reflect sentiments of neutrality and isolationism? Europe was warned not to re-colonize any part of Latin America. Brief Time line Federalists Hamilton Strong Central govt. Pro-British Democratic-Republicans Jefferson Strong State govt.’s Pro-French Foreign Policy 1789 French Revolution. Americans supportive of the French Republic 1793 Fr. Republic declares war on Britain, Spain, and Holland ****1778 Treaty of Alliance bound U.S. to France, however U.S. bound to British because it was a major trading partner. ****Citizen Genet travels the U.S. looking for support for the French. The U.S. govt. in a dilemma and considers neutrality. U.S. not ready for war 1794 Jay Treaty- Supreme Court Justice John Jay sent to Britain to resolve issues and patch up relationship. Jay was successful with some issues, but there was some partisan complaints. Washington signs the treaty but the House of Representatives appropriations committee battles with Washington. He will be verbally criticized by the D-R’s. 1796 Washington’s Farewell Address “no permanent alliances” John Adams (Federalist) becomes the new President The Directory in France continues to seize American ships 1798 X,Y,Z Affair Corrupt Directory/ Talleyrand “not a cent for tribute” causes the Quazi-War to continue. (undeclared war between U.S. and France) Alien and Sedition Acts – passed by a Federalist controlled Congress that adopted 4 laws intended to suppress dissent and prevent further growth of the D-R party. Aimed at immigrants. Virginia-Kentucky Resolutions – state legislatures try to override the Congressional law as Un-Constitutional. Declared the Va.-Ky. Resolutions null + void. 1800 Convention of 1800- Americans met with French to repair relations. Ended the Quazi-War and allowed U.S. out of the Alliance of 1778. 1803 Louisiana Purchase - France regained territory after losing it to Spain during the 7 years war (1763). France/Napoleon offered it to Jefferson for $15 million. Jefferson sends Lewis and Clarke out to explore the territory. 1805 British navy continues impressment of U.S. ships by the British ship in American waters 1807 Embargo Act- forbade exports to all countries. Jefferson attempts to squeeze British and French. Dissert . Disaseter Enbargo Act export fell All exports fell by 80 percent. 1809 Embargo Act is replaced by the non-intercourse act