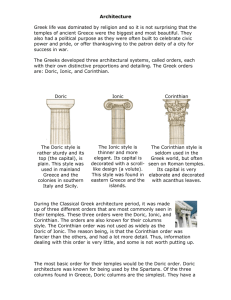
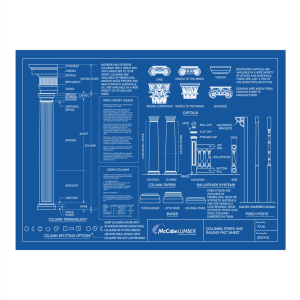
AP ART HISTORY: SHMERYKOWSKY GREEK ARCHIECTURE TERMS abacus
advertisement
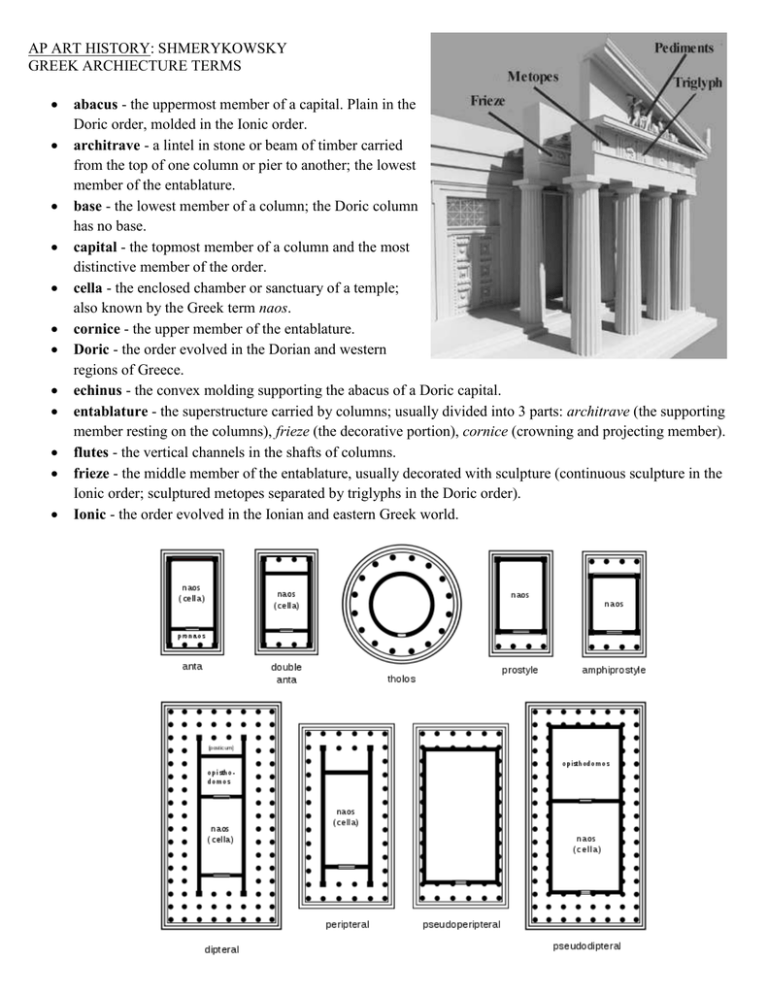
AP ART HISTORY: SHMERYKOWSKY GREEK ARCHIECTURE TERMS abacus - the uppermost member of a capital. Plain in the Doric order, molded in the Ionic order. architrave - a lintel in stone or beam of timber carried from the top of one column or pier to another; the lowest member of the entablature. base - the lowest member of a column; the Doric column has no base. capital - the topmost member of a column and the most distinctive member of the order. cella - the enclosed chamber or sanctuary of a temple; also known by the Greek term naos. cornice - the upper member of the entablature. Doric - the order evolved in the Dorian and western regions of Greece. echinus - the convex molding supporting the abacus of a Doric capital. entablature - the superstructure carried by columns; usually divided into 3 parts: architrave (the supporting member resting on the columns), frieze (the decorative portion), cornice (crowning and projecting member). flutes - the vertical channels in the shafts of columns. frieze - the middle member of the entablature, usually decorated with sculpture (continuous sculpture in the Ionic order; sculptured metopes separated by triglyphs in the Doric order). Ionic - the order evolved in the Ionian and eastern Greek world. metope - the sunken pictorial panels between triglyphs in the Doric order. opisthodomos - the recessed porch in the rear of a Greek temple order pediment - 'the gable': the recessed area within the angle formed by the meeting of the cornices at the roof; usually filled with sculpture. peripteral - a temple whose cella is surrounded by a covered colonnade. Peristyle- A series of columns surrounding a building or enclosing a court. A court enclosed by columns. pronaos - the porch in front of the naos or cella. raking cornice - upper frame of the pediment, below the roof line. shaft - the main body of a column of pier between base and capital. stylobate - the top step of a temple, forming the platform for the columns. triglyph - a raised rectangular divider beteen the metopes, marked with 3 vertical channels. volute - the spiral scroll of the Ionic capital. Skene: Play House. Right behind the orchestra orchestra, the “dancing place” of the chorus and the chief performance space The audience sat in the theatron, the “seeing place,” on semi-circular terraced rows of benches (in the earliest theaters these were wooden; they were later built of stone). On either side of the stage building were long ramps, called eisodoi or parodoi, that led into or away from the orchestra.