Overview
advertisement

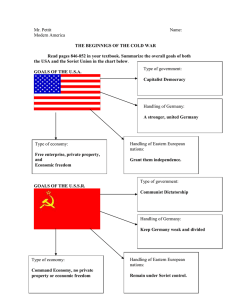
Overview • From 1945 to present the western world has undergone some changes. Europe was destroyed and its economy suffered, which affected the world. Communism was on the loose and the United States entered the Korean War. Global History II Chapter 33 Section 1: The Western World : An Overview • After the cold war, Europe was split into two parts. The eastern part which was dominated by Communism formed the Warsaw Pact. The western part which were mostly democracies formed NATO. The Berlin Wall • The Berlin Wall divided Germany into two a democratic West Germany and Communist East Germany. • Thousands of East Germans frustrated with Communism and how it has affected them, fled to West Germany. To prevent any further defectors, in 1961 the Soviet Union built a wall topped with barbed wire and patrolled by guards. Nuclear Threat • The Cold War triggered an arms race, with both sides producing a mass amount of nuclear weapons. They agreed to an agreement. The Nuclear Test Ban Treat, made in 1963 banned the testing of nuclear weapons in the atmosphere. End of the Cold War • The new Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev eased the Soviet grip on Communist Eastern Europe countries. As time went on Communist governments across Europe fell and broke away from the Soviet Union to form independent states. European Union In 1957, France, West Germany, Belgium, Italy ,the Netherlands, and Luxembourg signed a treaty to form the Common Market. The Common Market was to expand free trade. In the 1980s and the 1990s the Common Market expanded and took the name of the European Union. In 1999 the European Union issued the euro to all the members of the European Union. Section 2: The Western European Democracies • In 1969 West Germany’s chancellor Wily Brandt attempted to ease tension with East Germany. He called his policy Ostpolitik, or eastern policy. He created economic ties with eastern Europe and signed a treaty of mutual recognition with East Germany. In 1989, as Communism faded Germany was able to move closer to unification. East Germany’s Communist leaders were ousted. In both Germanys, people began to move to the wall and tear it down. In 1990, German voters approved unification. Section 3: North American Prosperity • In 1945,America had the world’s greatest military and was the only country to posses the atomic bomb. But America felt threatened by communism in the Soviet Union as they developed their own atomic bomb. • America started building bases overseas and organized military alliances from Europe to Southeast Asia. To contain communism, America aided emerging European democratic nations. • In Korea and Vietnam communism was on the rise. In 1950 communist North Korea invaded free South Korea, and so the Korean War began. By the early 1960’s, the United States became involved in Vietnam. In 1968 Richard Nixon was elected President. He promised to end American involvement in Vietnam. The Civil Rights Movement • In the mid 1950’s, the Civil rights began to set out to end discrimination. Although slavery was abolished a century before, some states denied equality to minority groups. They faced Jim Crow laws and segregation. Segregation is separation in which minorities were separated from whites. After World War II Harry Truman desegregated the armed forces. In 1954 Brown vs. Board of Education declared segregated schools were unconstitutional. • By 1956, gifted preacher, Martin Luther King, Jr. emerged as a leader of the civil Rights Movement. king organized boycotts and led peaceful marches throughout the 1960’s that ended segregation. In 1963 he led a huge rally in the nation’s capital and gave his infamous “ I Have A Dream” speech. He stated that all men should be created equal. On April 4, 1968 King was assassinated in Memphis, Tennessee. Section 4 : The Soviet Union: Rise and Fall of a Superpower • In 1956 Nikita Khrushchev succeeded Josef Stalin. He shocked communist leaders when he denounced Stalin’s abuse of power. He called for a peaceful coexistence with the west. • In 1985, a new leader emerged in the Soviet Union. Mikhail Gorbachev came to power. He called to reconstruct the economy and government. He backed free market and limited enterprise. Gorbachev’s plan backfired and caused economic turmoil. As more Soviet states declared independence and the economy collapsing, the Soviet Union was gone literally overnight. Section 5: A New Era in Eastern Europe • For centuries Eastern Europe was dominated by the Ottoman Empire, Austria, Germany and Russia. In 1989 the nations won their independence. • In 1989 a “Democratic Movement” was sweeping through Eastern Europe. One by one communist governments fell. • Yugoslavia as created after World War I as a haven for Slavs. It consisted of various republics- Serbia, Croatia, Macedonia, Slovenia, and Herzegovina. There were several ethnicities as well as religions. There were Muslims and Orthodox Christians and Roman Catholics. Josip Tito, the leader of Yugoslavia ruled the country with an iron fist. He jailed critics and silenced nationalist movements. With his death, Communism fell and nationalism ran rabid. In Kosovo and Bosnia, Muslims were brutally treated and killed. Slobodan Milosevic, an extreme Serbian nationalist supplied Serbs with weapons and money. Tens of thousands of Bosnian Muslims were killed.